Question Number 91024 by john santu last updated on 27/Apr/20
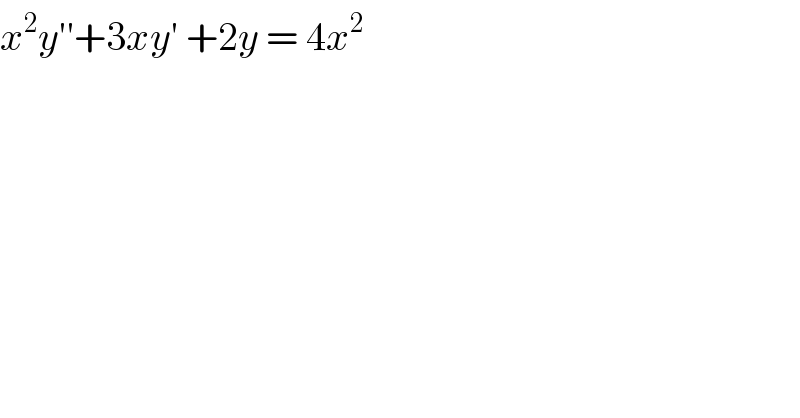
$${x}^{\mathrm{2}} {y}''+\mathrm{3}{xy}'\:+\mathrm{2}{y}\:=\:\mathrm{4}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
Commented by jagoll last updated on 27/Apr/20
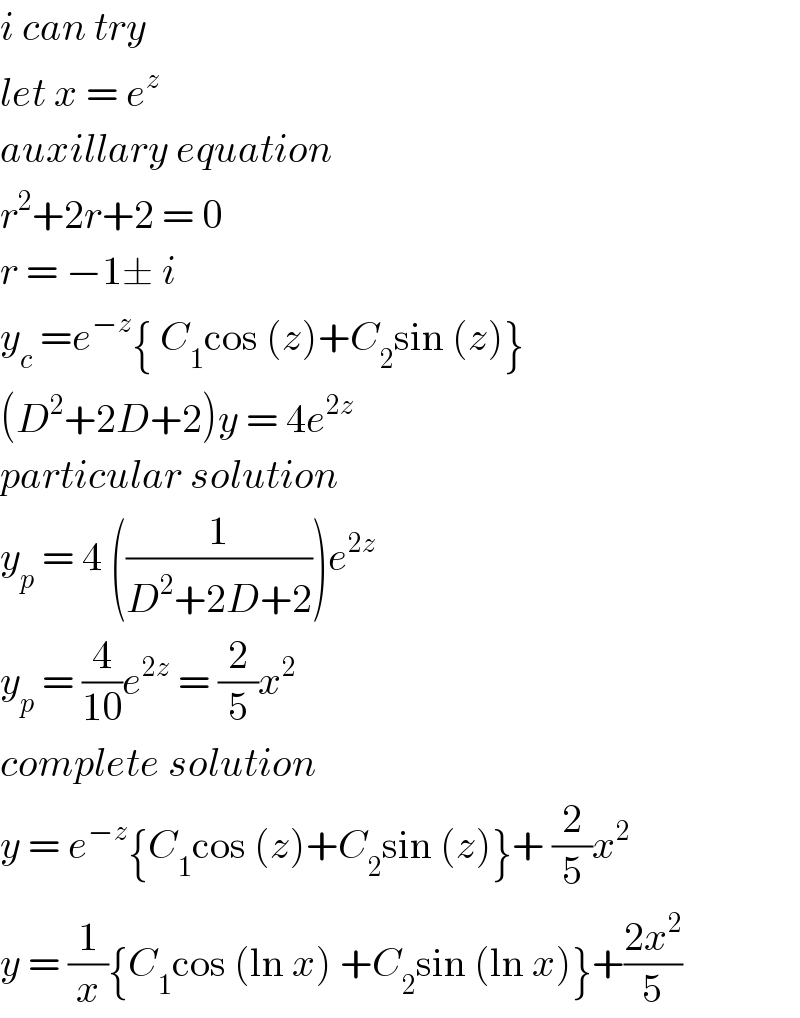
$${i}\:{can}\:{try} \\ $$$${let}\:{x}\:=\:{e}^{{z}} \\ $$$${auxillary}\:{equation}\: \\ $$$${r}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{r}+\mathrm{2}\:=\:\mathrm{0}\: \\ $$$${r}\:=\:−\mathrm{1}\pm\:{i}\: \\ $$$${y}_{{c}} \:={e}^{−{z}} \left\{\:{C}_{\mathrm{1}} \mathrm{cos}\:\left({z}\right)+{C}_{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{sin}\:\left({z}\right)\right\} \\ $$$$\left({D}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{D}+\mathrm{2}\right){y}\:=\:\mathrm{4}{e}^{\mathrm{2}{z}} \\ $$$${particular}\:{solution} \\ $$$${y}_{{p}} \:=\:\mathrm{4}\:\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{D}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{D}+\mathrm{2}}\right){e}^{\mathrm{2}{z}} \\ $$$${y}_{{p}} \:=\:\frac{\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{10}}{e}^{\mathrm{2}{z}} \:=\:\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{5}}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${complete}\:{solution} \\ $$$${y}\:=\:{e}^{−{z}} \left\{{C}_{\mathrm{1}} \mathrm{cos}\:\left({z}\right)+{C}_{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{sin}\:\left({z}\right)\right\}+\:\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{5}}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${y}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}\left\{{C}_{\mathrm{1}} \mathrm{cos}\:\left(\mathrm{ln}\:{x}\right)\:+{C}_{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{sin}\:\left(\mathrm{ln}\:{x}\right)\right\}+\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{5}} \\ $$
Commented by niroj last updated on 27/Apr/20
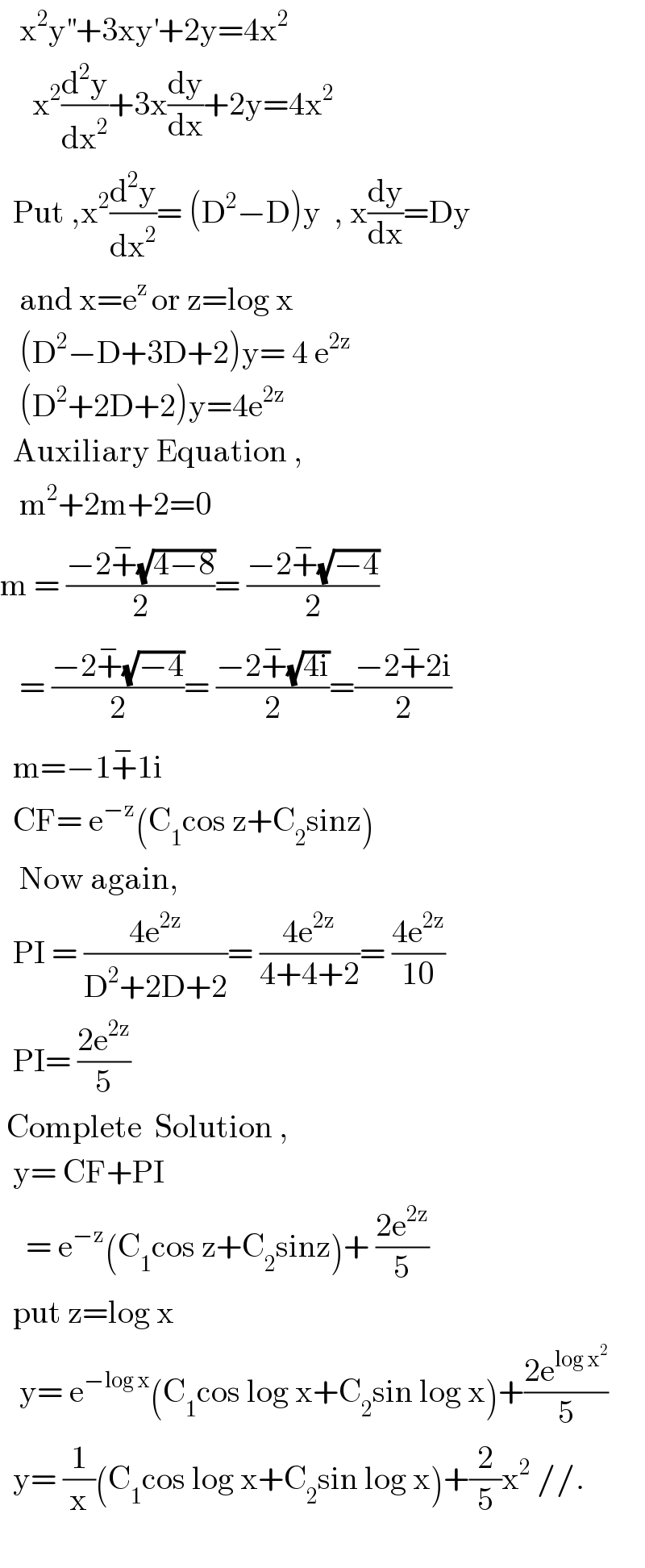
$$\:\:\:\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{y}^{''} +\mathrm{3xy}^{'} +\mathrm{2y}=\mathrm{4x}^{\mathrm{2}} \: \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \frac{\mathrm{d}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{y}}{\mathrm{dx}^{\mathrm{2}} }+\mathrm{3x}\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}+\mathrm{2y}=\mathrm{4x}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\:\:\mathrm{Put}\:,\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \frac{\mathrm{d}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{y}}{\mathrm{dx}^{\mathrm{2}} }=\:\left(\mathrm{D}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{D}\right)\mathrm{y}\:\:,\:\mathrm{x}\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}=\mathrm{Dy} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{x}=\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{z}\:} \mathrm{or}\:\mathrm{z}=\mathrm{log}\:\mathrm{x} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\left(\mathrm{D}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{D}+\mathrm{3D}+\mathrm{2}\right)\mathrm{y}=\:\mathrm{4}\:\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{2z}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\left(\mathrm{D}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2D}+\mathrm{2}\right)\mathrm{y}=\mathrm{4e}^{\mathrm{2z}} \\ $$$$\:\:\mathrm{Auxiliary}\:\mathrm{Equation}\:, \\ $$$$\:\:\:\mathrm{m}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2m}+\mathrm{2}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{m}\:=\:\frac{−\mathrm{2}\overset{−} {+}\sqrt{\mathrm{4}−\mathrm{8}}}{\mathrm{2}}=\:\frac{−\mathrm{2}\overset{−} {+}\sqrt{−\mathrm{4}}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:=\:\frac{−\mathrm{2}\overset{−} {+}\sqrt{−\mathrm{4}}}{\mathrm{2}}=\:\frac{−\mathrm{2}\overset{−} {+}\sqrt{\mathrm{4i}}}{\mathrm{2}}=\frac{−\mathrm{2}\overset{−} {+}\mathrm{2i}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\:\:\mathrm{m}=−\mathrm{1}\overset{−} {+}\mathrm{1i} \\ $$$$\:\:\mathrm{CF}=\:\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{z}} \left(\mathrm{C}_{\mathrm{1}} \mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{z}+\mathrm{C}_{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{sinz}\right) \\ $$$$\:\:\:\mathrm{Now}\:\mathrm{again}, \\ $$$$\:\:\mathrm{PI}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{4e}^{\mathrm{2z}} }{\mathrm{D}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2D}+\mathrm{2}}=\:\frac{\mathrm{4e}^{\mathrm{2z}} }{\mathrm{4}+\mathrm{4}+\mathrm{2}}=\:\frac{\mathrm{4e}^{\mathrm{2z}} }{\mathrm{10}} \\ $$$$\:\:\mathrm{PI}=\:\frac{\mathrm{2e}^{\mathrm{2z}} }{\mathrm{5}} \\ $$$$\:\mathrm{Complete}\:\:\mathrm{Solution}\:,\:\: \\ $$$$\:\:\mathrm{y}=\:\mathrm{CF}+\mathrm{PI} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:=\:\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{z}} \left(\mathrm{C}_{\mathrm{1}} \mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{z}+\mathrm{C}_{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{sinz}\right)+\:\frac{\mathrm{2e}^{\mathrm{2z}} }{\mathrm{5}} \\ $$$$\:\:\mathrm{put}\:\mathrm{z}=\mathrm{log}\:\mathrm{x} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\mathrm{y}=\:\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{log}\:\mathrm{x}} \left(\mathrm{C}_{\mathrm{1}} \mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{log}\:\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{C}_{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{log}\:\mathrm{x}\right)+\frac{\mathrm{2e}^{\mathrm{log}\:\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } }{\mathrm{5}} \\ $$$$\:\:\mathrm{y}=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{x}}\left(\mathrm{C}_{\mathrm{1}} \mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{log}\:\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{C}_{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{log}\:\mathrm{x}\right)+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{5}}\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \://. \\ $$$$\: \\ $$
Commented by jagoll last updated on 27/Apr/20
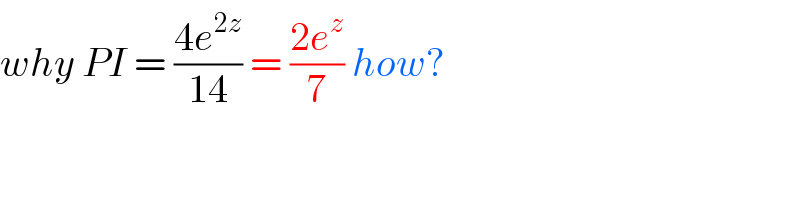
$${why}\:{PI}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{4}{e}^{\mathrm{2}{z}} }{\mathrm{14}}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{2}{e}^{{z}} }{\mathrm{7}}\:{how}? \\ $$
Commented by MWSuSon last updated on 27/Apr/20
$${check}\:{your}\: \\ $$$${i}\:{think}\:{its}\:{a}\:{mistake} \\ $$
Commented by niroj last updated on 27/Apr/20
$$\:{yess}\:{dear}\:{its}\:{now}\:{edited}\:. \\ $$
Answered by MWSuSon last updated on 27/Apr/20
![let x=e^z x^2 y′′=D(D−1)y xy′=Dy D(D−1)y+3Dy+2y=4e^(2z) (D^2 +2D+2)y=4e^(2z) Auxillary eqution m^2 +2m+2=0 m=−1±i y_c =e^(−z) (C_1 cos (z)+C_2 sin (z)) y_p =4(1/(D^2 +2D+2))e^(2z) =4(1/(4+4+2))e^(2z) =((4e^(2z) )/(10)) =((2e^(2z) )/5) y=e^(−z) (C_1 cos (z)+C_2 sin (z))+(2/5)e^(2z) but z=log_e x y=(1/x)[C_1 cos (log_e x)+C_2 sin (log_e x)]+(2/5)x^2](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q91028.png)
$${let}\:{x}={e}^{{z}} \: \\ $$$${x}^{\mathrm{2}} {y}''={D}\left({D}−\mathrm{1}\right){y} \\ $$$${xy}'={Dy} \\ $$$${D}\left({D}−\mathrm{1}\right){y}+\mathrm{3}{Dy}+\mathrm{2}{y}=\mathrm{4}{e}^{\mathrm{2}{z}} \\ $$$$\left({D}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{D}+\mathrm{2}\right){y}=\mathrm{4}{e}^{\mathrm{2}{z}} \\ $$$${Auxillary}\:{eqution}\: \\ $$$${m}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{m}+\mathrm{2}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${m}=−\mathrm{1}\pm{i} \\ $$$${y}_{{c}} ={e}^{−{z}} \left({C}_{\mathrm{1}} \mathrm{cos}\:\left({z}\right)+{C}_{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{sin}\:\left({z}\right)\right) \\ $$$${y}_{{p}} =\mathrm{4}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{D}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{D}+\mathrm{2}}{e}^{\mathrm{2}{z}} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{4}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}+\mathrm{4}+\mathrm{2}}{e}^{\mathrm{2}{z}} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{4}{e}^{\mathrm{2}{z}} }{\mathrm{10}} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{2}{e}^{\mathrm{2}{z}} }{\mathrm{5}} \\ $$$${y}={e}^{−{z}} \left({C}_{\mathrm{1}} \mathrm{cos}\:\left({z}\right)+{C}_{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{sin}\:\left({z}\right)\right)+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{5}}{e}^{\mathrm{2}{z}} \\ $$$${but}\:{z}={log}_{{e}} {x} \\ $$$${y}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}\left[{C}_{\mathrm{1}} \mathrm{cos}\:\left({log}_{{e}} {x}\right)+{C}_{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{sin}\:\left({log}_{{e}} {x}\right)\right]+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{5}}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
