Question Number 69327 by mhmd last updated on 22/Sep/19
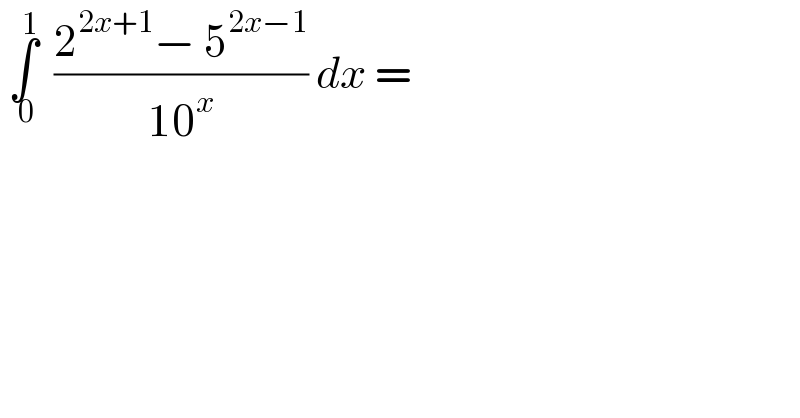
$$\:\underset{\:\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\mathrm{1}} {\int}}\:\:\frac{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}} −\:\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{1}} }{\mathrm{10}^{{x}} }\:{dx}\:=\: \\ $$
Answered by MJS last updated on 22/Sep/19
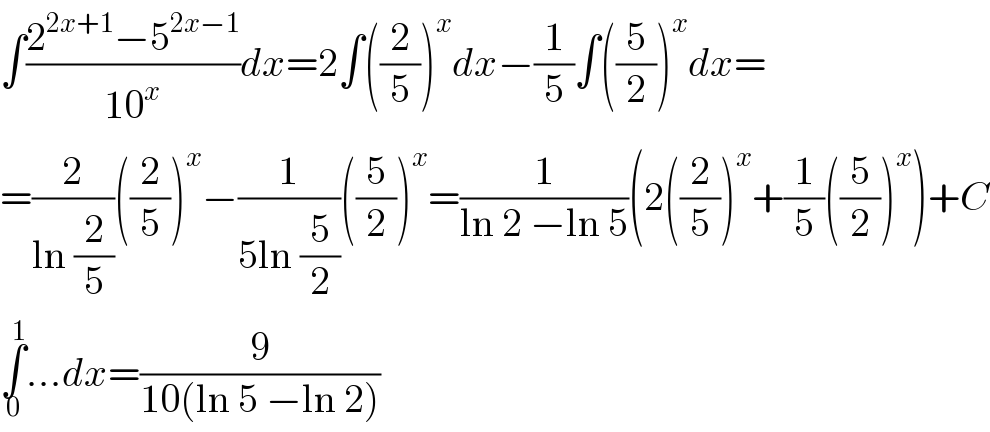
$$\int\frac{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}} −\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{1}} }{\mathrm{10}^{{x}} }{dx}=\mathrm{2}\int\left(\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{5}}\right)^{{x}} {dx}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}\int\left(\frac{\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)^{{x}} {dx}= \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{ln}\:\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{5}}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{5}}\right)^{{x}} −\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5ln}\:\frac{\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{2}}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)^{{x}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{2}\:−\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{5}}\left(\mathrm{2}\left(\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{5}}\right)^{{x}} +\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)^{{x}} \right)+{C} \\ $$$$\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\mathrm{1}} {\int}}…{dx}=\frac{\mathrm{9}}{\mathrm{10}\left(\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{5}\:−\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{2}\right)} \\ $$
