Question Number 37357 by math khazana by abdo last updated on 12/Jun/18

$${let}\:{a}>\mathrm{0}\:{b}\:{from}\:{C}\:{and}\:\:{Re}\left({b}\right)>\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{1}\right)\:{calculate}\:\:\int_{−\infty} ^{+\infty} \:\:\:\frac{{b}\:{cos}\left({ax}\right)}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+{b}^{\mathrm{2}} }{dx} \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{2}\right)\:{find}\:{the}\:{value}\:{of}\:\:\int_{−\infty} ^{+\infty} \:\:\:\frac{{x}\:{sin}\left({ax}\right)}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+{b}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:{dx}. \\ $$
Commented by abdo.msup.com last updated on 13/Jun/18

$$\left.\mathrm{1}\right)\:{let}\:{I}\:=\int_{−\infty} ^{+\infty} \:\:\:\frac{{b}\:{cos}\left({ax}\right)}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}\:} \:+{b}^{\mathrm{2}} }{dx} \\ $$$${I}\:=\:{Re}\left(\:\int_{−\infty} ^{+\infty} \:\:\:\frac{{b}\:{e}^{{iax}} }{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+{b}^{\mathrm{2}} }{dx}\right)\:{let}\:{consider} \\ $$$$\varphi\left({z}\right)\:=\:\frac{{b}\:{e}^{{iaz}} }{{z}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+{b}^{\mathrm{2}} }\: \\ $$$$\varphi\left({z}\right)\:=\frac{{be}^{{iax}} }{\left({z}−{ib}\right)\left({z}+{ib}\right)}\:{so}\:{the}\:{poles}\:{of}\:\varphi \\ $$$${are}\:{ib}\:{and}\:−{ib}\:\:{we}\:{have}\:{Re}\left({b}\right)>\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${Im}\left({ib}\right)>\mathrm{0}\:{so} \\ $$$$\int_{−\infty} ^{+\infty} \:\:\varphi\left({z}\right){dz}\:=\mathrm{2}{i}\pi\:{Res}\left(\varphi,{ib}\right) \\ $$$${Res}\left(\varphi,{ib}\right)\:={lim}_{{z}\rightarrow{ib}} \:\left({z}−{ib}\right)\varphi\left({z}\right) \\ $$$$=\:\frac{{b}\:{e}^{{ia}\left({ib}\right)} }{\mathrm{2}{ib}}\:=\:\frac{{e}^{−{ab}} }{\mathrm{2}{i}}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\int_{−\infty} ^{+\infty} \:\:\:\varphi\left({z}\right){dz}\:=\mathrm{2}{i}\pi\:\frac{{e}^{−{ab}} }{\mathrm{2}{i}}\:=\pi\:{e}^{−{ab}} \:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${I}\:\:=\:\pi\:{e}^{−{ab}} \:\:. \\ $$
Commented by abdo.msup.com last updated on 13/Jun/18
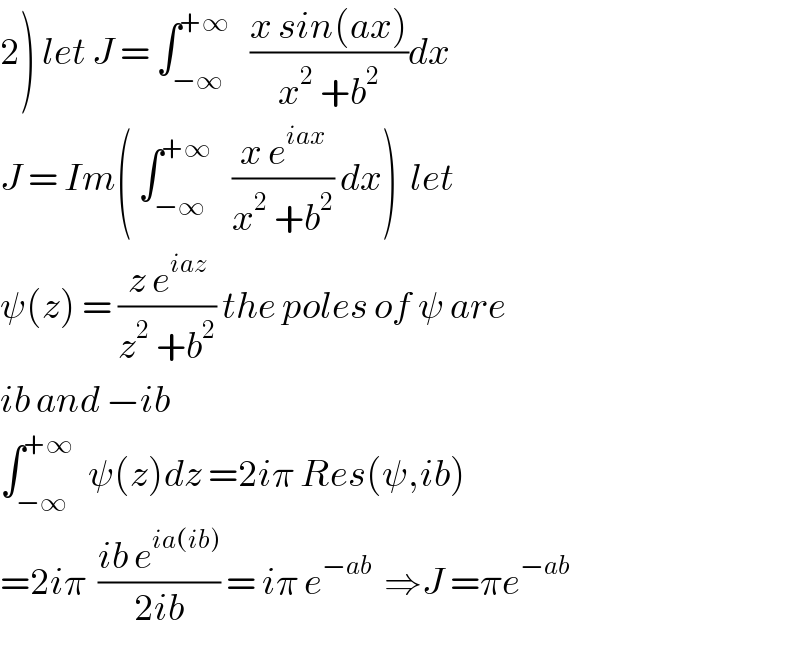
$$\left.\mathrm{2}\right)\:{let}\:{J}\:=\:\int_{−\infty} ^{+\infty} \:\:\:\frac{{x}\:{sin}\left({ax}\right)}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+{b}^{\mathrm{2}} }{dx}\: \\ $$$${J}\:=\:{Im}\left(\:\int_{−\infty} ^{+\infty} \:\:\:\frac{{x}\:{e}^{{iax}} }{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+{b}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:{dx}\right)\:\:{let} \\ $$$$\psi\left({z}\right)\:=\:\frac{{z}\:{e}^{{iaz}} }{{z}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+{b}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:{the}\:{poles}\:{of}\:\psi\:{are} \\ $$$${ib}\:{and}\:−{ib} \\ $$$$\int_{−\infty} ^{+\infty} \:\:\psi\left({z}\right){dz}\:=\mathrm{2}{i}\pi\:{Res}\left(\psi,{ib}\right) \\ $$$$=\mathrm{2}{i}\pi\:\:\frac{{ib}\:{e}^{{ia}\left({ib}\right)} }{\mathrm{2}{ib}}\:=\:{i}\pi\:{e}^{−{ab}} \:\:\Rightarrow{J}\:=\pi{e}^{−{ab}} \: \\ $$
