Question Number 205727 by mathzup last updated on 28/Mar/24
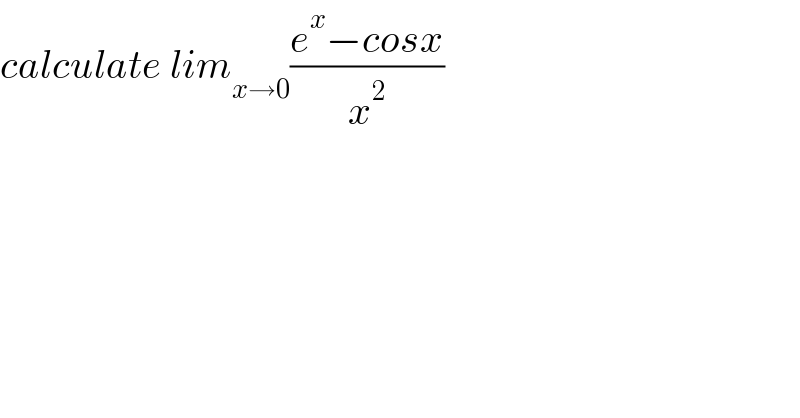
$${calculate}\:{lim}_{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} \frac{{e}^{{x}} −{cosx}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$
Commented by lepuissantcedricjunior last updated on 29/Mar/24
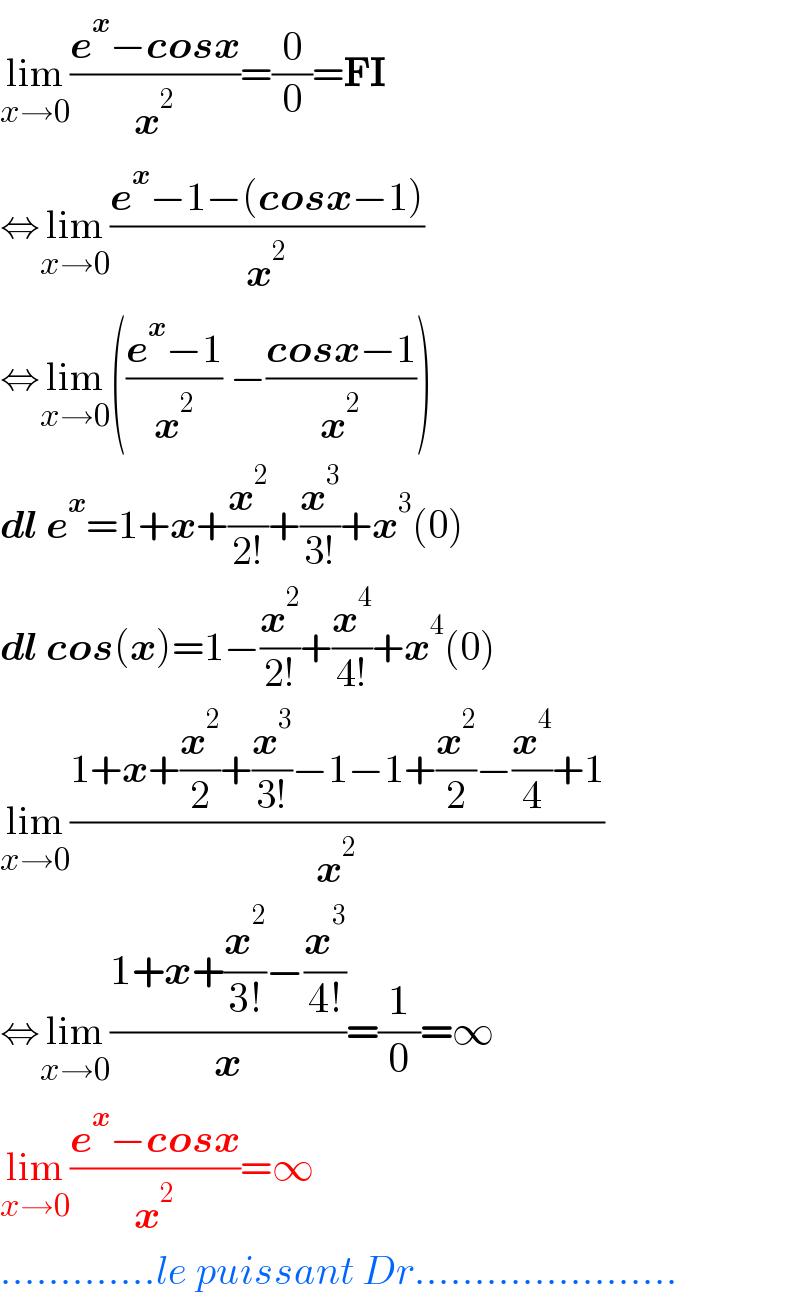
$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\boldsymbol{{x}}} −\boldsymbol{{cosx}}}{\boldsymbol{{x}}^{\mathrm{2}} }=\frac{\mathrm{0}}{\mathrm{0}}=\boldsymbol{\mathrm{FI}} \\ $$$$\Leftrightarrow\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\boldsymbol{{x}}} −\mathrm{1}−\left(\boldsymbol{{cosx}}−\mathrm{1}\right)}{\boldsymbol{{x}}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\Leftrightarrow\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\frac{\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\boldsymbol{{x}}} −\mathrm{1}}{\boldsymbol{{x}}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:−\frac{\boldsymbol{{cosx}}−\mathrm{1}}{\boldsymbol{{x}}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right) \\ $$$$\boldsymbol{{dl}}\:\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\boldsymbol{{x}}} =\mathrm{1}+\boldsymbol{{x}}+\frac{\boldsymbol{{x}}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}!}+\frac{\boldsymbol{{x}}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{3}!}+\boldsymbol{{x}}^{\mathrm{3}} \left(\mathrm{0}\right) \\ $$$$\boldsymbol{{dl}}\:\boldsymbol{{cos}}\left(\boldsymbol{{x}}\right)=\mathrm{1}−\frac{\boldsymbol{{x}}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}!}+\frac{\boldsymbol{{x}}^{\mathrm{4}} }{\mathrm{4}!}+\boldsymbol{{x}}^{\mathrm{4}} \left(\mathrm{0}\right) \\ $$$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{1}+\boldsymbol{{x}}+\frac{\boldsymbol{{x}}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}+\frac{\boldsymbol{{x}}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{3}!}−\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{1}+\frac{\boldsymbol{{x}}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}−\frac{\boldsymbol{{x}}^{\mathrm{4}} }{\mathrm{4}}+\mathrm{1}}{\boldsymbol{{x}}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\Leftrightarrow\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{1}+\boldsymbol{{x}}+\frac{\boldsymbol{{x}}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{3}!}−\frac{\boldsymbol{{x}}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{4}!}}{\boldsymbol{{x}}}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{0}}=\infty\: \\ $$$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\boldsymbol{{x}}} −\boldsymbol{{cosx}}}{\boldsymbol{{x}}^{\mathrm{2}} }=\infty \\ $$$$………….{le}\:{puissant}\:{Dr}…………………. \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 28/Mar/24
$${please}\:{post}\:{your}\:{answer}\:{to}\:{a}\:{question} \\ $$$${as}\:“{answer}'',\:{not}\:{as}\:“{comment}''!\:{thanks}! \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 28/Mar/24
veuillez poster votre réponse à une question
comme "réponse", pas comme "commentaire"! Merci!
Commented by York12 last updated on 29/Mar/24

$$ \\ $$Tu es Francis!?
Answered by mr W last updated on 28/Mar/24
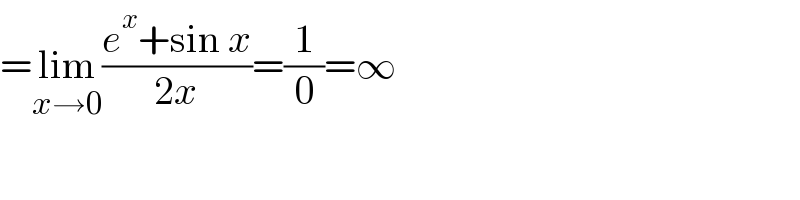
$$=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{{e}^{{x}} +\mathrm{sin}\:{x}}{\mathrm{2}{x}}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{0}}=\infty \\ $$
