Question Number 43643 by gunawan last updated on 13/Sep/18
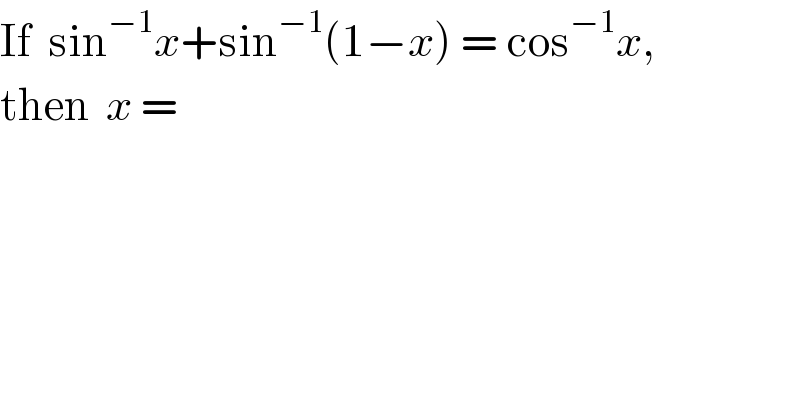
$$\mathrm{If}\:\:\mathrm{sin}^{−\mathrm{1}} {x}+\mathrm{sin}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left(\mathrm{1}−{x}\right)\:=\:\mathrm{cos}^{−\mathrm{1}} {x}, \\ $$$$\mathrm{then}\:\:{x}\:= \\ $$
Answered by behi83417@gmail.com last updated on 13/Sep/18

$${x}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
Answered by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 13/Sep/18
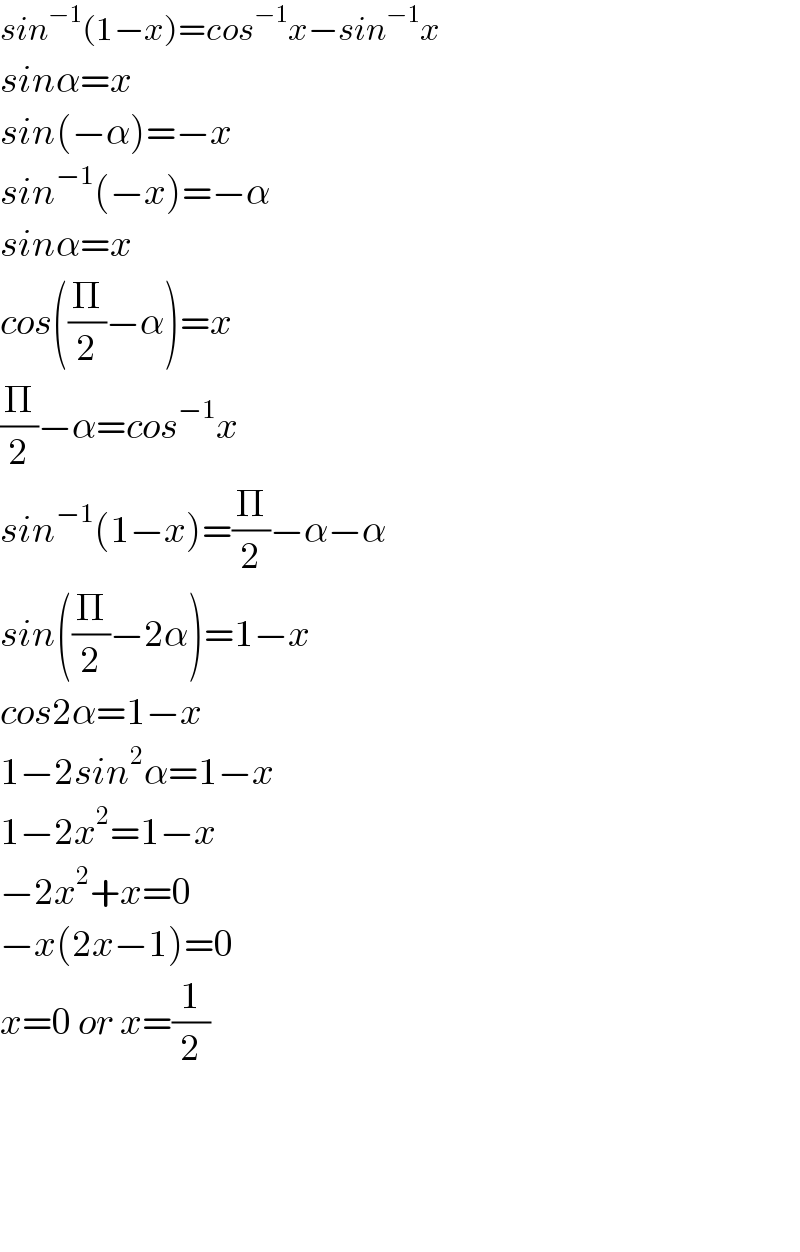
$${sin}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left(\mathrm{1}−{x}\right)={cos}^{−\mathrm{1}} {x}−{sin}^{−\mathrm{1}} {x} \\ $$$${sin}\alpha={x} \\ $$$${sin}\left(−\alpha\right)=−{x} \\ $$$${sin}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left(−{x}\right)=−\alpha \\ $$$${sin}\alpha={x} \\ $$$${cos}\left(\frac{\Pi}{\mathrm{2}}−\alpha\right)={x} \\ $$$$\frac{\Pi}{\mathrm{2}}−\alpha={cos}^{−\mathrm{1}} {x} \\ $$$${sin}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left(\mathrm{1}−{x}\right)=\frac{\Pi}{\mathrm{2}}−\alpha−\alpha \\ $$$${sin}\left(\frac{\Pi}{\mathrm{2}}−\mathrm{2}\alpha\right)=\mathrm{1}−{x} \\ $$$${cos}\mathrm{2}\alpha=\mathrm{1}−{x} \\ $$$$\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{2}{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} \alpha=\mathrm{1}−{x} \\ $$$$\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{2}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{1}−{x} \\ $$$$−\mathrm{2}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{x}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$−{x}\left(\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${x}=\mathrm{0}\:{or}\:{x}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by Joel578 last updated on 13/Sep/18
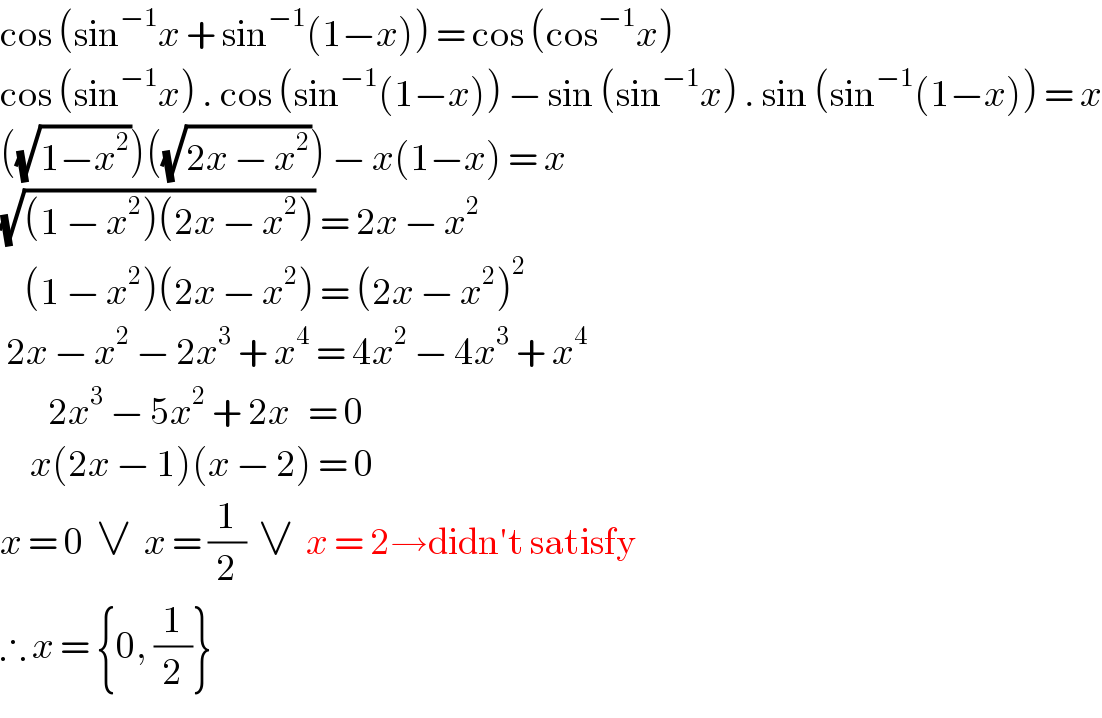
$$\mathrm{cos}\:\left(\mathrm{sin}^{−\mathrm{1}} {x}\:+\:\mathrm{sin}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left(\mathrm{1}−{x}\right)\right)\:=\:\mathrm{cos}\:\left(\mathrm{cos}^{−\mathrm{1}} {x}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{cos}\:\left(\mathrm{sin}^{−\mathrm{1}} {x}\right)\:.\:\mathrm{cos}\:\left(\mathrm{sin}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left(\mathrm{1}−{x}\right)\right)\:−\:\mathrm{sin}\:\left(\mathrm{sin}^{−\mathrm{1}} {x}\right)\:.\:\mathrm{sin}\:\left(\mathrm{sin}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left(\mathrm{1}−{x}\right)\right)\:=\:{x} \\ $$$$\left(\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right)\left(\sqrt{\mathrm{2}{x}\:−\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right)\:−\:{x}\left(\mathrm{1}−{x}\right)\:=\:{x} \\ $$$$\sqrt{\left(\mathrm{1}\:−\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\:−\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)}\:=\:\mathrm{2}{x}\:−\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\left(\mathrm{1}\:−\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\:−\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\:=\:\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\:−\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\:\mathrm{2}{x}\:−\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:−\:\mathrm{2}{x}^{\mathrm{3}} \:+\:{x}^{\mathrm{4}} \:=\:\mathrm{4}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:−\:\mathrm{4}{x}^{\mathrm{3}} \:+\:{x}^{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{2}{x}^{\mathrm{3}} \:−\:\mathrm{5}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\:\mathrm{2}{x}\:\:\:=\:\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:{x}\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\:−\:\mathrm{1}\right)\left({x}\:−\:\mathrm{2}\right)\:=\:\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${x}\:=\:\mathrm{0}\:\:\vee\:\:{x}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\:\vee\:\:{x}\:=\:\mathrm{2}\rightarrow\mathrm{didn}'\mathrm{t}\:\mathrm{satisfy} \\ $$$$\therefore\:{x}\:=\:\left\{\mathrm{0},\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right\} \\ $$
Commented by gunawan last updated on 13/Sep/18
$$\mathrm{Nice}\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{thank}\:\mathrm{you}\:\mathrm{very}\:\mathrm{much}\:\mathrm{Sir} \\ $$
