Question Number 151425 by peter frank last updated on 21/Aug/21
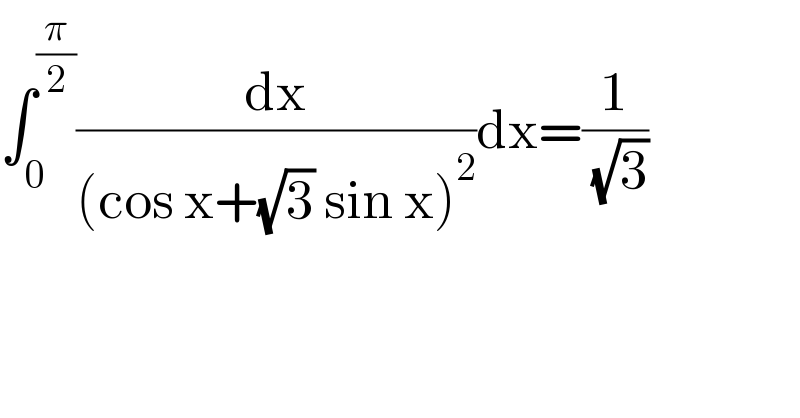
$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \frac{\mathrm{dx}}{\left(\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{x}+\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}\:\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }\mathrm{dx}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}} \\ $$
Answered by Olaf_Thorendsen last updated on 21/Aug/21
![I = ∫_0 ^(π/2) (dx/((cosx+(√3)sinx)^2 )) I = (1/4)∫_0 ^(π/2) (dx/(((1/2)cosx+((√3)/2)sinx)^2 )) I = (1/4)∫_0 ^(π/2) (dx/((cos(π/3)cosx+sin(π/3)sinx)^2 )) I = (1/4)∫_0 ^(π/2) (dx/(cos^2 (x−(π/3)))) I = (1/4)∫_(−(π/3)) ^(π/6) (du/(cos^2 u)) I = (1/4)[tanu]_(−(π/3)) ^(π/6) I = (1/4)((1/( (√3)))+(√3)) = (1/( (√3)))](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q151433.png)
$$\mathrm{I}\:=\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \frac{{dx}}{\left(\mathrm{cos}{x}+\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}\mathrm{sin}{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\mathrm{I}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \frac{{dx}}{\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{cos}{x}+\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{sin}{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\mathrm{I}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \frac{{dx}}{\left(\mathrm{cos}\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{3}}\mathrm{cos}{x}+\mathrm{sin}\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{3}}\mathrm{sin}{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\mathrm{I}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \frac{{dx}}{\mathrm{cos}^{\mathrm{2}} \left({x}−\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{3}}\right)} \\ $$$$\mathrm{I}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\int_{−\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{3}}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{6}}} \frac{{du}}{\mathrm{cos}^{\mathrm{2}} {u}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{I}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\left[\mathrm{tan}{u}\right]_{−\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{3}}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{6}}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{I}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}+\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}\right)\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}} \\ $$
Answered by MJS_new last updated on 21/Aug/21
![∫(dx/((cos x +(√3)sin x)^2 ))= [t=tan x → dx=cos^2 x dt] =∫(dt/(((√3)t+1)^2 ))=−(1/(3t+(√3)))=(1/( (√3)+3tan x))+C [(1/( (√3)+3tan x))]_0 ^(π/2) =((√3)/3)](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q151442.png)
$$\int\frac{{dx}}{\left(\mathrm{cos}\:{x}\:+\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}\mathrm{sin}\:{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }= \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\left[{t}=\mathrm{tan}\:{x}\:\rightarrow\:{dx}=\mathrm{cos}^{\mathrm{2}} \:{x}\:{dt}\right] \\ $$$$=\int\frac{{dt}}{\left(\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}{t}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}{t}+\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}+\mathrm{3tan}\:{x}}+{C} \\ $$$$\left[\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}+\mathrm{3tan}\:{x}}\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\pi/\mathrm{2}} =\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$
