Question Number 79761 by Najaah last updated on 28/Jan/20
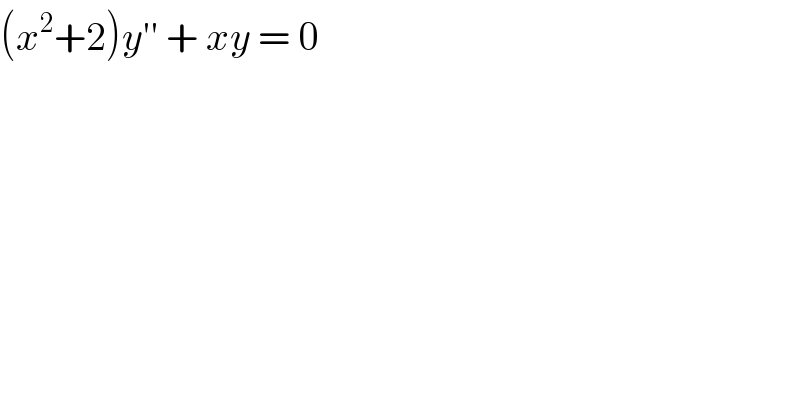
$$\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}\right){y}''\:+\:{xy}\:=\:\mathrm{0} \\ $$
Commented by abdomathmax last updated on 28/Jan/20

$${solution}\:{developpable}\:{at}?{integr}\:{serie} \\ $$$${y}\left({x}\right)=\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:{a}_{{n}} {x}^{{n}} \:\Rightarrow{y}^{'} =\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{1}} ^{\infty} {na}_{{n}} {x}^{{n}−\mathrm{1}} \:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${y}^{\left(\mathrm{2}\right)} \left({x}\right)=\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{2}} ^{\infty} {n}\left({n}−\mathrm{1}\right){a}_{{n}} {x}^{{n}−\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\left({e}\right)\:\Rightarrow\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}\right)\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{2}} ^{\infty} {n}\left({n}−\mathrm{1}\right){a}_{{n}} {x}^{{n}−\mathrm{2}} +\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} {a}_{{n}} {x}^{{n}+\mathrm{1}} =\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{2}} ^{\infty} {n}\left({n}−\mathrm{1}\right){a}_{{n}} {x}^{{n}} \:+\mathrm{2}\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{2}} ^{\infty} {n}\left({n}−\mathrm{1}\right){a}_{{n}} \:{x}^{{n}−\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$+\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{1}} ^{\infty} {a}_{{n}−\mathrm{1}} {x}^{{n}} \:=\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${a}_{\mathrm{0}} \:+\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{2}} ^{\infty} \left\{{n}\left({n}−\mathrm{1}\right){a}_{{n}} +{a}_{{n}−\mathrm{1}} \right\}{x}^{{n}} \:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:+\mathrm{2}{a}_{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$+\mathrm{2}\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{1}} ^{\infty} \:\left({n}+\mathrm{2}\right)\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right){a}_{{n}+\mathrm{2}} \:{x}^{{n}} =\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{a}_{\mathrm{0}} \:+\mathrm{2}{a}_{\mathrm{2}} \:\:+\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{2}} ^{\infty} \left\{{n}\left({n}−\mathrm{1}\right){a}_{{n}} +{a}_{{n}−\mathrm{1}} +\left({n}+\mathrm{2}\right)\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right){a}_{{n}+\mathrm{2}} \right\}{x}^{{n}} =\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{a}_{\mathrm{0}} \:+\mathrm{2}{a}_{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{0}\:{and} \\ $$$$\left({n}+\mathrm{2}\right)\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right){a}_{{n}+\mathrm{2}} +{n}\left({n}−\mathrm{1}\right){a}_{{n}} \:+{a}_{{n}−\mathrm{1}} =\mathrm{0}\:\forall{n}\geqslant\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$…{be}\:{continued}… \\ $$
Answered by Henri Boucatchou last updated on 28/Jan/20
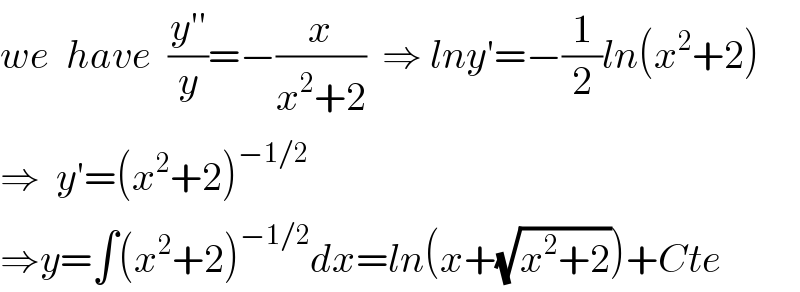
$${we}\:\:{have}\:\:\frac{{y}''}{{y}}=−\frac{{x}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}}\:\:\Rightarrow\:{lny}'=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{ln}\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}\right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\:{y}'=\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}\right)^{−\mathrm{1}/\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{y}=\int\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}\right)^{−\mathrm{1}/\mathrm{2}} {dx}={ln}\left({x}+\sqrt{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}}\right)+{Cte} \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 28/Jan/20
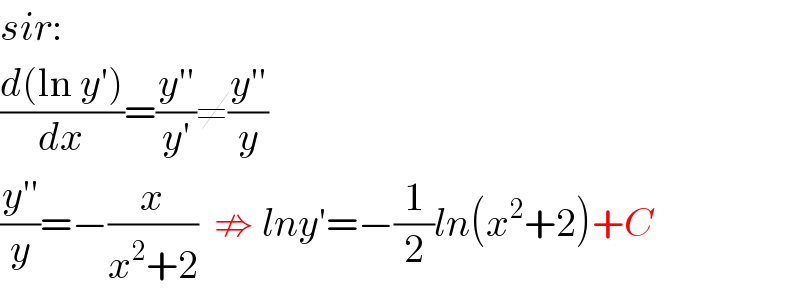
$${sir}: \\ $$$$\frac{{d}\left(\mathrm{ln}\:{y}'\right)}{{dx}}=\frac{{y}''}{{y}'}\neq\frac{{y}''}{{y}} \\ $$$$\frac{{y}''}{{y}}=−\frac{{x}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}}\:\:\nRightarrow\:{lny}'=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{ln}\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}\right)+{C} \\ $$
Commented by abdomathmax last updated on 28/Jan/20

$${not}\:{correct} \\ $$
Commented by jagoll last updated on 28/Jan/20

$$\mathrm{how}\:\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{get}\:\mathrm{it}? \\ $$
