Question Number 14267 by Tinkutara last updated on 30/May/17
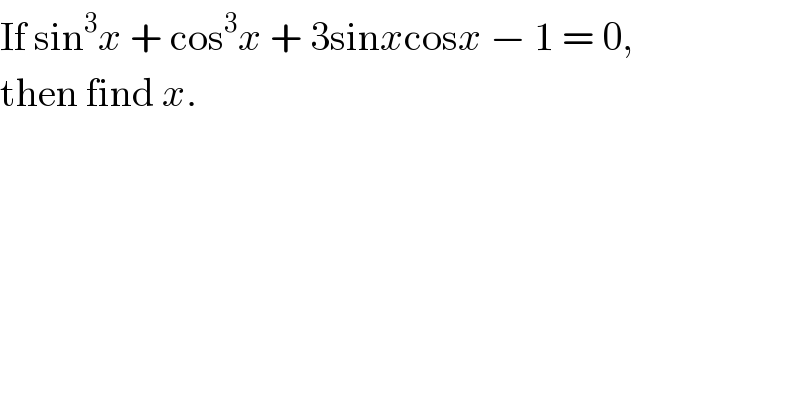
$$\mathrm{If}\:\mathrm{sin}^{\mathrm{3}} {x}\:+\:\mathrm{cos}^{\mathrm{3}} {x}\:+\:\mathrm{3sin}{x}\mathrm{cos}{x}\:−\:\mathrm{1}\:=\:\mathrm{0}, \\ $$$$\mathrm{then}\:\mathrm{find}\:{x}. \\ $$
Answered by linkelly0615 last updated on 30/May/17
![set { ((A=sinx+cosx)),((B=sinx−cosx)) :} ⇒ sin^3 x + cos^3 x + 3sinxcosx − 1=0 ⇒A(A^2 −2sinxcosx)−3Asinxcosx+3sinxcosx−1=0 ⇒(1−A)[3sinxcosx−(1+A+A^2 )]=0 ⇒(1−A)[(3/4)(A^2 −B^2 )−(1+A+A^2 )]=0 ⇒(A−1){(1/4)[(A+2)^2 +3B^2 ]}=0 ⇒A=1 or { ((A=(−2))),((B=0)) :} !!BUT!! ∵A=sinx+cosx=(√2)sin (x+(π/4)) ∴∣A∣≤(√2)⇒A won′t be (−2) ⇒so, A=1 {sorry, that′s my fault.} ⇒sinx+cosx=1 [sinx+cosx=(√)2(((sinx)/( (√2)))+((cosx)/( (√2))))=(√2)sin(x+(π/4))] ⇒sin(x+π/4)=1/(√2) ⇒x+π/4=2kπ+π/4 or 2kπ+3π/4 ,k∈Z ⇒x=2kπ or (2k+(1/2))π, k∈Z](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q14281.png)
$${set} \\ $$$$\begin{cases}{{A}={sinx}+{cosx}}\\{{B}={sinx}−{cosx}}\end{cases} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\mathrm{sin}^{\mathrm{3}} {x}\:+\:\mathrm{cos}^{\mathrm{3}} {x}\:+\:\mathrm{3sin}{x}\mathrm{cos}{x}\:−\:\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{A}\left({A}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}{sinxcosx}\right)−\mathrm{3}{Asinxcosx}+\mathrm{3}{sinxcosx}−\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\left(\mathrm{1}−{A}\right)\left[\mathrm{3}{sinxcosx}−\left(\mathrm{1}+{A}+{A}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\right]=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\left(\mathrm{1}−{A}\right)\left[\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{4}}\left({A}^{\mathrm{2}} −{B}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)−\left(\mathrm{1}+{A}+{A}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\right]=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\left({A}−\mathrm{1}\right)\left\{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\left[\left({A}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{3}{B}^{\mathrm{2}} \right]\right\}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{A}=\mathrm{1}\:{or\begin{cases}{{A}=\left(−\mathrm{2}\right)}\\{{B}=\mathrm{0}}\end{cases}} \\ $$$$!!{BUT}!! \\ $$$$\because{A}={sinx}+{cosx}=\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{sin}\:\left({x}+\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}\right) \\ $$$$\therefore\mid{A}\mid\leqslant\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\Rightarrow{A}\:{won}'{t}\:{be}\:\left(−\mathrm{2}\right) \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{so},\:{A}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\left\{{sorry},\:{that}'{s}\:{my}\:{fault}.\right\} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{sinx}+{cosx}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\left[{sinx}+{cosx}=\sqrt{}\mathrm{2}\left(\frac{{sinx}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}+\frac{{cosx}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\right)=\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}{sin}\left({x}+\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}\right)\right] \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{sin}\left({x}+\pi/\mathrm{4}\right)=\mathrm{1}/\sqrt{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{x}+\pi/\mathrm{4}=\mathrm{2}{k}\pi+\pi/\mathrm{4}\:{or}\:\mathrm{2}{k}\pi+\mathrm{3}\pi/\mathrm{4}\:,{k}\in\mathbb{Z} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{x}=\mathrm{2}{k}\pi\:{or}\:\left(\mathrm{2}{k}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)\pi,\:{k}\in\mathbb{Z} \\ $$
Commented by Tinkutara last updated on 30/May/17
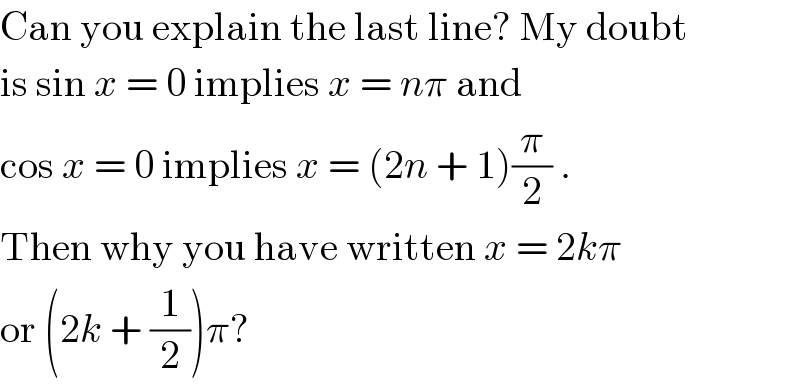
$$\mathrm{Can}\:\mathrm{you}\:\mathrm{explain}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{last}\:\mathrm{line}?\:\mathrm{My}\:\mathrm{doubt} \\ $$$$\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{sin}\:{x}\:=\:\mathrm{0}\:\mathrm{implies}\:{x}\:=\:{n}\pi\:\mathrm{and} \\ $$$$\mathrm{cos}\:{x}\:=\:\mathrm{0}\:\mathrm{implies}\:{x}\:=\:\left(\mathrm{2}{n}\:+\:\mathrm{1}\right)\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\:. \\ $$$$\mathrm{Then}\:\mathrm{why}\:\mathrm{you}\:\mathrm{have}\:\mathrm{written}\:{x}\:=\:\mathrm{2}{k}\pi \\ $$$$\mathrm{or}\:\left(\mathrm{2}{k}\:+\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)\pi? \\ $$
