Question Number 81887 by lalitchand last updated on 16/Feb/20

Commented by mr W last updated on 16/Feb/20
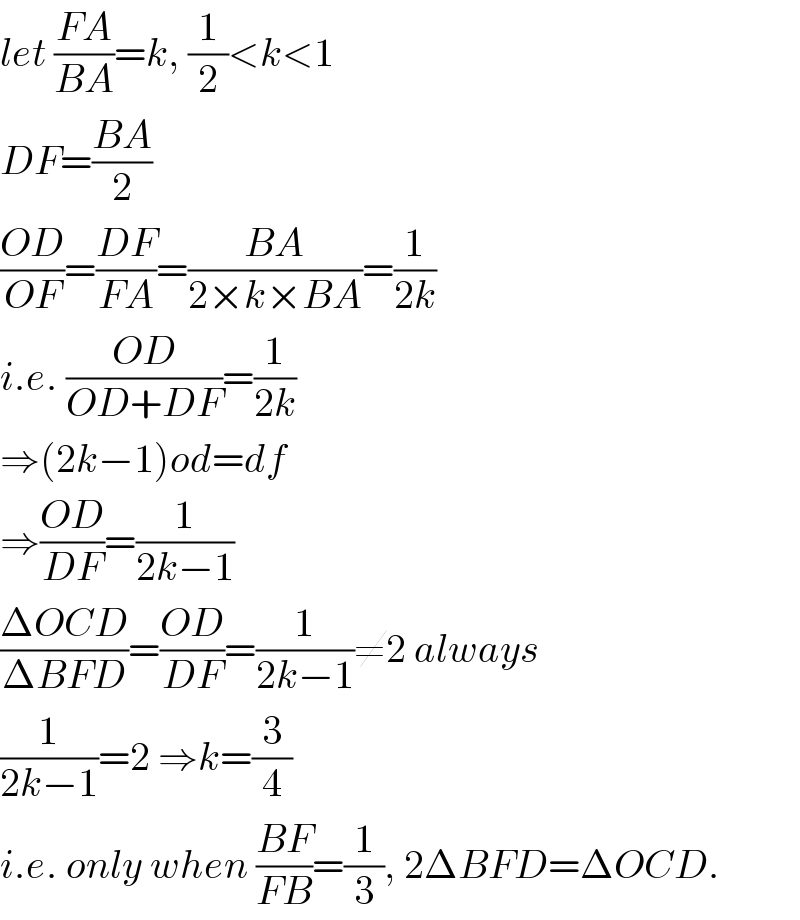
$${let}\:\frac{{FA}}{{BA}}={k},\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}<{k}<\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${DF}=\frac{{BA}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\frac{{OD}}{{OF}}=\frac{{DF}}{{FA}}=\frac{{BA}}{\mathrm{2}×{k}×{BA}}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{k}} \\ $$$${i}.{e}.\:\frac{{OD}}{{OD}+{DF}}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{k}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\left(\mathrm{2}{k}−\mathrm{1}\right){od}={df} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\frac{{OD}}{{DF}}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{k}−\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\frac{\Delta{OCD}}{\Delta{BFD}}=\frac{{OD}}{{DF}}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{k}−\mathrm{1}}\neq\mathrm{2}\:{always} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{k}−\mathrm{1}}=\mathrm{2}\:\Rightarrow{k}=\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$${i}.{e}.\:{only}\:{when}\:\frac{{BF}}{{FB}}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}},\:\mathrm{2}\Delta{BFD}=\Delta{OCD}. \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 16/Feb/20
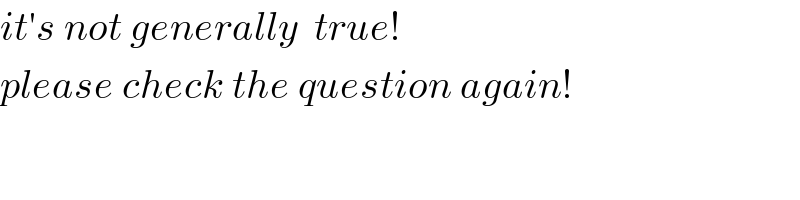
$${it}'{s}\:{not}\:{generally}\:\:{true}! \\ $$$${please}\:{check}\:{the}\:{question}\:{again}! \\ $$
