Question Number 99529 by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 21/Jun/20

Answered by mr W last updated on 21/Jun/20
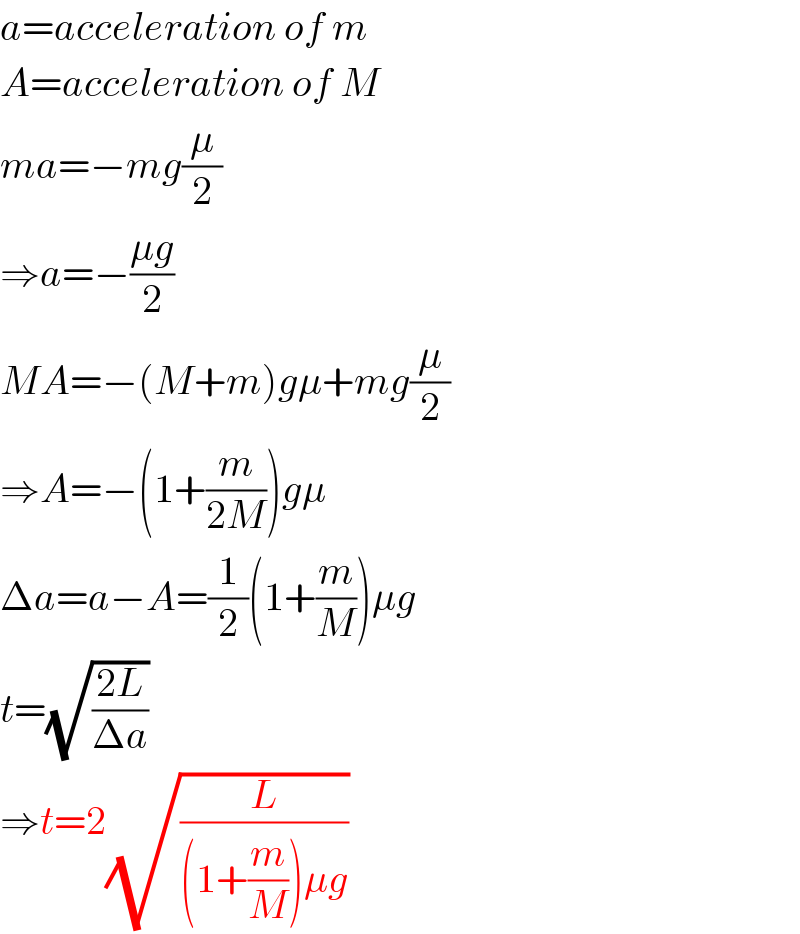
$${a}={acceleration}\:{of}\:{m} \\ $$$${A}={acceleration}\:{of}\:{M} \\ $$$${ma}=−{mg}\frac{\mu}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{a}=−\frac{\mu{g}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${MA}=−\left({M}+{m}\right){g}\mu+{mg}\frac{\mu}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{A}=−\left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{{m}}{\mathrm{2}{M}}\right){g}\mu \\ $$$$\Delta{a}={a}−{A}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{{m}}{{M}}\right)\mu{g} \\ $$$${t}=\sqrt{\frac{\mathrm{2}{L}}{\Delta{a}}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{t}=\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\frac{{L}}{\left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{{m}}{{M}}\right)\mu{g}}} \\ $$
Commented by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 21/Jun/20
You are right! sir.
Commented by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 21/Jun/20
I want to thank you for spending your valuable time
