Question Number 163751 by amin96 last updated on 10/Jan/22
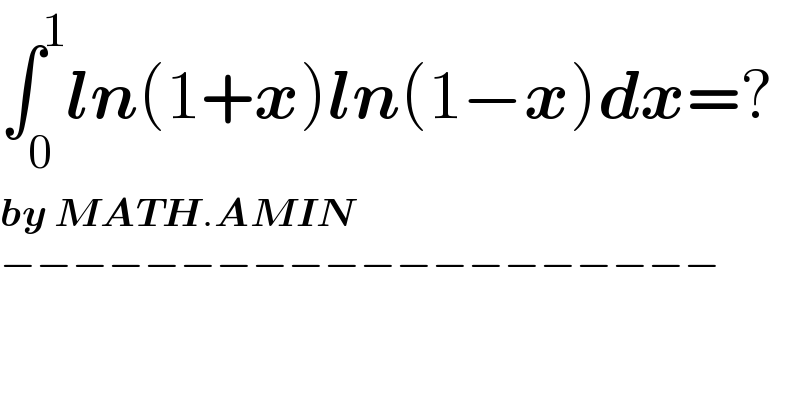
$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \boldsymbol{{ln}}\left(\mathrm{1}+\boldsymbol{{x}}\right)\boldsymbol{{ln}}\left(\mathrm{1}−\boldsymbol{{x}}\right)\boldsymbol{{dx}}=? \\ $$$$\boldsymbol{{by}}\:\boldsymbol{{MATH}}.\boldsymbol{{AMIN}} \\ $$$$−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−− \\ $$
Answered by Kamel last updated on 10/Jan/22
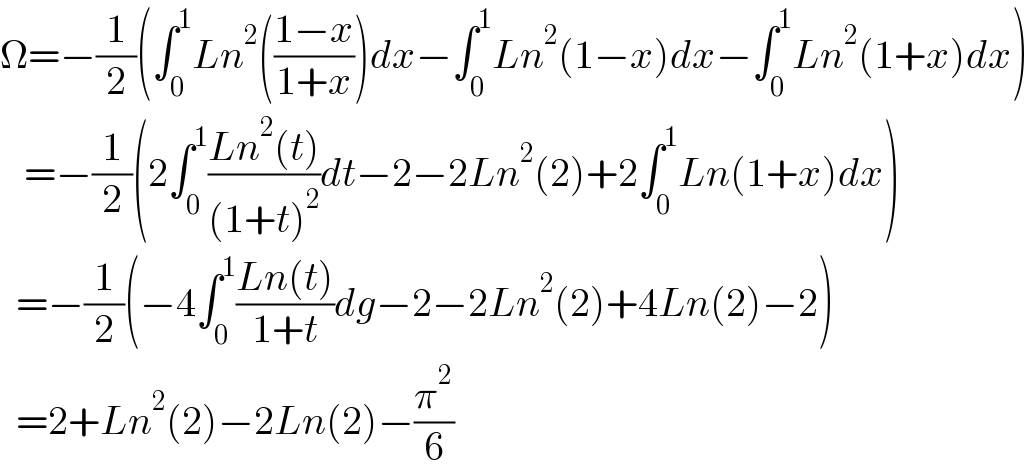
$$\Omega=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left(\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} {Ln}^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\frac{\mathrm{1}−{x}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}}\right){dx}−\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} {Ln}^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{1}−{x}\right){dx}−\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} {Ln}^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right){dx}\right) \\ $$$$\:\:\:=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left(\mathrm{2}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \frac{{Ln}^{\mathrm{2}} \left({t}\right)}{\left(\mathrm{1}+{t}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{dt}−\mathrm{2}−\mathrm{2}{Ln}^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{2}\right)+\mathrm{2}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} {Ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right){dx}\right) \\ $$$$\:\:=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left(−\mathrm{4}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \frac{{Ln}\left({t}\right)}{\mathrm{1}+{t}}{dg}−\mathrm{2}−\mathrm{2}{Ln}^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{2}\right)+\mathrm{4}{Ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)−\mathrm{2}\right) \\ $$$$\:\:=\mathrm{2}+{Ln}^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{2}\right)−\mathrm{2}{Ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)−\frac{\pi^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{6}} \\ $$
