Question Number 37304 by math khazana by abdo last updated on 11/Jun/18
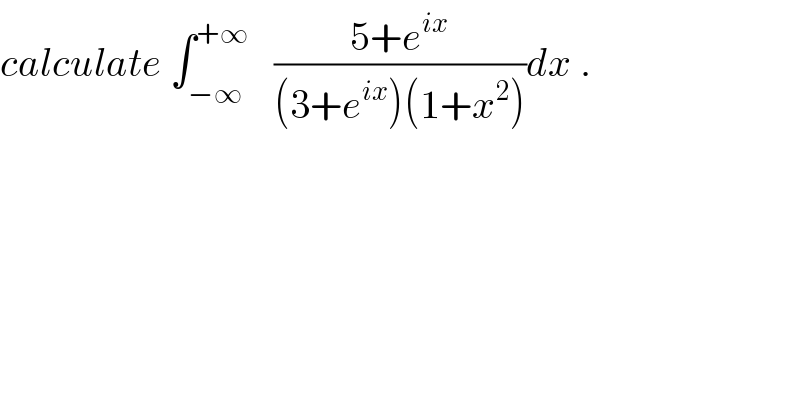
$${calculate}\:\int_{−\infty} ^{+\infty} \:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{5}+{e}^{{ix}} }{\left(\mathrm{3}+{e}^{{ix}} \right)\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)}{dx}\:. \\ $$
Commented by prof Abdo imad last updated on 16/Jun/18
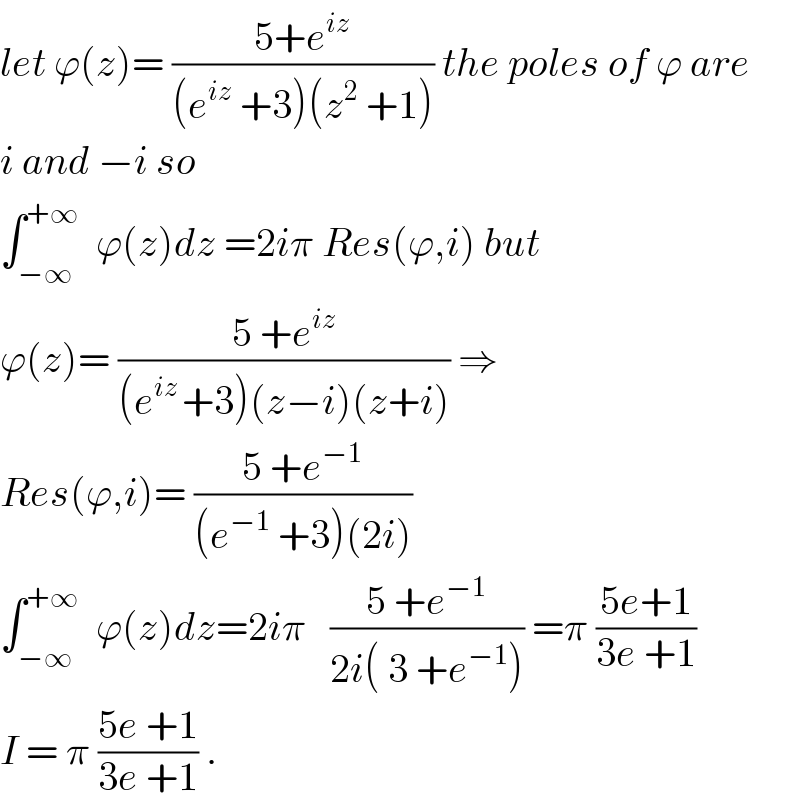
$${let}\:\varphi\left({z}\right)=\:\frac{\mathrm{5}+{e}^{{iz}} }{\left({e}^{{iz}} \:+\mathrm{3}\right)\left({z}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{1}\right)}\:{the}\:{poles}\:{of}\:\varphi\:{are} \\ $$$${i}\:{and}\:−{i}\:{so} \\ $$$$\int_{−\infty} ^{+\infty} \:\:\varphi\left({z}\right){dz}\:=\mathrm{2}{i}\pi\:{Res}\left(\varphi,{i}\right)\:{but} \\ $$$$\varphi\left({z}\right)=\:\frac{\mathrm{5}\:+{e}^{{iz}} }{\left({e}^{{iz}\:} +\mathrm{3}\right)\left({z}−{i}\right)\left({z}+{i}\right)}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${Res}\left(\varphi,{i}\right)=\:\frac{\mathrm{5}\:+{e}^{−\mathrm{1}} }{\left({e}^{−\mathrm{1}} \:+\mathrm{3}\right)\left(\mathrm{2}{i}\right)} \\ $$$$\int_{−\infty} ^{+\infty} \:\:\varphi\left({z}\right){dz}=\mathrm{2}{i}\pi\:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{5}\:+{e}^{−\mathrm{1}} }{\mathrm{2}{i}\left(\:\mathrm{3}\:+{e}^{−\mathrm{1}} \right)}\:=\pi\:\frac{\mathrm{5}{e}+\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}{e}\:+\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$${I}\:=\:\pi\:\frac{\mathrm{5}{e}\:+\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}{e}\:+\mathrm{1}}\:. \\ $$
