Question Number 166660 by mnjuly1970 last updated on 24/Feb/22
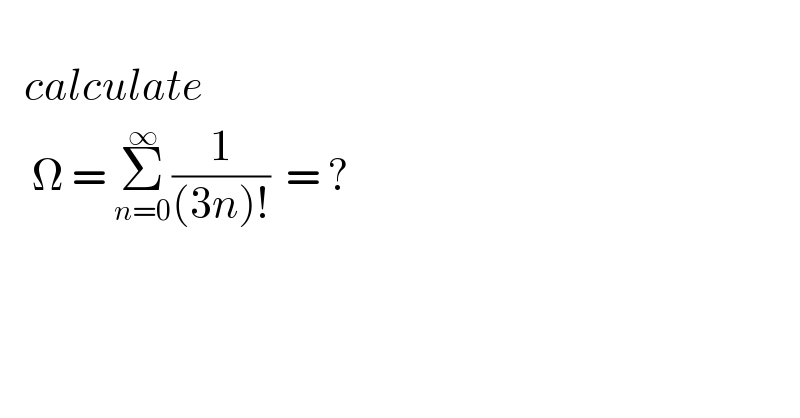
$$ \\ $$$$\:\:\:{calculate} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\Omega\:=\:\underset{{n}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left(\mathrm{3}{n}\right)!}\:\:=\:? \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\: \\ $$
Answered by amin96 last updated on 24/Feb/22
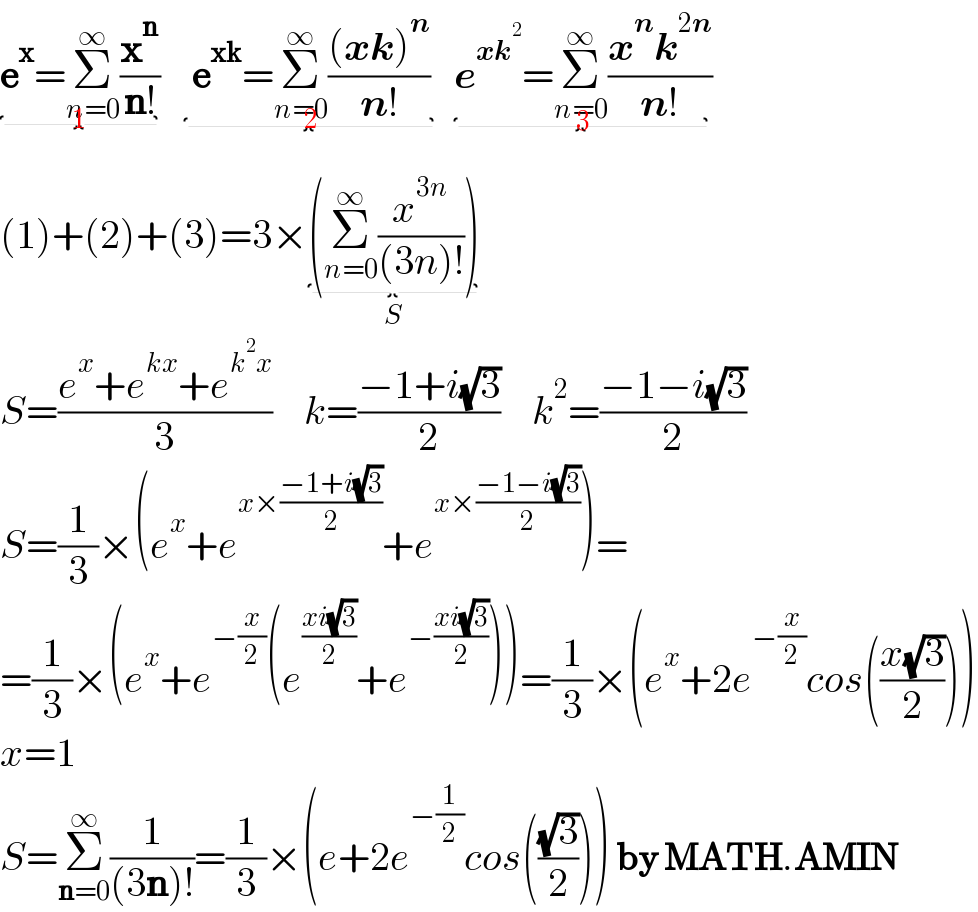
$$\underset{\mathrm{1}} {\underbrace{\boldsymbol{\mathrm{e}}^{\boldsymbol{\mathrm{x}}} =\underset{{n}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\boldsymbol{\mathrm{x}}^{\boldsymbol{\mathrm{n}}} }{\boldsymbol{\mathrm{n}}!}}}\:\:\:\underset{\mathrm{2}} {\underbrace{\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{e}}^{\boldsymbol{\mathrm{xk}}} =\underset{{n}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\left(\boldsymbol{{xk}}\right)^{\boldsymbol{{n}}} }{\boldsymbol{{n}}!}\:}}\:\:\underset{\mathrm{3}} {\underbrace{\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\boldsymbol{{xk}}^{\mathrm{2}} } =\underset{{n}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\boldsymbol{{x}}^{\boldsymbol{{n}}} \boldsymbol{{k}}^{\mathrm{2}\boldsymbol{{n}}} }{\boldsymbol{{n}}!}}} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{1}\right)+\left(\mathrm{2}\right)+\left(\mathrm{3}\right)=\mathrm{3}×\underset{{S}} {\underbrace{\left(\underset{{n}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{3}{n}} }{\left(\mathrm{3}{n}\right)!}\right)}} \\ $$$${S}=\frac{{e}^{{x}} +{e}^{{kx}} +{e}^{{k}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}} }{\mathrm{3}}\:\:\:\:{k}=\frac{−\mathrm{1}+{i}\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\:\:\:{k}^{\mathrm{2}} =\frac{−\mathrm{1}−{i}\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${S}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}×\left({e}^{{x}} +{e}^{{x}×\frac{−\mathrm{1}+{i}\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}{\mathrm{2}}} +{e}^{{x}×\frac{−\mathrm{1}−{i}\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}{\mathrm{2}}} \right)= \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}×\left({e}^{{x}} +{e}^{−\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}} \left({e}^{\frac{{xi}\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}{\mathrm{2}}} +{e}^{−\frac{{xi}\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}{\mathrm{2}}} \right)\right)=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}×\left({e}^{{x}} +\mathrm{2}{e}^{−\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}} {cos}\left(\frac{{x}\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)\right) \\ $$$${x}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${S}=\underset{\boldsymbol{\mathrm{n}}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left(\mathrm{3}\boldsymbol{\mathrm{n}}\right)!}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}×\left({e}+\mathrm{2}{e}^{−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}} {cos}\left(\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)\right)\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{by}}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{MATH}}.\boldsymbol{\mathrm{AMIN}} \\ $$
Commented by mnjuly1970 last updated on 25/Feb/22

$$\:\:\:{bravo}\:{sir} \\ $$
