Question Number 149757 by iloveisrael last updated on 07/Aug/21

Commented by amin96 last updated on 07/Aug/21
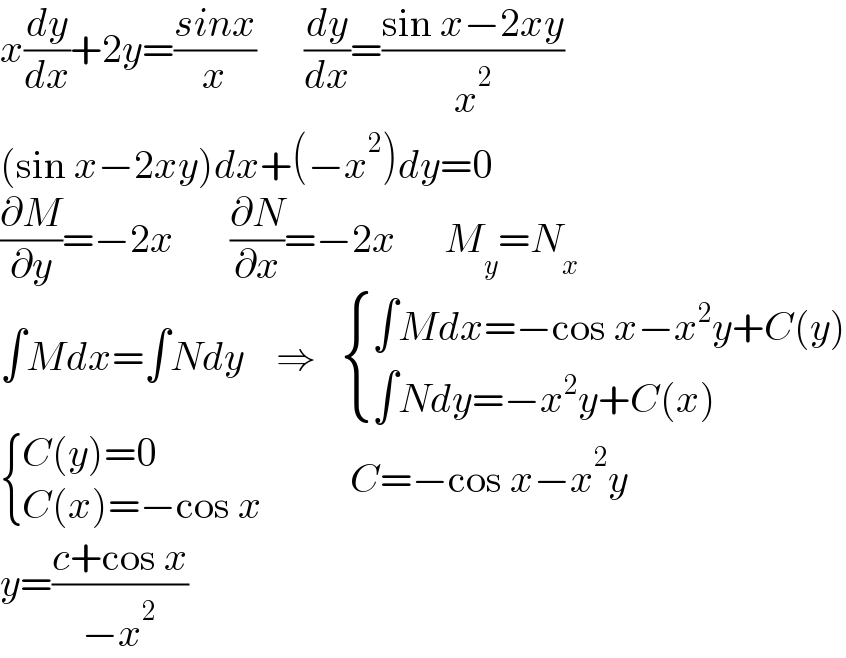
$${x}\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}+\mathrm{2}{y}=\frac{{sinx}}{{x}}\:\:\:\:\:\:\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}=\frac{\mathrm{sin}\:{x}−\mathrm{2}{xy}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{sin}\:{x}−\mathrm{2}{xy}\right){dx}+\left(−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right){dy}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\frac{\partial{M}}{\partial{y}}=−\mathrm{2}{x}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\frac{\partial{N}}{\partial{x}}=−\mathrm{2}{x}\:\:\:\:\:\:{M}_{{y}} ={N}_{{x}} \:\:\: \\ $$$$\int{Mdx}=\int{Ndy}\:\:\:\:\Rightarrow\:\:\:\begin{cases}{\int{Mdx}=−\mathrm{cos}\:{x}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} {y}+{C}\left({y}\right)}\\{\int{Ndy}=−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} {y}+{C}\left({x}\right)}\end{cases} \\ $$$$\begin{cases}{{C}\left({y}\right)=\mathrm{0}}\\{{C}\left({x}\right)=−\mathrm{cos}\:{x}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:}\end{cases}\:\:\:\:{C}=−\mathrm{cos}\:{x}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} {y} \\ $$$${y}=\frac{{c}+\mathrm{cos}\:{x}}{−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$
