Question Number 93764 by DuDono last updated on 14/May/20
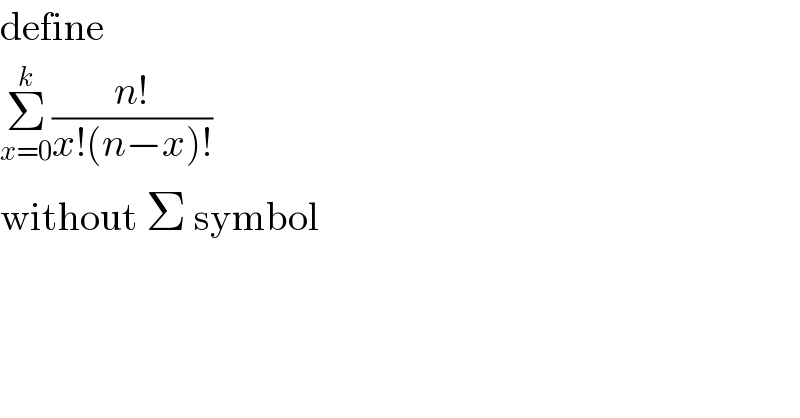
$$\mathrm{define} \\ $$$$\underset{{x}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{{k}} {\sum}}\frac{{n}!}{{x}!\left({n}−{x}\right)!} \\ $$$$\mathrm{without}\:\Sigma\:\mathrm{symbol} \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 14/May/20
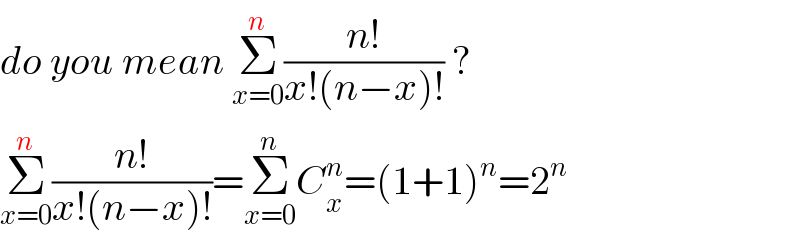
$${do}\:{you}\:{mean}\:\underset{{x}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{{n}} {\sum}}\frac{{n}!}{{x}!\left({n}−{x}\right)!}\:? \\ $$$$\underset{{x}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{{n}} {\sum}}\frac{{n}!}{{x}!\left({n}−{x}\right)!}=\underset{{x}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{{n}} {\sum}}{C}_{{x}} ^{{n}} =\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} =\mathrm{2}^{{n}} \\ $$
Commented by DuDono last updated on 14/May/20

$$ \\ $$$$\mathrm{no},\:{x}\:\mathrm{must}\:\mathrm{appear}\:\mathrm{somewhere}.\:\mathrm{You}\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{can}\:\mathrm{imagine}\:\mathrm{it}\:\mathrm{as}\:\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{function}\:\mathrm{if}\:\mathrm{you}\:\mathrm{want} \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 14/May/20

$${THEN}\:{YOUR}\:{QUESTION}\:{IS} \\ $$$${WRONG}!\: \\ $$$${in}\:\underset{{x}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{{k}} {\sum}}\:{a}_{{x}} \:{the}\:{symbol}\:{x}\:{is}\:{just}\:{a}\:{counter}, \\ $$$${you}\:{can}\:{replace}\:{it}\:{with}\:{any}\:{symbol}. \\ $$$$\underset{{x}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{{k}} {\sum}}\:{a}_{{x}} =\underset{{y}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{{k}} {\sum}}\:{a}_{{y}} =\:\underset{\psi=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{{k}} {\sum}}\:{a}_{\psi} . \\ $$$$\underset{{x}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{{k}} {\sum}}\:\frac{{n}!}{{x}!\left({n}−{x}\right)!}\:{can}\:{be}\:{a}\:{function}\:{of}\:{n} \\ $$$${or}\:{a}\:{function}\:{of}\:{k},\:{but}\:{never}\:{a} \\ $$$${function}\:{of}\:{x}.\:{this}\:{is}\:{such}\:{basic}\:{in} \\ $$$${mathematics}\:{as}\:\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{2}. \\ $$
