Question Number 66778 by Tony Lin last updated on 19/Aug/19
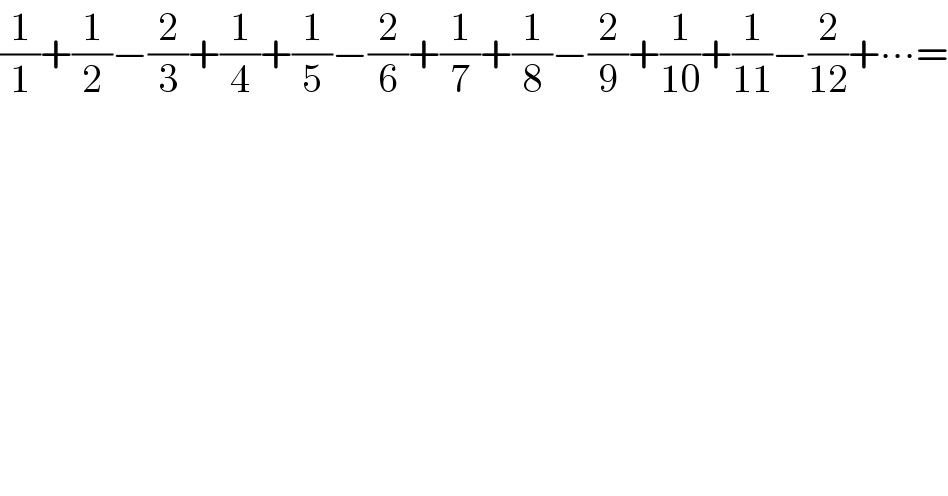
$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{6}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{7}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{8}}−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{9}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{10}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{11}}−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{12}}+\centerdot\centerdot\centerdot= \\ $$
Commented by Prithwish sen last updated on 19/Aug/19
![((1/1)+(1/2)+(1/3)+(1/4)+......)−[((1/3)+(2/3))+((1/6)+(2/6))+((1/9)+(2/9))+((1/(12))+(2/(12)))+...] =Σ_(k=1) ^∞ (1/k) −Σ_(k=1) ^∞ (1/k) = 0 please check.](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q66783.png)
$$\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}+……\right)−\left[\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}\right)+\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{6}}+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{6}}\right)+\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{9}}+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{9}}\right)+\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{12}}+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{12}}\right)+…\right] \\ $$$$=\underset{\mathrm{k}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{k}}\:−\underset{\mathrm{k}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{k}}\:=\:\mathrm{0}\:\:\mathrm{please}\:\mathrm{check}. \\ $$
Commented by MJS last updated on 19/Aug/19

$$\mathrm{I}\:\mathrm{don}'\mathrm{t}\:\mathrm{think}\:\mathrm{this}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{allowed}… \\ $$$$\mathrm{i}.\mathrm{e}. \\ $$$$\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{1}… \\ $$$$\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{not}\:\mathrm{defined} \\ $$$$\mathrm{but} \\ $$$$\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{1}+…\:−\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{1}+…\right)=\underset{{i}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{{n}} {\sum}}\mathrm{1}−\underset{{i}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{{n}} {\sum}}\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{0}\forall{n}\geqslant\mathrm{1} \\ $$
Commented by MJS last updated on 19/Aug/19
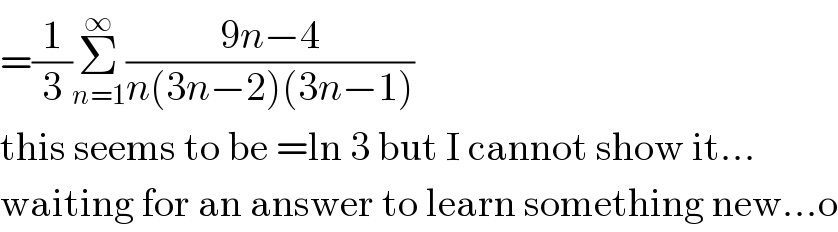
$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{9}{n}−\mathrm{4}}{{n}\left(\mathrm{3}{n}−\mathrm{2}\right)\left(\mathrm{3}{n}−\mathrm{1}\right)} \\ $$$$\mathrm{this}\:\mathrm{seems}\:\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{be}\:=\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{3}\:\mathrm{but}\:\mathrm{I}\:\mathrm{cannot}\:\mathrm{show}\:\mathrm{it}… \\ $$$$\mathrm{waiting}\:\mathrm{for}\:\mathrm{an}\:\mathrm{answer}\:\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{learn}\:\mathrm{something}\:\mathrm{new}…\mathrm{o} \\ $$
Commented by Tony Lin last updated on 20/Aug/19
![lim_(n→∞) {((1/1)+(1/2)+(1/3)+∙∙∙+(1/n))−[((1/3)+(2/3))+((1/6)+(2/6))+∙∙∙+((1/n)+(2/n))]} =lim_(n→∞) [((1/1)+(1/2)+(1/3)+∙∙∙+(1/(n/3))+(1/((n/3)+1))∙∙∙+(1/n))−((1/1)+(1/2)+(1/3)+∙∙∙+(1/(n/3)))] =lim_(n→∞) ((1/((n/3)+1))+(1/((n/3)+2))+∙∙∙+(1/((3n)/3))) =lim_(n→∞) (3/n)((1/(1+(3/n)))+(1/(1+(6/n) ))+∙∙∙+(1/(1+((2n)/n)))) =∫_0 ^2 (1/(1+x))dx =ln∣1+x∣_0 ^2 =ln3](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q66840.png)
$$\underset{{n}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\left\{\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}+\centerdot\centerdot\centerdot+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}\right)−\left[\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}\right)+\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{6}}+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{6}}\right)+\centerdot\centerdot\centerdot+\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{{n}}\right)\right]\right\} \\ $$$$=\underset{{n}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\left[\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}+\centerdot\centerdot\centerdot+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\frac{{n}}{\mathrm{3}}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\frac{{n}}{\mathrm{3}}+\mathrm{1}}\centerdot\centerdot\centerdot+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}\right)−\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}+\centerdot\centerdot\centerdot+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\frac{{n}}{\mathrm{3}}}\right)\right] \\ $$$$=\underset{{n}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\frac{{n}}{\mathrm{3}}+\mathrm{1}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\frac{{n}}{\mathrm{3}}+\mathrm{2}}+\centerdot\centerdot\centerdot+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\frac{\mathrm{3}{n}}{\mathrm{3}}}\right) \\ $$$$=\underset{{n}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{3}}{{n}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{3}}{{n}}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{6}}{{n}}\:\:}+\centerdot\centerdot\centerdot+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{2}{n}}{{n}}}\right) \\ $$$$=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{2}} \frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}}{dx} \\ $$$$={ln}\mid\mathrm{1}+{x}\mid_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$={ln}\mathrm{3} \\ $$
Answered by Smail last updated on 20/Aug/19
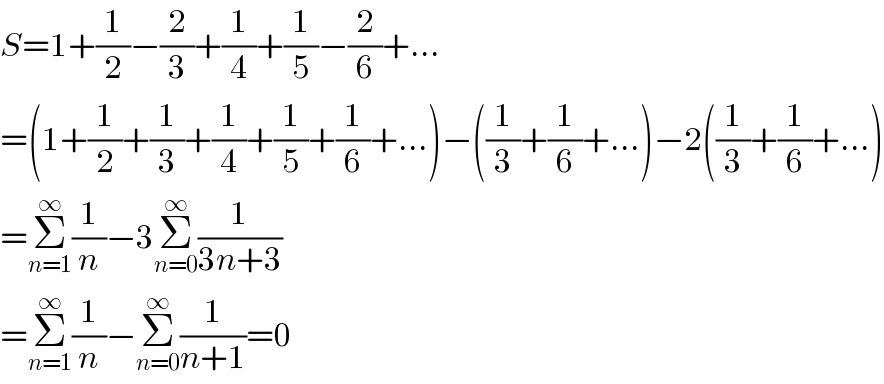
$${S}=\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{6}}+… \\ $$$$=\left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{6}}+…\right)−\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{6}}+…\right)−\mathrm{2}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{6}}+…\right) \\ $$$$=\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}−\mathrm{3}\underset{{n}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}{n}+\mathrm{3}} \\ $$$$=\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}−\underset{{n}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}+\mathrm{1}}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$
Commented by MJS last updated on 20/Aug/19
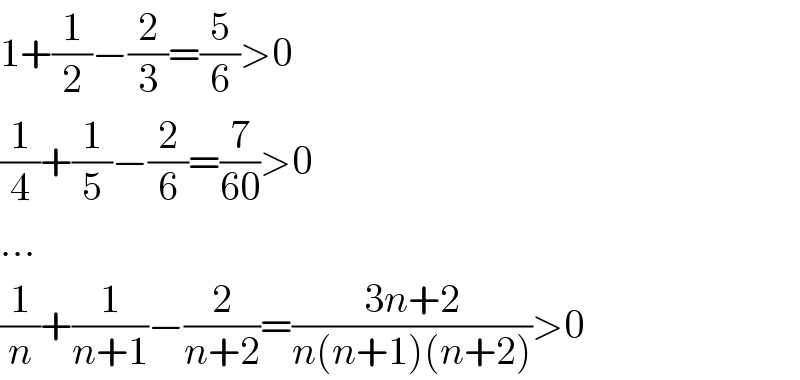
$$\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}=\frac{\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{6}}>\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{6}}=\frac{\mathrm{7}}{\mathrm{60}}>\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$… \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}+\mathrm{1}}−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{{n}+\mathrm{2}}=\frac{\mathrm{3}{n}+\mathrm{2}}{{n}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)\left({n}+\mathrm{2}\right)}>\mathrm{0} \\ $$
Commented by Prithwish sen last updated on 20/Aug/19
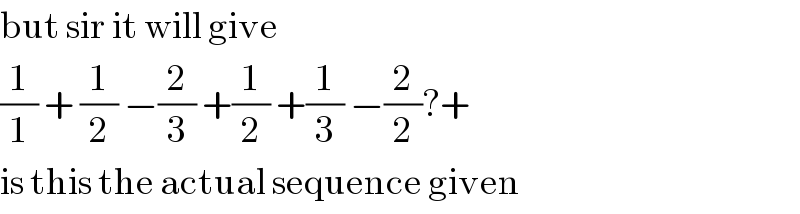
$$\mathrm{but}\:\mathrm{sir}\:\mathrm{it}\:\mathrm{will}\:\mathrm{give} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}}\:+\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}\:+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\:−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{2}}?+ \\ $$$$\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{this}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{actual}\:\mathrm{sequence}\:\mathrm{given} \\ $$
