Question Number 204478 by a.lgnaoui last updated on 18/Feb/24

$$\mathrm{soit}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{f}}:\:\:\mathbb{R}^{\mathrm{3}} \rightarrow\mathbb{R}^{\mathrm{3}} \:\:\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{f}}\left(\boldsymbol{\mathrm{x}},\boldsymbol{\mathrm{y}},\boldsymbol{\mathrm{z}}\right)=\left(\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{y},\mathrm{2x}−\mathrm{y},\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{z}\right) \\ $$$$\bullet\mathrm{1}\:\:\mathrm{Ecrire}\:\mathrm{la}\:\mathrm{matrice}\:\mathrm{M}\:\mathrm{de}\:\mathrm{cette}\:\mathrm{application} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\mathrm{dans}\:\mathrm{la}\:\mathrm{base}\:\mathrm{canonique}\:{B}\:\mathrm{de}\:\:\mathbb{R}^{\mathrm{3}} \: \\ $$$$\bullet\mathrm{2}\:\:\mathrm{Calculer}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{f}}\left(\mathrm{1},\mathrm{2},\mathrm{3}\right)\mathrm{de}\:\mathrm{2}\:\mathrm{manieres}\:\mathrm{differentes} \\ $$$$\:−\mathrm{en}\:\mathrm{utilisant}\:\mathrm{la}\:\mathrm{definition}\:\mathrm{de}\:\mathrm{f} \\ $$$$−\mathrm{en}\:\mathrm{utilisant}\:\mathrm{la}\:\mathrm{matrice}\:{M}\: \\ $$$$\bullet\mathrm{3}\:\:\mathrm{determiner}\:\mathrm{bsse}\:\mathrm{de}\:\mathrm{Ker}\left(\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{f}}\right)\:\mathrm{et}\:\mathrm{de}\:{I}\mathrm{m}\left(\boldsymbol{\mathrm{f}}\right) \\ $$$$\bullet\mathrm{4}\:\:\mathrm{soient}\:\mathrm{v}_{\mathrm{1}} =\left(\mathrm{1},\mathrm{1},\mathrm{0}\right)\:\mathrm{v}_{\mathrm{2}} =\left(\mathrm{1},\mathrm{2},\mathrm{1}\right)\:\:\mathrm{v}_{\mathrm{3}} =\left(\mathrm{1},\mathrm{3},\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{Montrer}\:\mathrm{que}\:\mathrm{la}\:\mathrm{famille}\:{E}=\left(\mathrm{v}_{\mathrm{1}} ,\:\mathrm{v}_{\mathrm{2}} ,\:\mathrm{v}_{\mathrm{3}} \right)\mathrm{est} \\ $$$$\mathrm{une}\:\mathrm{base}\:\mathrm{de}\:\mathbb{R}^{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$$$\bullet\mathrm{5Calculer}\:\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{v}_{\mathrm{1}} \right)\:\mathrm{donner}\:\mathrm{ses}\:\mathrm{coordonnes}\left(\boldsymbol{\mathrm{locus}}\right) \\ $$$$\:\mathrm{dans}\:\mathrm{bass}\:{E} \\ $$$$\:\:\mathrm{avec}\:\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{v}_{\mathrm{2}} \right)=\mathrm{v}_{\mathrm{1}} +\mathrm{6v}_{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4v}_{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{v}_{\mathrm{3}} \right)=\mathrm{2v}_{\mathrm{1}} +\mathrm{8v}_{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{6v}_{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$$$\bullet\mathrm{6}\:\:\mathrm{Ecrire}\:\mathrm{la}\:\mathrm{matrice}\:{N}\:\mathrm{de}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{f}}\:\:\mathrm{dans}\:\mathrm{base}\:{F} \\ $$$$\bullet\mathrm{7}\:\:\mathrm{Retrouver}\:\mathrm{cette}\:\mathrm{matrice}\:\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{partir}\:\mathrm{de}\:{M} \\ $$$$\mathrm{en}\:\mathrm{utilisant}\:\mathrm{la}\:\mathrm{formule}\:\mathrm{de}\:\mathrm{changement}\:\mathrm{de}\:\mathrm{base} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by A5T last updated on 21/Feb/24
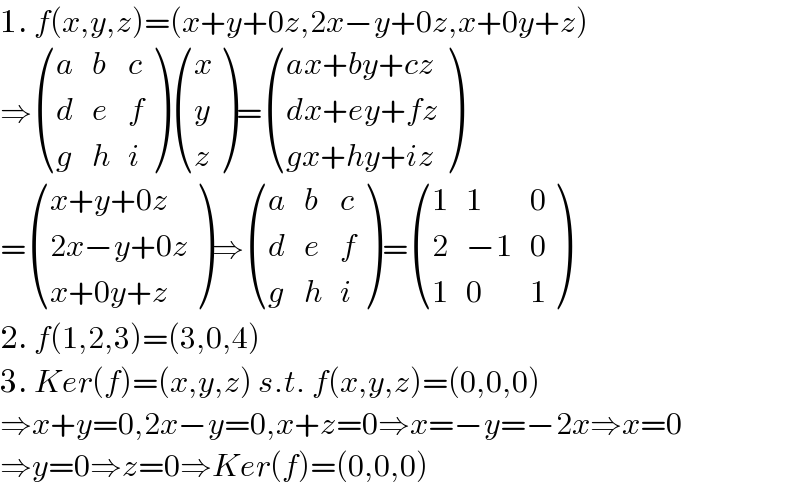
$$\mathrm{1}.\:{f}\left({x},{y},{z}\right)=\left({x}+{y}+\mathrm{0}{z},\mathrm{2}{x}−{y}+\mathrm{0}{z},{x}+\mathrm{0}{y}+{z}\right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\begin{pmatrix}{{a}}&{{b}}&{{c}}\\{{d}}&{{e}}&{{f}}\\{{g}}&{{h}}&{{i}}\end{pmatrix}\begin{pmatrix}{{x}}\\{{y}}\\{{z}}\end{pmatrix}=\begin{pmatrix}{{ax}+{by}+{cz}}\\{{dx}+{ey}+{fz}}\\{{gx}+{hy}+{iz}}\end{pmatrix} \\ $$$$=\begin{pmatrix}{{x}+{y}+\mathrm{0}{z}}\\{\mathrm{2}{x}−{y}+\mathrm{0}{z}}\\{{x}+\mathrm{0}{y}+{z}}\end{pmatrix}\Rightarrow\begin{pmatrix}{{a}}&{{b}}&{{c}}\\{{d}}&{{e}}&{{f}}\\{{g}}&{{h}}&{{i}}\end{pmatrix}=\begin{pmatrix}{\mathrm{1}}&{\mathrm{1}}&{\mathrm{0}}\\{\mathrm{2}}&{−\mathrm{1}}&{\mathrm{0}}\\{\mathrm{1}}&{\mathrm{0}}&{\mathrm{1}}\end{pmatrix} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}.\:{f}\left(\mathrm{1},\mathrm{2},\mathrm{3}\right)=\left(\mathrm{3},\mathrm{0},\mathrm{4}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{3}.\:{Ker}\left({f}\right)=\left({x},{y},{z}\right)\:{s}.{t}.\:{f}\left({x},{y},{z}\right)=\left(\mathrm{0},\mathrm{0},\mathrm{0}\right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{x}+{y}=\mathrm{0},\mathrm{2}{x}−{y}=\mathrm{0},{x}+{z}=\mathrm{0}\Rightarrow{x}=−{y}=−\mathrm{2}{x}\Rightarrow{x}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{y}=\mathrm{0}\Rightarrow{z}=\mathrm{0}\Rightarrow{Ker}\left({f}\right)=\left(\mathrm{0},\mathrm{0},\mathrm{0}\right) \\ $$
