Question Number 166770 by mr W last updated on 27/Feb/22

$${In}\:{how}\:{many}\:{ways}\:{can}\:{you}\:{go}\:{up}\:{a}\: \\ $$$${staircase}\:{with}\:\mathrm{20}\:{steps}\:{if}\:{you}\:{take}\: \\ $$$${one},\:{two}\:{or}\:{three}\:{steps}\:{at}\:{a}\:{time}? \\ $$
Commented by MJS_new last updated on 27/Feb/22

$$\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{it}\:\mathrm{121415}? \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 28/Feb/22
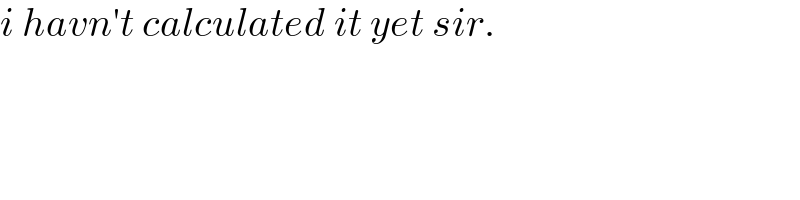
$${i}\:{havn}'{t}\:{calculated}\:{it}\:{yet}\:{sir}. \\ $$
Commented by peter frank last updated on 28/Feb/22

$$\mathrm{very}\:\mathrm{tough}\: \\ $$
Commented by MJS_new last updated on 28/Feb/22

$$\mathrm{not}\:\mathrm{tough}.\:\mathrm{just}\:\mathrm{arrange}\:\mathrm{as}\:\mathrm{follows}: \\ $$$$\mathrm{333333}\:\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\mathrm{333333}\:\mathrm{11} \\ $$$$\mathrm{33333}\:\mathrm{221} \\ $$$$\mathrm{33333}\:\mathrm{2111} \\ $$$$\mathrm{33333}\:\mathrm{11111} \\ $$$$\mathrm{3333}\:\mathrm{2222} \\ $$$$\mathrm{3333}\:\mathrm{22211} \\ $$$$… \\ $$$$\mathrm{then}\:\mathrm{count}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{permutations}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{each}\:\mathrm{row} \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 28/Feb/22
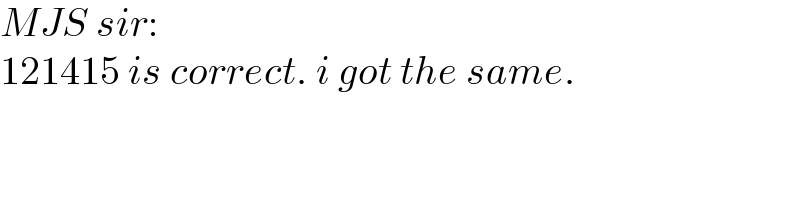
$${MJS}\:{sir}: \\ $$$$\mathrm{121415}\:{is}\:{correct}.\:{i}\:{got}\:{the}\:{same}. \\ $$
Commented by MJS_new last updated on 28/Feb/22

$$\mathrm{thank}\:\mathrm{you}! \\ $$
Answered by nadovic last updated on 27/Feb/22
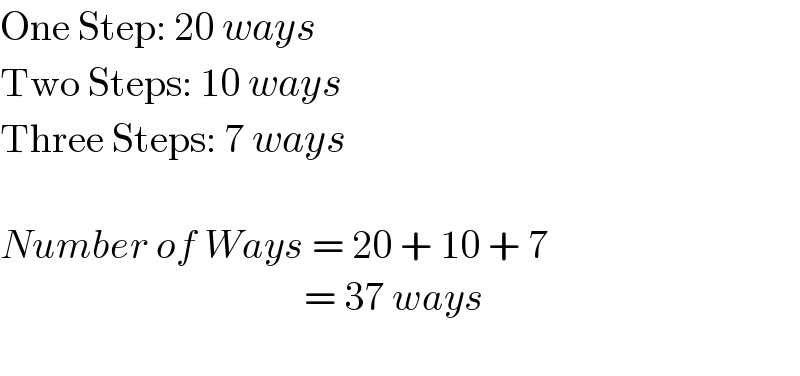
$$\mathrm{One}\:\mathrm{Step}:\:\mathrm{20}\:{ways} \\ $$$$\mathrm{Two}\:\mathrm{Steps}:\:\mathrm{10}\:{ways} \\ $$$$\mathrm{Three}\:\mathrm{Steps}:\:\mathrm{7}\:{ways} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${Number}\:{of}\:{Ways}\:=\:\mathrm{20}\:+\:\mathrm{10}\:+\:\mathrm{7} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=\:\mathrm{37}\:{ways} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 27/Feb/22

$${wrong}! \\ $$
Answered by nadovic last updated on 28/Feb/22
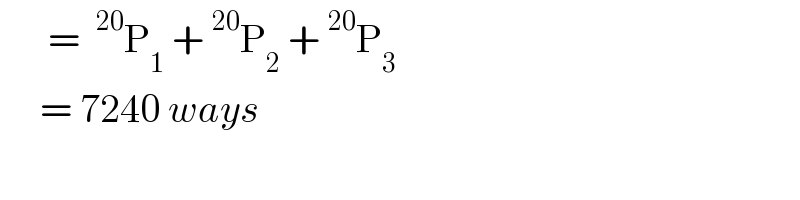
$$\:\:\:\:\:\:=\:\:^{\mathrm{20}} \mathrm{P}_{\mathrm{1}} \:+\:^{\mathrm{20}} \mathrm{P}_{\mathrm{2}} \:+\:^{\mathrm{20}} \mathrm{P}_{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:=\:\mathrm{7240}\:{ways} \\ $$
Commented by MJS_new last updated on 28/Feb/22

$$\mathrm{maybe}\:\mathrm{test}\:\mathrm{your}\:\mathrm{hypothetical}\:\mathrm{formula}\:\mathrm{with} \\ $$$$\mathrm{an}\:\mathrm{easy}\:\mathrm{example}? \\ $$$$\mathrm{5}\:\mathrm{stairs}: \\ $$$$\mathrm{32}\:\mathrm{23}\:\mathrm{311}\:\mathrm{131}\:\mathrm{113}\:\mathrm{221}\:\mathrm{212}\:\mathrm{122}\:\mathrm{2111}\:\mathrm{1211} \\ $$$$\mathrm{1121}\:\mathrm{1112}\:\mathrm{11111} \\ $$$$\mathrm{13}\:\mathrm{possibilities} \\ $$$$\mathrm{6}\:\mathrm{stairs}: \\ $$$$\mathrm{33}\:\mathrm{321}\:\mathrm{312}\:\mathrm{231}\:\mathrm{213}\:\mathrm{132}\:\mathrm{123}\:\mathrm{3111}\:\mathrm{1311}\:\mathrm{1131} \\ $$$$\mathrm{1113}\:\mathrm{222}\:\mathrm{2211}\:\mathrm{2121}\:\mathrm{2112}\:\mathrm{1221}\:\mathrm{1212}\:\mathrm{1122} \\ $$$$\mathrm{21111}\:\mathrm{12111}\:\mathrm{11211}\:\mathrm{11121}\:\mathrm{11112}\:\mathrm{111111} \\ $$$$\mathrm{24}\:\mathrm{possibilities} \\ $$$$… \\ $$
Answered by mr W last updated on 01/Mar/22

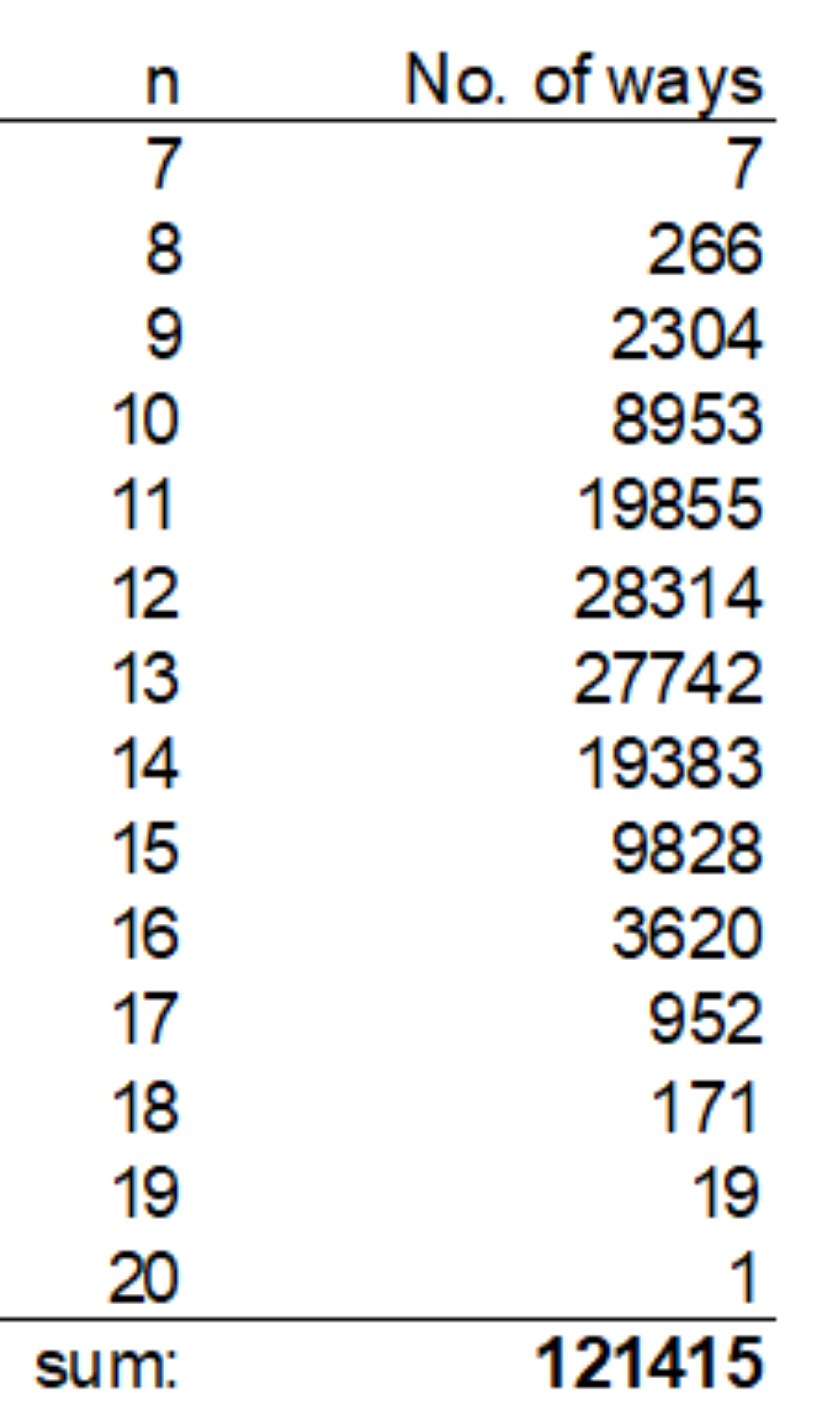
$${let}'{s}\:{look}\:{at}\:{the}\:{case}\:{that}\:{we}\:{make}\:{n}\: \\ $$$${moves}\:{to}\:{go}\:{up}\:{the}\:{staircase}.\:{each}\: \\ $$$${move}\:{can}\:{be}\:{of}\:{one},\:{two}\:{or}\:{three}\: \\ $$$${steps}. \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${the}\:{number}\:{of}\:{ways}\:{to}\:{go}\:{up}\:{the} \\ $$$${staircase}\:{in}\:{n}\:{moves}\:{is}\:{the}\:{number} \\ $$$${of}\:{integer}\:{solutions}\:{of}\:{the}\:{equation} \\ $$$${a}_{\mathrm{1}} +{a}_{\mathrm{2}} +{a}_{\mathrm{3}} +…+{a}_{{n}} =\mathrm{20} \\ $$$${with}\:\mathrm{1}\leqslant{a}_{{i}} \leqslant\mathrm{3}. \\ $$$${using}\:{generating}\:{function}\:{it}\:{is}\:{the}\: \\ $$$${coefficient}\:{of}\:{the}\:{x}^{\mathrm{20}} \:{term}\:{in}\:{the} \\ $$$${expansion}\:{of}\:\left({x}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{x}^{\mathrm{3}} \right)^{{n}} . \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\left({x}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{x}^{\mathrm{3}} \right)^{{n}} \\ $$$$={x}^{{n}} \left(\mathrm{1}+{x}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)^{{n}} \\ $$$$=\frac{{x}^{{n}} \left(\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{3}} \right)^{{n}} }{\left(\mathrm{1}−{x}\right)^{{n}} } \\ $$$$={x}^{{n}} \left\{\underset{{k}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{{n}} {\sum}}\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{k}} {C}_{{k}} ^{{n}} {x}^{\mathrm{3}{k}} \right\}\left\{\underset{{m}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}{C}_{{n}−\mathrm{1}} ^{{m}+{n}−\mathrm{1}} {x}^{{m}} \right\} \\ $$$${x}^{{n}} {x}^{\mathrm{3}{k}} {x}^{{m}} ={x}^{{n}+\mathrm{3}{k}+{m}} \overset{!} {=}{x}^{\mathrm{20}} \\ $$$${n}+\mathrm{3}{k}+{m}\overset{!} {=}\mathrm{20} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{3}{k}+{m}=\mathrm{20}−{n} \\ $$$$\mathrm{0}\leqslant{k}\leqslant{n},\:{m}\geqslant\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{7}\leqslant{n}\leqslant\mathrm{20}\:\left({this}\:{is}\:{clear},\:{we}\:{need}\:{at}\right. \\ $$$${least}\:\mathrm{7}\:{moves}\:{and}\:{at}\:{most}\:\mathrm{20}\:{moves} \\ $$$$\left.{to}\:{go}\:{up}\:{the}\:{staircase}.\right) \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${example}\:{n}=\mathrm{10}: \\ $$$${k}=\mathrm{0},\:{m}=\mathrm{10}\:\Rightarrow{C}_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{10}} {C}_{\mathrm{9}} ^{\mathrm{19}} =\mathrm{92378} \\ $$$${k}=\mathrm{1},\:{m}=\mathrm{7}\:\Rightarrow−{C}_{\mathrm{1}} ^{\mathrm{10}} {C}_{\mathrm{9}} ^{\mathrm{16}} =−\mathrm{114400} \\ $$$${k}=\mathrm{2},\:{m}=\mathrm{4}\:\Rightarrow{C}_{\mathrm{2}} ^{\mathrm{10}} {C}_{\mathrm{9}} ^{\mathrm{13}} =\mathrm{32175} \\ $$$${k}=\mathrm{3},\:{m}=\mathrm{1}\:\Rightarrow−{C}_{\mathrm{3}} ^{\mathrm{10}} {C}_{\mathrm{9}} ^{\mathrm{10}} =−\mathrm{1200} \\ $$$${that}\:{means}\:{the}\:{coef}.\:{of}\:{x}^{\mathrm{20}} \:{is} \\ $$$$\mathrm{92378}−\mathrm{114400}+\mathrm{32175}−\mathrm{1200}=\mathrm{8953} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${the}\:{results}\:{for}\:{all}\:{values}\:{of}\:{n}\:{see} \\ $$$${following}\:{table}. \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${the}\:{total}\:{result}\:{is}\:\mathrm{121415}.\:{i}.{e}.\:{there} \\ $$$${are}\:\mathrm{121415}\:{ways}\:{to}\:{go}\:{up}\:{the}\:{staircase}. \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 28/Feb/22
Commented by Tawa11 last updated on 28/Feb/22

$$\mathrm{Great}\:\mathrm{sir} \\ $$
Answered by mr W last updated on 02/Mar/22
![AN OTHER METHOD let′s say there are N(n) ways to go up a staircase with n steps. if we make a move with one step, then there are n−1 steps remaining and there are N(n−1) ways to go up the remaining steps. if we make a move with two steps, then there are n−2 steps remaining and there are N(n−2) ways to go up the remaining steps. similarly if we make a move with three steps, then there are N(n−3) ways to go up the remaining steps. therefore we have following recurrence relation: N(n)=N(n−1)+N(n−2)+N(n−3) we also have N(1)=1 N(2)=2 N(3)=4 applying the recurrence relation above, we get N(4)=7 N(5)=13 N(6)=24 N(7)=44 N(8)=81 N(9)=149 N(10)=274 N(11)=504 N(12)=927 N(13)=1705 N(14)=3136 N(15)=5768 N(16)=10609 N(17)=19513 N(18)=35890 N(19)=66012 N(20)=121415 ✓ we can also find a closed formula for N(n) by solving following characteristic equation λ^3 −λ^2 −λ−1=0 let λ=s+(1/3) s^2 −(4/3)s−((38)/(27))=0 with u=((3(√(33))+19))^(1/3) , v=((3(√(33))−19))^(1/3) λ_1 =(1/3)(1+u−v) λ_(2,3) =(1/6)[2−u+v±(√3)(u+v)i] ⇒N(n)=Aλ_1 ^n +Bλ_2 ^n +Cλ_3 ^n N(0)=N(3)−N(2)−N(1)=1 N(−1)=N(2)−N(1)−N(0)=0 N(1)=Aλ_1 +Bλ_2 +Cλ_3 =1 N(0)=A+B+C=1 N(−1)=(A/λ_1 )+(B/λ_2 )+(C/λ_3 )=0 [(λ_1 ,λ_2 ,λ_3 ),(1,1,1),((1/λ_1 ),(1/λ_2 ),(1/λ_3 )) ] ((A),(B),(C) ) = ((1),(1),(0) ) ⇒ ((A),(B),(C) ) = [(λ_1 ,λ_2 ,λ_3 ),(1,1,1),((1/λ_1 ),(1/λ_2 ),(1/λ_3 )) ]^(−1) ((1),(1),(0) )](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q166880.png)
$$\boldsymbol{{AN}}\:\boldsymbol{{OTHER}}\:\boldsymbol{{METHOD}} \\ $$$${let}'{s}\:{say}\:{there}\:{are}\:{N}\left({n}\right)\:{ways}\:{to}\:{go}\:{up} \\ $$$${a}\:{staircase}\:{with}\:{n}\:{steps}.\:{if}\:{we}\:{make} \\ $$$${a}\:{move}\:{with}\:{one}\:{step},\:{then}\:{there}\:{are} \\ $$$${n}−\mathrm{1}\:{steps}\:{remaining}\:{and}\:{there}\:{are} \\ $$$${N}\left({n}−\mathrm{1}\right)\:{ways}\:{to}\:{go}\:{up}\:{the}\:{remaining} \\ $$$${steps}.\:{if}\:{we}\:{make}\:{a}\:{move}\:{with} \\ $$$${two}\:{steps},\:{then}\:{there}\:{are}\:{n}−\mathrm{2}\:{steps}\: \\ $$$${remaining}\:{and}\:{there}\:{are}\:{N}\left({n}−\mathrm{2}\right)\: \\ $$$${ways}\:{to}\:{go}\:{up}\:{the}\:{remaining}\:{steps}.\: \\ $$$${similarly}\:{if}\:{we}\:{make}\:{a}\:{move}\:{with}\: \\ $$$${three}\:{steps},\:{then}\:{there}\:{are}\:{N}\left({n}−\mathrm{3}\right)\: \\ $$$${ways}\:{to}\:{go}\:{up}\:{the}\:{remaining}\:{steps}.\: \\ $$$${therefore}\:{we}\:{have}\:{following} \\ $$$${recurrence}\:{relation}: \\ $$$${N}\left({n}\right)={N}\left({n}−\mathrm{1}\right)+{N}\left({n}−\mathrm{2}\right)+{N}\left({n}−\mathrm{3}\right) \\ $$$${we}\:{also}\:{have}\: \\ $$$${N}\left(\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${N}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)=\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${N}\left(\mathrm{3}\right)=\mathrm{4} \\ $$$${applying}\:{the}\:{recurrence}\:{relation}\:{above},\: \\ $$$${we}\:{get} \\ $$$${N}\left(\mathrm{4}\right)=\mathrm{7} \\ $$$${N}\left(\mathrm{5}\right)=\mathrm{13} \\ $$$${N}\left(\mathrm{6}\right)=\mathrm{24} \\ $$$${N}\left(\mathrm{7}\right)=\mathrm{44} \\ $$$${N}\left(\mathrm{8}\right)=\mathrm{81} \\ $$$${N}\left(\mathrm{9}\right)=\mathrm{149} \\ $$$${N}\left(\mathrm{10}\right)=\mathrm{274} \\ $$$${N}\left(\mathrm{11}\right)=\mathrm{504} \\ $$$${N}\left(\mathrm{12}\right)=\mathrm{927} \\ $$$${N}\left(\mathrm{13}\right)=\mathrm{1705} \\ $$$${N}\left(\mathrm{14}\right)=\mathrm{3136} \\ $$$${N}\left(\mathrm{15}\right)=\mathrm{5768} \\ $$$${N}\left(\mathrm{16}\right)=\mathrm{10609} \\ $$$${N}\left(\mathrm{17}\right)=\mathrm{19513} \\ $$$${N}\left(\mathrm{18}\right)=\mathrm{35890} \\ $$$${N}\left(\mathrm{19}\right)=\mathrm{66012} \\ $$$${N}\left(\mathrm{20}\right)=\mathrm{121415}\:\checkmark \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${we}\:{can}\:{also}\:{find}\:{a}\:{closed}\:{formula} \\ $$$${for}\:{N}\left({n}\right)\:{by}\:{solving}\:{following} \\ $$$${characteristic}\:{equation} \\ $$$$\lambda^{\mathrm{3}} −\lambda^{\mathrm{2}} −\lambda−\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${let}\:\lambda={s}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$$${s}^{\mathrm{2}} −\frac{\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{3}}{s}−\frac{\mathrm{38}}{\mathrm{27}}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${with}\:{u}=\sqrt[{\mathrm{3}}]{\mathrm{3}\sqrt{\mathrm{33}}+\mathrm{19}},\:{v}=\sqrt[{\mathrm{3}}]{\mathrm{3}\sqrt{\mathrm{33}}−\mathrm{19}} \\ $$$$\lambda_{\mathrm{1}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\left(\mathrm{1}+{u}−{v}\right) \\ $$$$\lambda_{\mathrm{2},\mathrm{3}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{6}}\left[\mathrm{2}−{u}+{v}\pm\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}\left({u}+{v}\right){i}\right] \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{N}\left({n}\right)={A}\lambda_{\mathrm{1}} ^{{n}} +{B}\lambda_{\mathrm{2}} ^{{n}} +{C}\lambda_{\mathrm{3}} ^{{n}} \\ $$$${N}\left(\mathrm{0}\right)={N}\left(\mathrm{3}\right)−{N}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)−{N}\left(\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${N}\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)={N}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)−{N}\left(\mathrm{1}\right)−{N}\left(\mathrm{0}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${N}\left(\mathrm{1}\right)={A}\lambda_{\mathrm{1}} +{B}\lambda_{\mathrm{2}} +{C}\lambda_{\mathrm{3}} =\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${N}\left(\mathrm{0}\right)={A}+{B}+{C}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${N}\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)=\frac{{A}}{\lambda_{\mathrm{1}} }+\frac{{B}}{\lambda_{\mathrm{2}} }+\frac{{C}}{\lambda_{\mathrm{3}} }=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\begin{bmatrix}{\lambda_{\mathrm{1}} }&{\lambda_{\mathrm{2}} }&{\lambda_{\mathrm{3}} }\\{\mathrm{1}}&{\mathrm{1}}&{\mathrm{1}}\\{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\lambda_{\mathrm{1}} }}&{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\lambda_{\mathrm{2}} }}&{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\lambda_{\mathrm{3}} }}\end{bmatrix}\begin{pmatrix}{{A}}\\{{B}}\\{{C}}\end{pmatrix}\:=\begin{pmatrix}{\mathrm{1}}\\{\mathrm{1}}\\{\mathrm{0}}\end{pmatrix} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\begin{pmatrix}{{A}}\\{{B}}\\{{C}}\end{pmatrix}\:=\begin{bmatrix}{\lambda_{\mathrm{1}} }&{\lambda_{\mathrm{2}} }&{\lambda_{\mathrm{3}} }\\{\mathrm{1}}&{\mathrm{1}}&{\mathrm{1}}\\{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\lambda_{\mathrm{1}} }}&{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\lambda_{\mathrm{2}} }}&{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\lambda_{\mathrm{3}} }}\end{bmatrix}^{−\mathrm{1}} \begin{pmatrix}{\mathrm{1}}\\{\mathrm{1}}\\{\mathrm{0}}\end{pmatrix} \\ $$
