Question Number 2645 by Filup last updated on 24/Nov/15
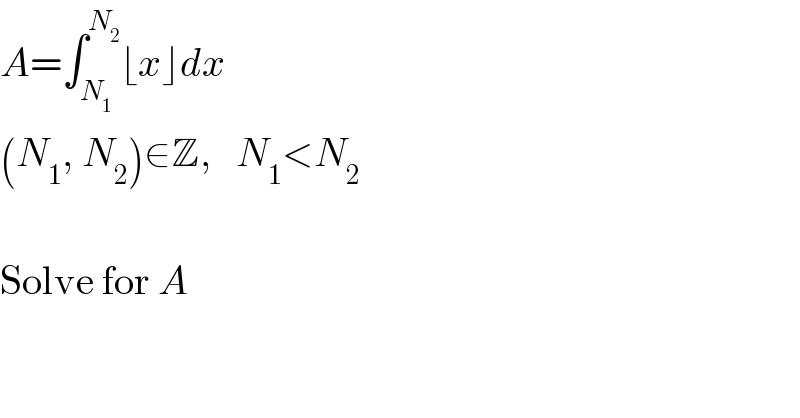
$${A}=\int_{{N}_{\mathrm{1}} } ^{{N}_{\mathrm{2}} } \lfloor{x}\rfloor{dx} \\ $$$$\left({N}_{\mathrm{1}} ,\:{N}_{\mathrm{2}} \right)\in\mathbb{Z},\:\:\:{N}_{\mathrm{1}} <{N}_{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\mathrm{Solve}\:\mathrm{for}\:{A} \\ $$
Answered by Filup last updated on 24/Nov/15

$$\mathrm{let}\:\:\:\:{N}_{\mathrm{1}} ={N},\:\:\:\:{N}_{\mathrm{2}} ={N}+{k} \\ $$$$\left({N}_{\mathrm{1}} ,\:{N}_{\mathrm{2}} \right)\in\mathbb{Z},\:\:\:\therefore\left({N},\:{k}\right)\in\mathbb{Z} \\ $$$${N}_{\mathrm{1}} <{N}_{\mathrm{2}} ,\:\:\:\therefore{k}>\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${N}\leqslant{x}<{N}+\mathrm{1}\Rightarrow\lfloor{x}\rfloor={N} \\ $$$${N}+\mathrm{1}\leqslant{x}<{N}+\mathrm{2}\Rightarrow\lfloor{x}\rfloor={N}+\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\vdots \\ $$$${N}+{k}−\mathrm{1}\leqslant{x}<{N}+{k}\Rightarrow\lfloor{x}\rfloor={N}+{k}−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\mathrm{The}\:\mathrm{area}\:\mathrm{between}\:{a}\rightarrow{a}+\mathrm{1}\:\mathrm{for}\:\lfloor{x}\rfloor \\ $$$$=\int_{{a}} ^{\:{a}+\mathrm{1}} \lfloor{x}\rfloor={a} \\ $$$$\because\mathrm{It}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{rectangle}\:\mathrm{with}\:\:{l}=\mathrm{1},\:\:{h}={a} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\mathrm{For}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{total}\:\mathrm{area}\:\mathrm{of}\:{A},\:\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{need}\:\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{sum} \\ $$$$\mathrm{all}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{rectangular}\:\mathrm{areas} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\int_{{N}} ^{{N}+{k}} \lfloor{x}\rfloor{dx}={N}+\left({N}+\mathrm{1}\right)+…+\left({N}+{k}−\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$$={N}\left({k}\right)+\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{2}+…+\left({k}−\mathrm{1}\right)\right) \\ $$$$={Nk}+\underset{{i}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{{k}−\mathrm{1}} {\sum}}{i} \\ $$$$={Nk}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left({k}−\mathrm{1}\right)\left(\mathrm{1}+{k}−\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$$={Nk}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{k}\left({k}−\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\therefore{A}=\int_{{N}} ^{\:{N}+{k}} \lfloor{x}\rfloor{dx}={Nk}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{k}\left({k}−\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${Test}: \\ $$$$\int_{\mathrm{2}} ^{\:\mathrm{5}} \lfloor{x}\rfloor{dx}=\mathrm{9}\:\:\:\left({wolfram}\right) \\ $$$${N}=\mathrm{2},\:\:\:{N}+{k}=\mathrm{5}\Rightarrow{k}=\mathrm{3} \\ $$$${A}=\mathrm{2}×\mathrm{3}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{3}\left(\mathrm{3}−\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$$=\mathrm{6}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\mathrm{3} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{9}\:\: \\ $$$$={True} \\ $$
Commented by Yozzi last updated on 24/Nov/15
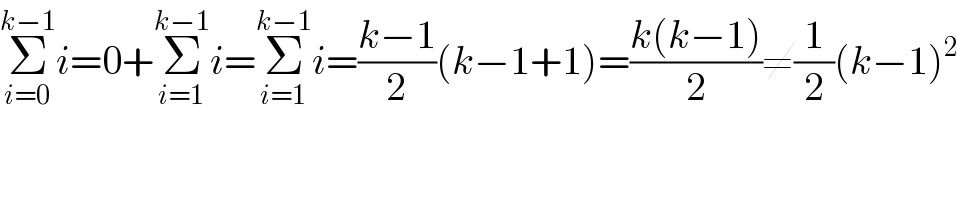
$$\underset{{i}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{{k}−\mathrm{1}} {\sum}}{i}=\mathrm{0}+\underset{{i}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{{k}−\mathrm{1}} {\sum}}{i}=\underset{{i}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{{k}−\mathrm{1}} {\sum}}{i}=\frac{{k}−\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left({k}−\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{1}\right)=\frac{{k}\left({k}−\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}\neq\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left({k}−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by Filup last updated on 24/Nov/15
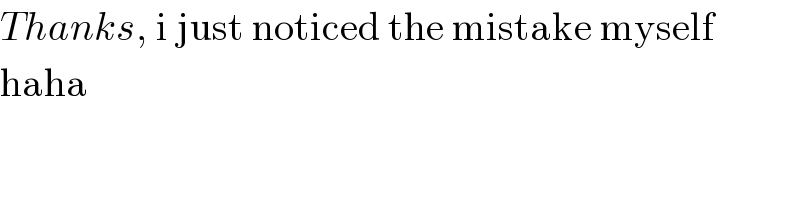
$${Thanks},\:\mathrm{i}\:\mathrm{just}\:\mathrm{noticed}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{mistake}\:\mathrm{myself} \\ $$$$\mathrm{haha} \\ $$
