Question Number 151894 by peter frank last updated on 24/Aug/21
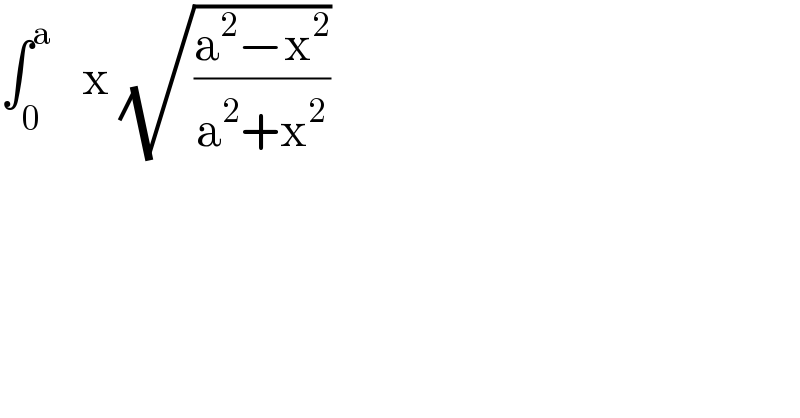
$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{a}} \:\:\:\mathrm{x}\:\sqrt{\frac{\mathrm{a}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{a}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }} \\ $$
Commented by peter frank last updated on 24/Aug/21

$$\mathrm{limit}\:\mathrm{from}\:\mathrm{a}\rightarrow\mathrm{0} \\ $$
Answered by Ar Brandon last updated on 24/Aug/21
![I=∫_0 ^a x(√((a^2 −x^2 )/(a^2 +x^2 )))dx=(1/2)∫_0 ^a^2 (√((a^2 −u)/(a^2 +u)))du =(a^2 /2)∫_0 ^1 (√((1−v)/(1+v)))dv=(a^2 /2)∫_0 ^1 ((1−v)/( (√(1−v^2 ))))dv =(a^2 /2)[arcsin(v)+(√(1−v^2 ))]_0 ^1 =(a^2 /2)((π/2)−1) −a≤x≤a](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q151920.png)
$${I}=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{{a}} {x}\sqrt{\frac{{a}^{\mathrm{2}} −{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{a}^{\mathrm{2}} +{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }}{dx}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{{a}^{\mathrm{2}} } \sqrt{\frac{{a}^{\mathrm{2}} −{u}}{{a}^{\mathrm{2}} +{u}}}{du} \\ $$$$\:\:=\frac{{a}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \sqrt{\frac{\mathrm{1}−{v}}{\mathrm{1}+{v}}}{dv}=\frac{{a}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \frac{\mathrm{1}−{v}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−{v}^{\mathrm{2}} }}{dv} \\ $$$$\:\:=\frac{{a}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}\left[\mathrm{arcsin}\left({v}\right)+\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−{v}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} =\frac{{a}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}\left(\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}−\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$$−{a}\leqslant{x}\leqslant{a} \\ $$
Commented by peter frank last updated on 24/Aug/21
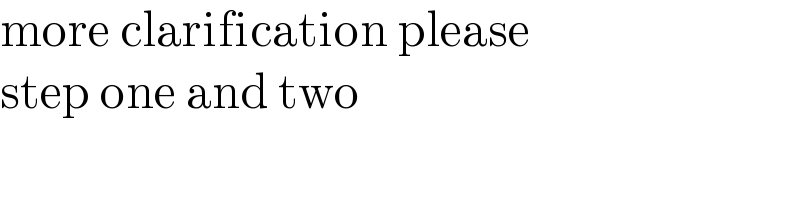
$$\mathrm{more}\:\mathrm{clarification}\:\mathrm{please} \\ $$$$\mathrm{step}\:\mathrm{one}\:\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{two} \\ $$
Commented by Ar Brandon last updated on 24/Aug/21
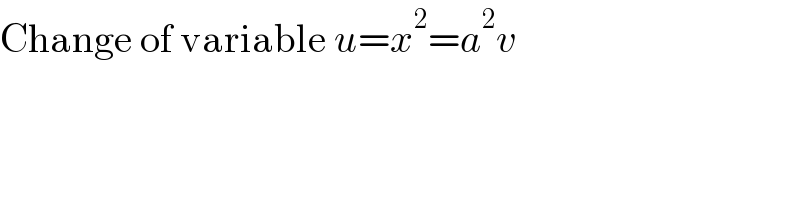
$$\mathrm{Change}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{variable}\:{u}={x}^{\mathrm{2}} ={a}^{\mathrm{2}} {v} \\ $$
