Question Number 3048 by Syaka last updated on 03/Dec/15

$$\left.\mathrm{1}\right)\:\underset{{x}\:\rightarrow\:−\infty} {{lim}}\:\left(\mathrm{1}\:+\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}\right)_{} ^{{x}\:} \:=\:? \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by 123456 last updated on 04/Dec/15

$$\mathrm{L}=\underset{{x}\rightarrow−\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}\right)^{{x}} \\ $$$${u}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}} \\ $$$${x}\rightarrow−\infty\equiv{u}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}^{−} \\ $$$$\mathrm{L}=\underset{{u}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}^{−} } {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\mathrm{1}+{u}\right)^{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{u}}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{remember}\:\mathrm{that} \\ $$$${e}=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right)^{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{so} \\ $$$$\mathrm{L}={e} \\ $$
Commented by prakash jain last updated on 04/Dec/15
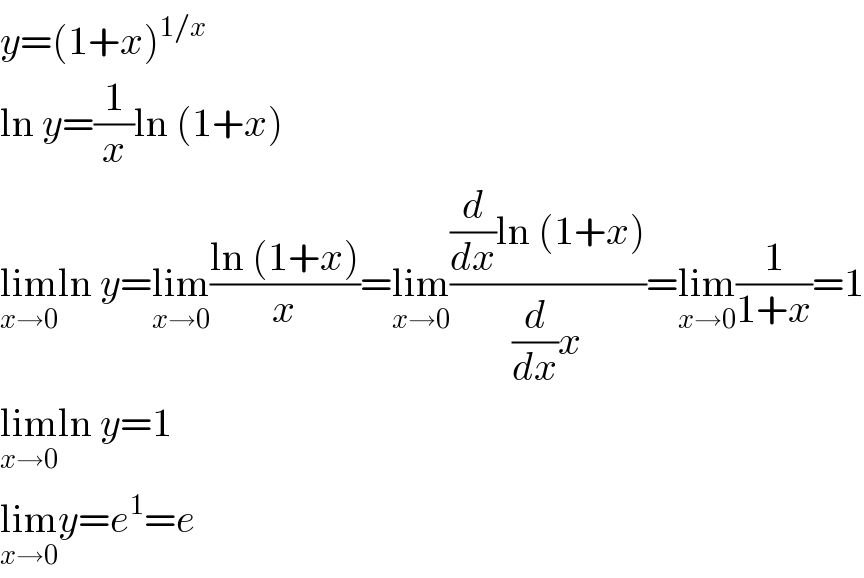
$${y}=\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right)^{\mathrm{1}/{x}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{ln}\:{y}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}\mathrm{ln}\:\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right) \\ $$$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}ln}\:{y}=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{ln}\:\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right)}{{x}}=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\frac{{d}}{{dx}}\mathrm{ln}\:\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right)}{\frac{{d}}{{dx}}{x}}=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}ln}\:{y}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}{y}={e}^{\mathrm{1}} ={e} \\ $$
