Question Number 53695 by gunawan last updated on 25/Jan/19
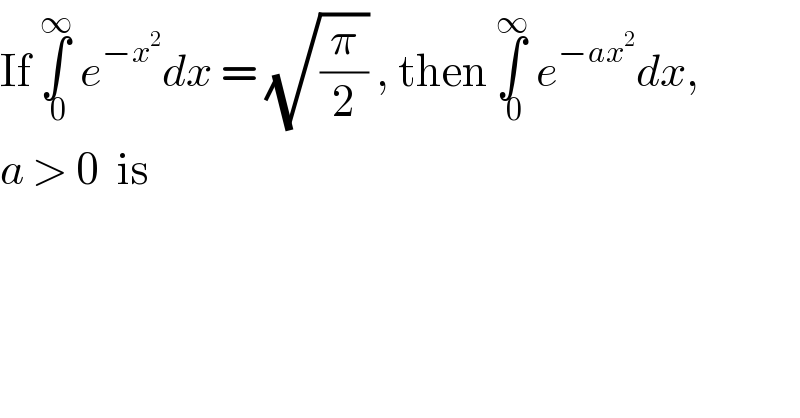
$$\mathrm{If}\:\underset{\:\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\int}}\:{e}^{−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } {dx}\:=\:\sqrt{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}}\:,\:\mathrm{then}\:\underset{\:\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\int}}\:{e}^{−{ax}^{\mathrm{2}} } {dx}, \\ $$$${a}\:>\:\mathrm{0}\:\:\mathrm{is} \\ $$
Commented by Abdo msup. last updated on 25/Jan/19
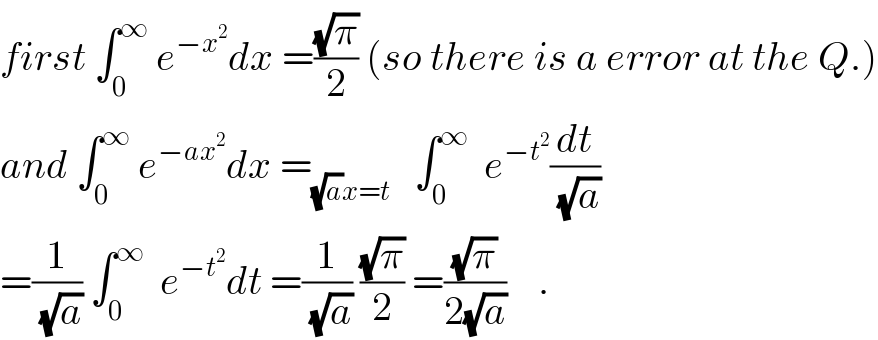
$${first}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:{e}^{−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } {dx}\:=\frac{\sqrt{\pi}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\left({so}\:{there}\:{is}\:{a}\:{error}\:{at}\:{the}\:{Q}.\right) \\ $$$${and}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:{e}^{−{ax}^{\mathrm{2}} } {dx}\:=_{\sqrt{{a}}{x}={t}} \:\:\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\:{e}^{−{t}^{\mathrm{2}} } \frac{{dt}}{\:\sqrt{{a}}} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\:\sqrt{{a}}}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\:{e}^{−{t}^{\mathrm{2}} } {dt}\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\:\sqrt{{a}}}\:\frac{\sqrt{\pi}}{\mathrm{2}}\:=\frac{\sqrt{\pi}}{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{{a}}}\:\:\:\:. \\ $$
Answered by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 25/Jan/19
![t=ax^2 x=((√t)/( (√a))) dx=(1/(2(√a)))×(1/( (√t)))dt ∫_0 ^∞ e^(−t) ×(dt/(2(√a)))×(1/( (√t))) (1/(2(√a)))∫_0 ^∞ e^(−t) ×t^((1/2)−1) dt gamma function ∫_0 ^∞ e^(−t) t^(n−1) dt=⌈(n) ⌈(n+1)=n! [factorial of n] ⌈((1/2))=(√π) so (1/(2(√a)))∫_0 ^∞ e^(−t) ×t^((1/2)−1) dt =(1/(2(√a) ))×(√π) let calculate ∫_0 ^∞ e^(−x^2 ) dx y=x^2 x=(√y) dx=(1/(2(√y)))dy ∫_0 ^∞ e^(−y) ×(1/2)×y^(−(1/2)) dy (1/2)∫_0 ^∞ e^(−y) y^((1/2)−1) dy (1/2)×⌈((1/2))=((√π)/2) so i think ∫_0 ^∞ e^(−x^2 ) dx=((√π)/2) ( not ((√π)/( (√2))))](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q53706.png)
$${t}={ax}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\:{x}=\frac{\sqrt{{t}}}{\:\sqrt{{a}}}\:\:{dx}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{{a}}}×\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\:\sqrt{{t}}}{dt} \\ $$$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} {e}^{−{t}} ×\frac{{dt}}{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{{a}}}×\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\:\sqrt{{t}}} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{{a}}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} {e}^{−{t}} ×{t}^{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}−\mathrm{1}} {dt} \\ $$$${gamma}\:{function}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} {e}^{−{t}} {t}^{{n}−\mathrm{1}} {dt}=\lceil\left({n}\right) \\ $$$$\lceil\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)={n}!\:\:\left[{factorial}\:{of}\:{n}\right] \\ $$$$\lceil\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)=\sqrt{\pi}\: \\ $$$${so} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{{a}}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} {e}^{−{t}} ×{t}^{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}−\mathrm{1}} {dt} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{{a}}\:}×\sqrt{\pi}\: \\ $$$${let}\:{calculate}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} {e}^{−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } {dx} \\ $$$${y}={x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\:\:{x}=\sqrt{{y}}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:{dx}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{{y}}}{dy} \\ $$$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} {e}^{−{y}} ×\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}×{y}^{−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}} {dy} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} {e}^{−{y}} {y}^{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}−\mathrm{1}} {dy} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}×\lceil\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)=\frac{\sqrt{\pi}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${so}\:{i}\:{think}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} {e}^{−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } {dx}=\frac{\sqrt{\pi}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\left(\:\:\boldsymbol{{not}}\:\frac{\sqrt{\pi}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\right) \\ $$
