Question Number 202865 by Mathspace last updated on 04/Jan/24
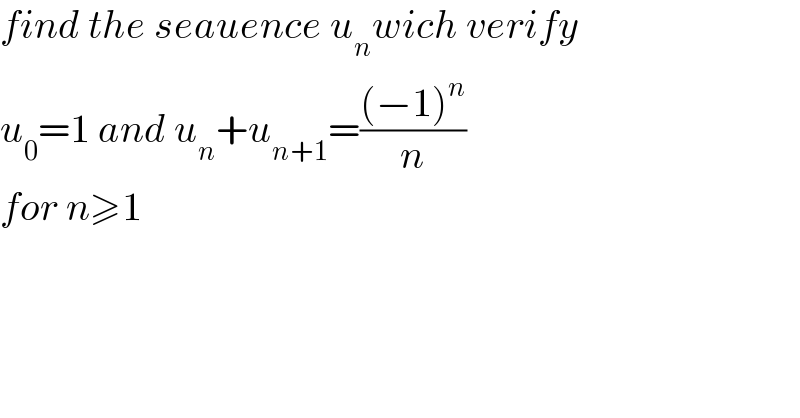
$${find}\:{the}\:{seauence}\:{u}_{{n}} {wich}\:{verify} \\ $$$${u}_{\mathrm{0}} =\mathrm{1}\:{and}\:{u}_{{n}} +{u}_{{n}+\mathrm{1}} =\frac{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} }{{n}} \\ $$$${for}\:{n}\geqslant\mathrm{1} \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 05/Jan/24

$${you}\:{mean}\:{u}_{\mathrm{1}} =\mathrm{1}? \\ $$
Answered by witcher3 last updated on 04/Jan/24
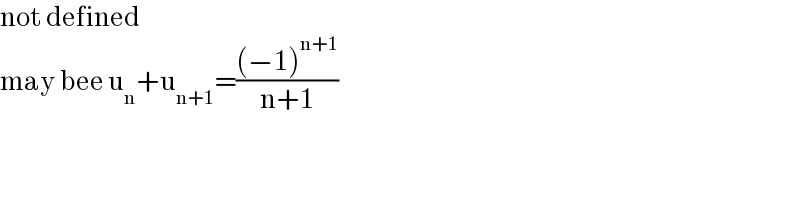
$$\mathrm{not}\:\mathrm{defined}\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{may}\:\mathrm{bee}\:\mathrm{u}_{\mathrm{n}} +\mathrm{u}_{\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{1}} =\frac{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{1}} }{\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by Mathspace last updated on 05/Jan/24
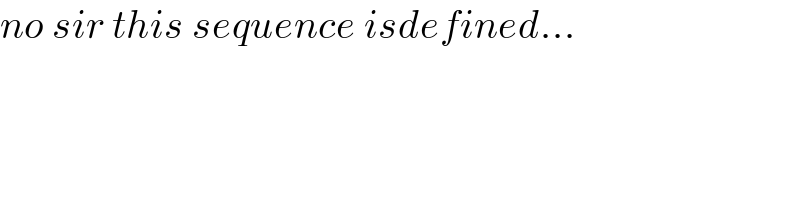
$${no}\:{sir}\:{this}\:{sequence}\:{isdefined}… \\ $$
Answered by Mathspace last updated on 05/Jan/24

$${take}\:{u}_{\mathrm{1}} =\mathrm{1} \\ $$
Answered by witcher3 last updated on 05/Jan/24
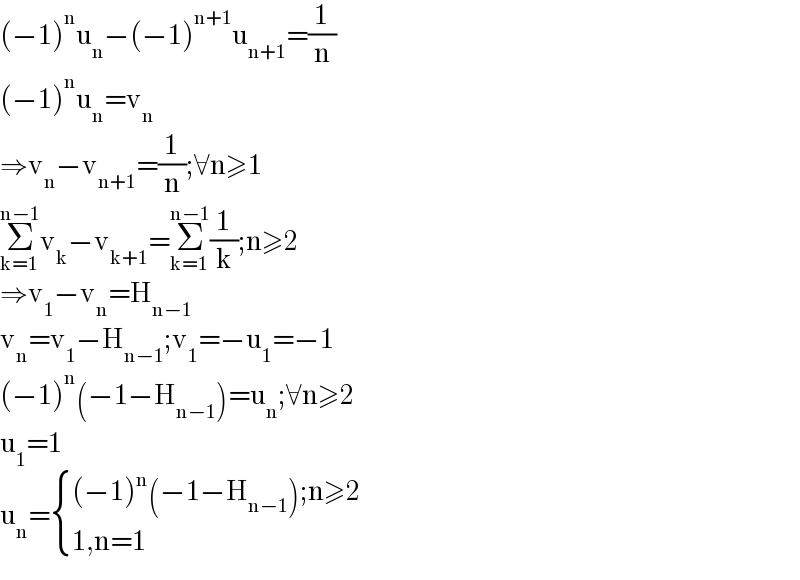
$$\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{n}} \mathrm{u}_{\mathrm{n}} −\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{1}} \mathrm{u}_{\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{1}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{n}} \\ $$$$\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{n}} \mathrm{u}_{\mathrm{n}} =\mathrm{v}_{\mathrm{n}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{v}_{\mathrm{n}} −\mathrm{v}_{\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{1}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{n}};\forall\mathrm{n}\geqslant\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\underset{\mathrm{k}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\mathrm{n}−\mathrm{1}} {\sum}}\mathrm{v}_{\mathrm{k}} −\mathrm{v}_{\mathrm{k}+\mathrm{1}} =\underset{\mathrm{k}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\mathrm{n}−\mathrm{1}} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{k}};\mathrm{n}\geqslant\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{v}_{\mathrm{1}} −\mathrm{v}_{\mathrm{n}} =\mathrm{H}_{\mathrm{n}−\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{v}_{\mathrm{n}} =\mathrm{v}_{\mathrm{1}} −\mathrm{H}_{\mathrm{n}−\mathrm{1}} ;\mathrm{v}_{\mathrm{1}} =−\mathrm{u}_{\mathrm{1}} =−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{n}} \left(−\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{H}_{\mathrm{n}−\mathrm{1}} \right)=\mathrm{u}_{\mathrm{n}} ;\forall\mathrm{n}\geqslant\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\mathrm{u}_{\mathrm{1}} =\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\mathrm{u}_{\mathrm{n}} =\begin{cases}{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{n}} \left(−\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{H}_{\mathrm{n}−\mathrm{1}} \right);\mathrm{n}\geqslant\mathrm{2}}\\{\mathrm{1},\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{1}}\end{cases} \\ $$
