Question Number 1698 by Rasheed Ahmad last updated on 01/Sep/15

$$\bullet{Are}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{A}}\cup\boldsymbol{\mathrm{B}}=\boldsymbol{\mathrm{A}}\cap\boldsymbol{\mathrm{B}}\:\:{and}\:\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{A}}=\boldsymbol{\mathrm{B}}\: \\ $$$${completely}\:{equivalent}? \\ $$$$\bullet{Simplify}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{A}}\cup\boldsymbol{\mathrm{B}}=\boldsymbol{\mathrm{A}}\cap\boldsymbol{\mathrm{B}}\:{to}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{A}}=\boldsymbol{\mathrm{B}} \\ $$$${using}\:{set}\:{operations}\:{and}\:{their} \\ $$$${properties}. \\ $$
Answered by 123456 last updated on 01/Sep/15

$$\mathrm{if}\:\mathrm{A}\cup\mathrm{B}=\mathrm{A}\cap\mathrm{B}\:\mathrm{them}\:\mathrm{A}=\mathrm{B} \\ $$$$\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{have}\:\mathrm{that}\:\mathrm{A}\cup\mathrm{B}=\mathrm{A}\cap\mathrm{B}\:\mathrm{them}\:\forall{x},{x}\in\mathrm{A}\cup\mathrm{B},{x}\in\mathrm{A}\cap\mathrm{B} \\ $$$$\mathrm{them}\:\mathrm{supose}\:\mathrm{that}\:\mathrm{A}\neq\mathrm{B},\:\mathrm{without}\:\mathrm{loss} \\ $$$$\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{generality}\:\mathrm{suppose}\:\mathrm{tbat}\:\mid\mathrm{A}\mid>\mid\mathrm{B}\mid \\ $$$${x}\in\mathrm{A},{x}\notin\mathrm{B} \\ $$$${x}\in\mathrm{A}\cup\mathrm{B},{x}\notin\mathrm{A}\cap\mathrm{B}\:\left(\mathrm{contradition}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{hence}\:\mathrm{A}=\mathrm{B} \\ $$$$\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{if}\:\mathrm{A}=\mathrm{B},\:\mathrm{the} \\ $$$$\mathrm{A}\cup\mathrm{B}=\mathrm{A}\cup\mathrm{A}=\mathrm{A} \\ $$$$\mathrm{A}\cap\mathrm{B}=\mathrm{A}\cap\mathrm{A}=\mathrm{A} \\ $$$$\mathrm{A}\cup\mathrm{B}=\mathrm{A}\cap\mathrm{B} \\ $$$$\mathrm{so} \\ $$$$\mathrm{A}\cup\mathrm{B}=\mathrm{A}\cap\mathrm{B}\Leftrightarrow\mathrm{A}=\mathrm{B} \\ $$
Answered by 123456 last updated on 01/Sep/15
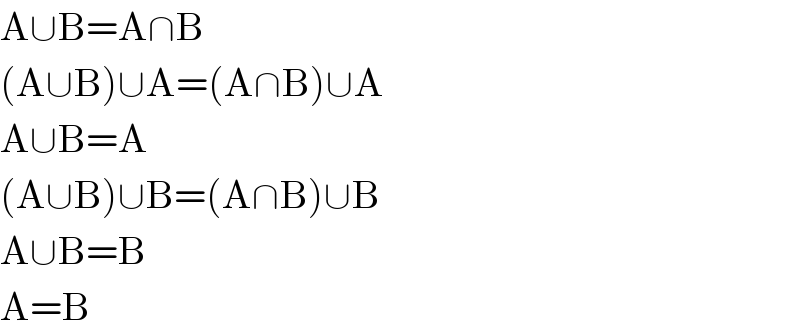
$$\mathrm{A}\cup\mathrm{B}=\mathrm{A}\cap\mathrm{B} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{A}\cup\mathrm{B}\right)\cup\mathrm{A}=\left(\mathrm{A}\cap\mathrm{B}\right)\cup\mathrm{A} \\ $$$$\mathrm{A}\cup\mathrm{B}=\mathrm{A} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{A}\cup\mathrm{B}\right)\cup\mathrm{B}=\left(\mathrm{A}\cap\mathrm{B}\right)\cup\mathrm{B} \\ $$$$\mathrm{A}\cup\mathrm{B}=\mathrm{B} \\ $$$$\mathrm{A}=\mathrm{B} \\ $$
Commented by 123456 last updated on 01/Sep/15
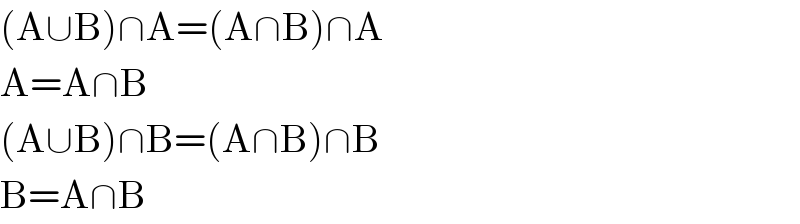
$$\left(\mathrm{A}\cup\mathrm{B}\right)\cap\mathrm{A}=\left(\mathrm{A}\cap\mathrm{B}\right)\cap\mathrm{A} \\ $$$$\mathrm{A}=\mathrm{A}\cap\mathrm{B} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{A}\cup\mathrm{B}\right)\cap\mathrm{B}=\left(\mathrm{A}\cap\mathrm{B}\right)\cap\mathrm{B} \\ $$$$\mathrm{B}=\mathrm{A}\cap\mathrm{B} \\ $$
Commented by Rasheed Ahmad last updated on 01/Sep/15

$$\mathrm{G}^{{oo}} \mathrm{DD}_{\mathrm{eductio}} \mathrm{N}\:_{!} ^{!} \\ $$
Commented by 123456 last updated on 02/Sep/15
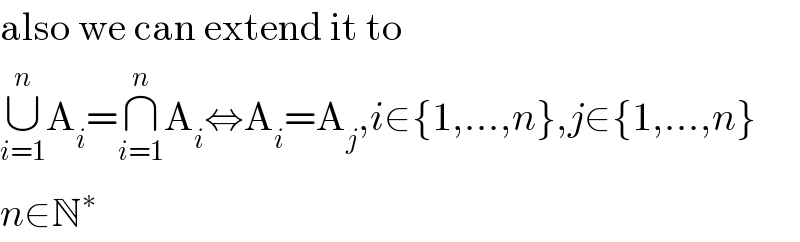
$$\mathrm{also}\:\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{can}\:\mathrm{extend}\:\mathrm{it}\:\mathrm{to} \\ $$$$\underset{{i}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{{n}} {\cup}}\mathrm{A}_{{i}} =\underset{{i}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{{n}} {\cap}}\mathrm{A}_{{i}} \Leftrightarrow\mathrm{A}_{{i}} =\mathrm{A}_{{j}} ,{i}\in\left\{\mathrm{1},…,{n}\right\},{j}\in\left\{\mathrm{1},…,{n}\right\} \\ $$$${n}\in\mathbb{N}^{\ast} \\ $$
Commented by Rasheed Soomro last updated on 03/Sep/15
$${Generalization}!\:{V}.\:{Good}! \\ $$
