Question Number 131334 by Algoritm last updated on 03/Feb/21

Answered by bluberry508 last updated on 06/Feb/21
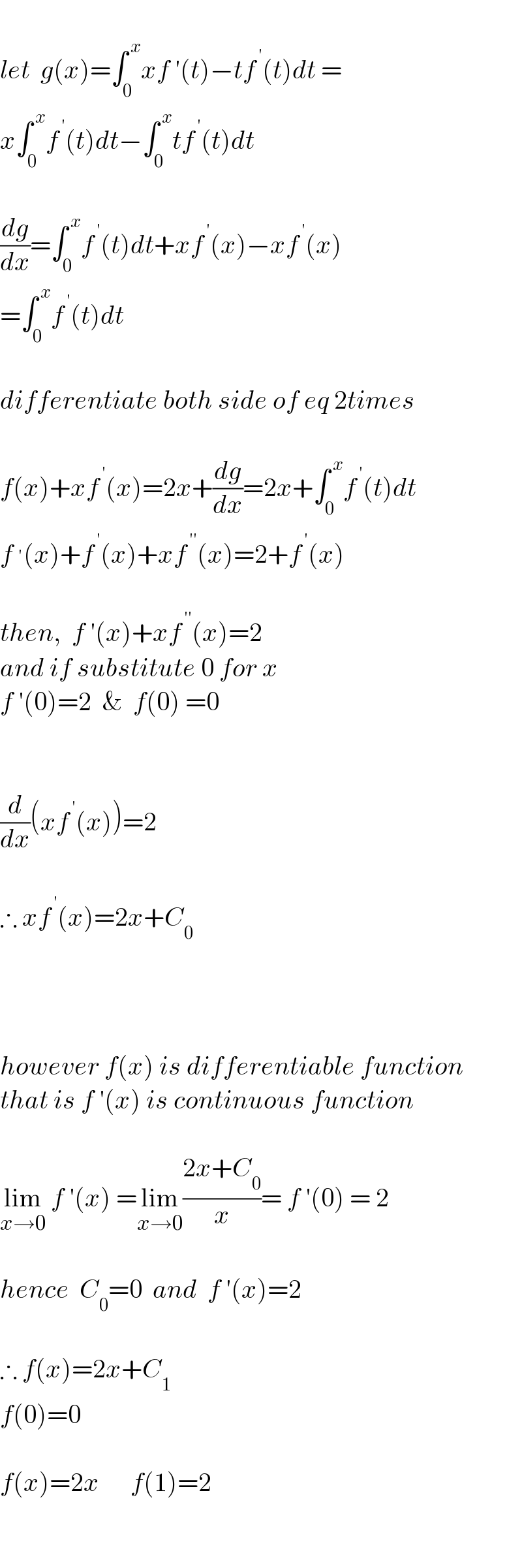
$$ \\ $$$${let}\:\:{g}\left({x}\right)=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\:{x}} {xf}\:'\left({t}\right)−{tf}^{\:'} \left({t}\right){dt}\:= \\ $$$${x}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\:{x}} {f}^{\:'} \left({t}\right){dt}−\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\:{x}} {tf}^{\:'} \left({t}\right){dt} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\frac{{dg}}{{dx}}=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\:{x}} {f}^{\:'} \left({t}\right){dt}+{xf}^{\:'} \left({x}\right)−{xf}^{\:'} \left({x}\right) \\ $$$$=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\:{x}} {f}^{\:'} \left({t}\right){dt} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${differentiate}\:{both}\:{side}\:{of}\:{eq}\:\mathrm{2}{times} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${f}\left({x}\right)+{xf}^{\:'} \left({x}\right)=\mathrm{2}{x}+\frac{{dg}}{{dx}}=\mathrm{2}{x}+\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\:{x}} {f}^{\:'} \left({t}\right){dt} \\ $$$${f}\:^{'} \left({x}\right)+{f}^{\:'} \left({x}\right)+{xf}^{\:''} \left({x}\right)=\mathrm{2}+{f}^{\:'} \left({x}\right) \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${then},\:\:{f}\:'\left({x}\right)+{xf}^{\:''} \left({x}\right)=\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${and}\:{if}\:{substitute}\:\mathrm{0}\:{for}\:{x}\: \\ $$$${f}\:'\left(\mathrm{0}\right)=\mathrm{2}\:\:\&\:\:{f}\left(\mathrm{0}\right)\:=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\frac{{d}}{{dx}}\left({xf}^{\:'} \left({x}\right)\right)=\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\therefore\:{xf}^{\:'} \left({x}\right)=\mathrm{2}{x}+{C}_{\mathrm{0}} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${however}\:{f}\left({x}\right)\:{is}\:{differentiable}\:{function} \\ $$$${that}\:{is}\:{f}\:'\left({x}\right)\:{is}\:{continuous}\:{function} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:{f}\:'\left({x}\right)\:=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}+{C}_{\mathrm{0}} }{{x}}=\:{f}\:'\left(\mathrm{0}\right)\:=\:\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${hence}\:\:{C}_{\mathrm{0}} =\mathrm{0}\:\:{and}\:\:{f}\:'\left({x}\right)=\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\therefore\:{f}\left({x}\right)=\mathrm{2}{x}+{C}_{\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$${f}\left(\mathrm{0}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${f}\left({x}\right)=\mathrm{2}{x}\:\:\:\:\:\:{f}\left(\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$
