Question Number 98768 by bemath last updated on 16/Jun/20
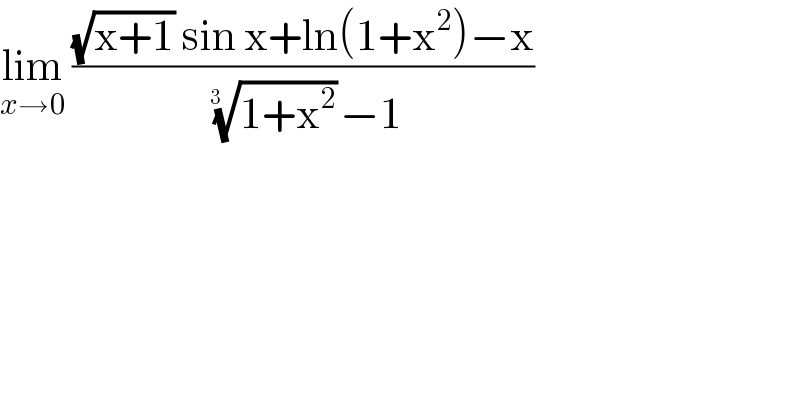
$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{1}}\:\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)−\mathrm{x}}{\:\sqrt[{\mathrm{3}\:\:}]{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }−\mathrm{1}} \\ $$
Answered by john santu last updated on 16/Jun/20

Commented by Farruxjano last updated on 16/Jun/20
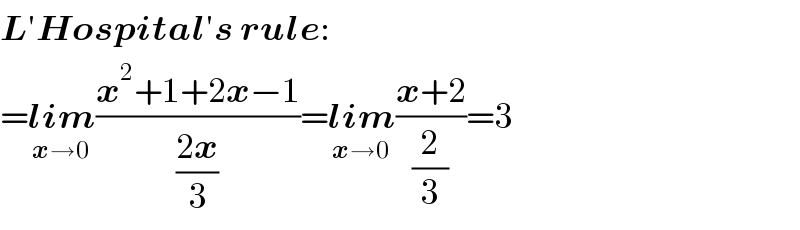
$$\boldsymbol{{L}}'\boldsymbol{{Hospital}}'\boldsymbol{{s}}\:\boldsymbol{{rule}}: \\ $$$$=\underset{\boldsymbol{{x}}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\boldsymbol{{lim}}}\frac{\boldsymbol{{x}}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{2}\boldsymbol{{x}}−\mathrm{1}}{\frac{\mathrm{2}\boldsymbol{{x}}}{\mathrm{3}}}=\underset{\boldsymbol{{x}}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\boldsymbol{{lim}}}\frac{\boldsymbol{{x}}+\mathrm{2}}{\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}}=\mathrm{3} \\ $$
Commented by bemath last updated on 16/Jun/20
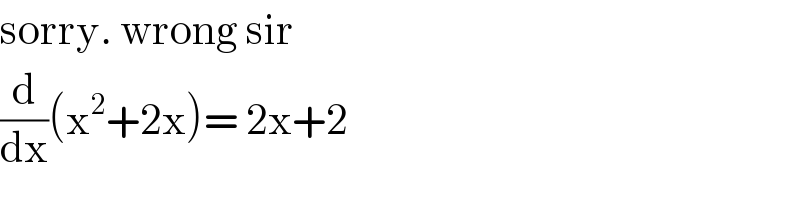
$$\mathrm{sorry}.\:\mathrm{wrong}\:\mathrm{sir} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{d}}{\mathrm{dx}}\left(\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2x}\right)=\:\mathrm{2x}+\mathrm{2} \\ $$
Commented by john santu last updated on 16/Jun/20

$$\mathrm{your}\:\mathrm{answer}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{wrong}.\:\mathrm{please}\:\mathrm{check} \\ $$
Commented by HamraboyevFarruxjon last updated on 16/Jun/20
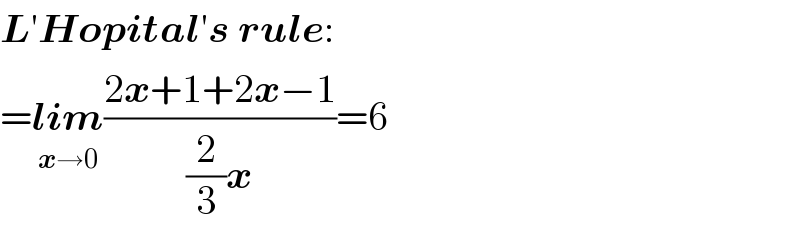
$$\boldsymbol{{L}}'\boldsymbol{{Hopital}}'\boldsymbol{{s}}\:\boldsymbol{{rule}}: \\ $$$$=\underset{\boldsymbol{{x}}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\boldsymbol{{lim}}}\frac{\mathrm{2}\boldsymbol{{x}}+\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{2}\boldsymbol{{x}}−\mathrm{1}}{\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}\boldsymbol{{x}}}=\mathrm{6} \\ $$
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 16/Jun/20
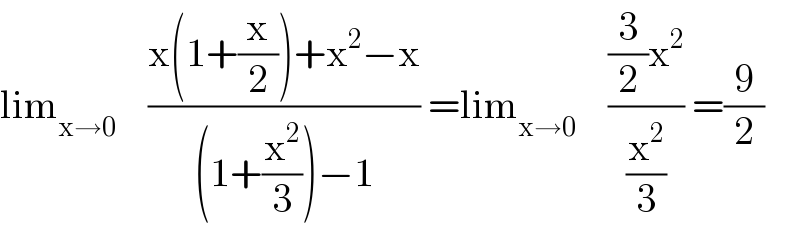
$$\mathrm{lim}_{\mathrm{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} \:\:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{x}\left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)+\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{x}}{\left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{3}}\right)−\mathrm{1}}\:=\mathrm{lim}_{\mathrm{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} \:\:\:\:\frac{\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\frac{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{3}}}\:=\frac{\mathrm{9}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
Answered by bramlex last updated on 16/Jun/20

$$\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right)^{{n}} \:\sim\:\left(\mathrm{1}+{nx}\right)\:;\:{x}\:\rightarrow\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{sin}\:{x}\:\sim{x}\:;\:{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right)\sim{x}\:;\:{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${then}\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\sqrt{{x}+\mathrm{1}}\:\mathrm{sin}\:{x}+\:\mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)−{x}}{\:\sqrt[{\mathrm{3}\:\:}]{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }−\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$=\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{\left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\right){x}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −{x}}{\left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{3}}\right)−\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$=\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{\left(\frac{\mathrm{3}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}\right)}{\left(\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{3}}\right)}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}×\mathrm{3}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{9}}{\mathrm{2}}\:. \\ $$
