Question Number 161697 by mnjuly1970 last updated on 21/Dec/21
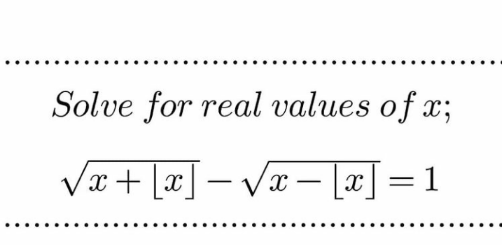
Answered by aleks041103 last updated on 21/Dec/21

$${let}\:{n}=\lfloor{x}\rfloor\:{and}\:{r}={x}−\lfloor{x}\rfloor\Rightarrow\mathrm{0}\leqslant{r}<\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{0}\leqslant\sqrt{{r}}<\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\sqrt{\mathrm{2}{n}+{r}}−\sqrt{{r}}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\sqrt{\mathrm{2}{n}+{r}}=\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{{r}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{1}\leqslant\sqrt{\mathrm{2}{n}+{r}}<\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{1}\leqslant\mathrm{2}{n}+{r}<\mathrm{4} \\ $$$${Onviously}\:{n}=\mathrm{1}. \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\sqrt{\mathrm{2}+{r}}−\sqrt{{r}}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{2}+{r}=\mathrm{1}+{r}+\mathrm{2}\sqrt{{r}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{2}\sqrt{{r}}\Rightarrow{r}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{x}=\mathrm{1}.\mathrm{25} \\ $$$$\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{1}.\mathrm{25}}−\sqrt{\mathrm{0}.\mathrm{25}}=\mathrm{1}.\mathrm{5}−\mathrm{0}.\mathrm{5}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${Ans}.\:{x}=\mathrm{1}.\mathrm{25} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
