Question Number 26198 by sorour87 last updated on 22/Dec/17
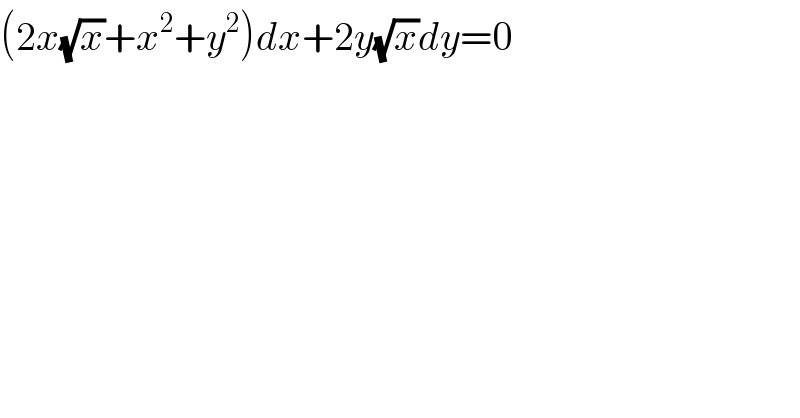
$$\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\sqrt{{x}}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{y}^{\mathrm{2}} \right){dx}+\mathrm{2}{y}\sqrt{{x}}{dy}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$
Answered by ajfour last updated on 22/Dec/17
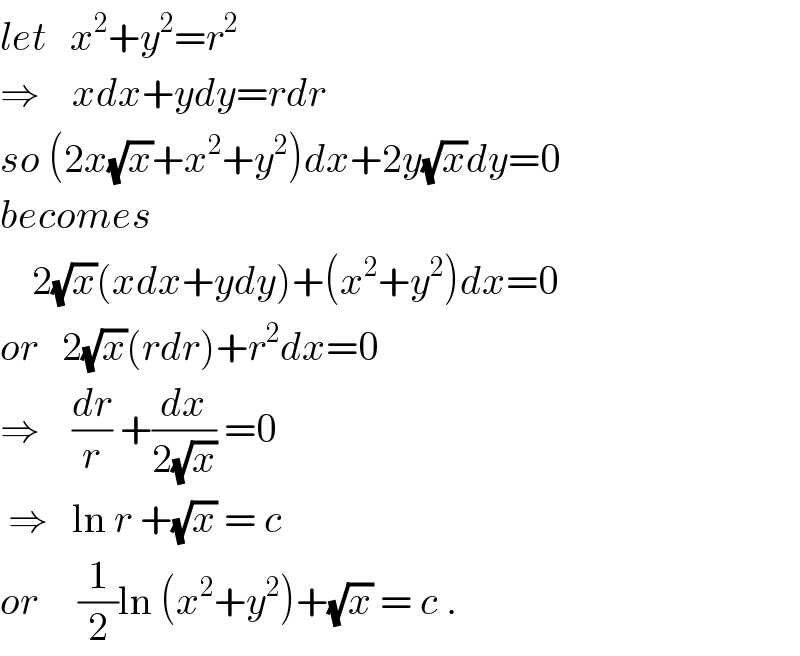
$${let}\:\:\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{y}^{\mathrm{2}} ={r}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\:\:\:{xdx}+{ydy}={rdr} \\ $$$${so}\:\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\sqrt{{x}}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{y}^{\mathrm{2}} \right){dx}+\mathrm{2}{y}\sqrt{{x}}{dy}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${becomes} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\mathrm{2}\sqrt{{x}}\left({xdx}+{ydy}\right)+\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{y}^{\mathrm{2}} \right){dx}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${or}\:\:\:\mathrm{2}\sqrt{{x}}\left({rdr}\right)+{r}^{\mathrm{2}} {dx}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\:\:\:\frac{{dr}}{{r}}\:+\frac{{dx}}{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{{x}}}\:=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\:\Rightarrow\:\:\:\mathrm{ln}\:{r}\:+\sqrt{{x}}\:=\:{c} \\ $$$${or}\:\:\:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{ln}\:\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{y}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)+\sqrt{{x}}\:=\:{c}\:. \\ $$
Commented by sorour87 last updated on 22/Dec/17

$${thank}\:{you} \\ $$
