Question Number 92056 by john santu last updated on 04/May/20

$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}^{+} } {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{\mathrm{ln}\left({x}\right)}{\mathrm{cot}\:{x}} \\ $$
Commented by Prithwish Sen 1 last updated on 05/May/20
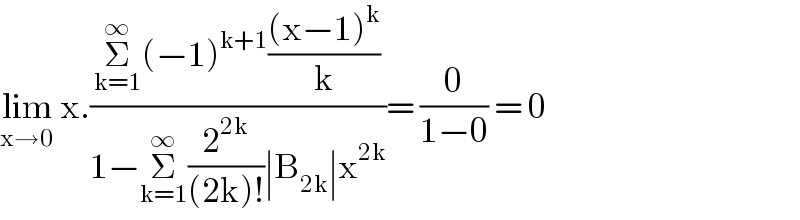
$$\underset{\mathrm{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\mathrm{x}.\frac{\underset{\mathrm{k}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{k}+\mathrm{1}} \frac{\left(\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{k}} }{\mathrm{k}}}{\mathrm{1}−\underset{\mathrm{k}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{2k}} }{\left(\mathrm{2k}\right)!}\mid\mathrm{B}_{\mathrm{2k}} \mid\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2k}} }=\:\frac{\mathrm{0}}{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{0}}\:=\:\mathrm{0} \\ $$
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 04/May/20
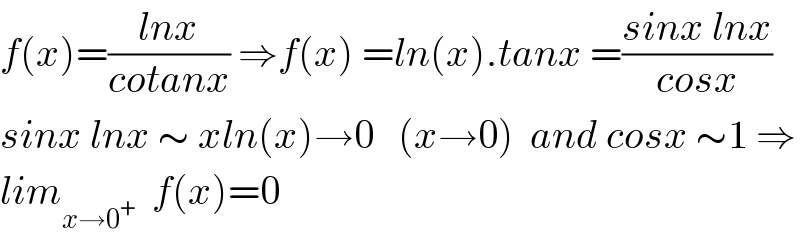
$${f}\left({x}\right)=\frac{{lnx}}{{cotanx}}\:\Rightarrow{f}\left({x}\right)\:={ln}\left({x}\right).{tanx}\:=\frac{{sinx}\:{lnx}}{{cosx}} \\ $$$${sinx}\:{lnx}\:\sim\:{xln}\left({x}\right)\rightarrow\mathrm{0}\:\:\:\left({x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}\right)\:\:{and}\:{cosx}\:\sim\mathrm{1}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${lim}_{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}^{+} } \:\:{f}\left({x}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$
