Question Number 168518 by LEKOUMA last updated on 12/Apr/22
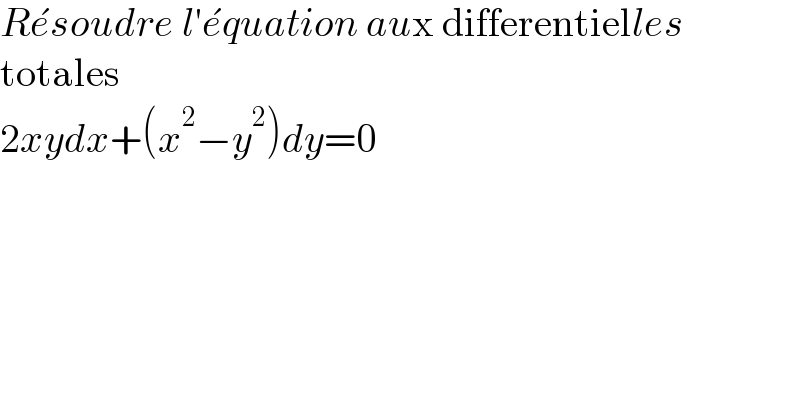
$${R}\acute {{e}soudre}\:{l}'\acute {{e}quation}\:{au}\mathrm{x}\:\mathrm{differentiel}{les} \\ $$$$\mathrm{totales} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}{xydx}+\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} −{y}^{\mathrm{2}} \right){dy}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$
Commented by mokys last updated on 12/Apr/22
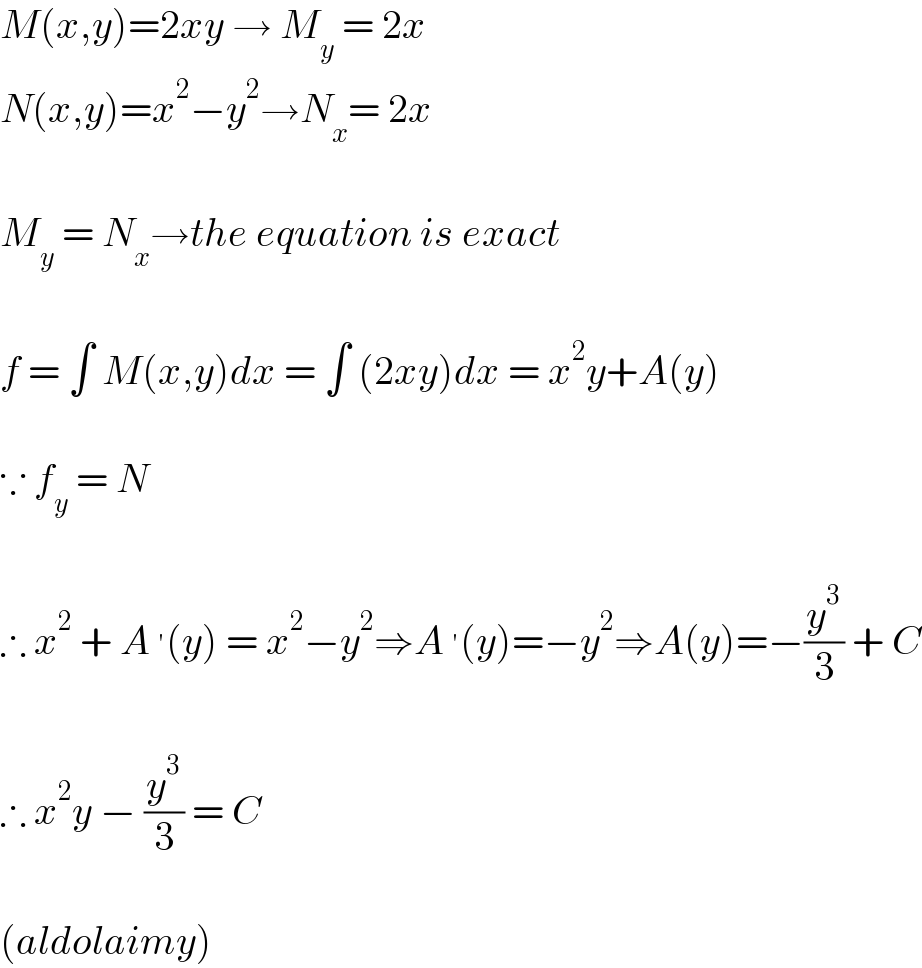
$${M}\left({x},{y}\right)=\mathrm{2}{xy}\:\rightarrow\:{M}_{{y}} \:=\:\mathrm{2}{x} \\ $$$${N}\left({x},{y}\right)={x}^{\mathrm{2}} −{y}^{\mathrm{2}} \rightarrow{N}_{{x}} =\:\mathrm{2}{x} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${M}_{{y}} \:=\:{N}_{{x}} \rightarrow{the}\:{equation}\:{is}\:{exact} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${f}\:=\:\int\:{M}\left({x},{y}\right){dx}\:=\:\int\:\left(\mathrm{2}{xy}\right){dx}\:=\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} {y}+{A}\left({y}\right) \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\because\:{f}_{{y}} \:=\:{N} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\therefore\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\:{A}\:^{'} \left({y}\right)\:=\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −{y}^{\mathrm{2}} \Rightarrow{A}\:^{'} \left({y}\right)=−{y}^{\mathrm{2}} \Rightarrow{A}\left({y}\right)=−\frac{{y}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{3}}\:+\:{C} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\therefore\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} {y}\:−\:\frac{{y}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{3}}\:=\:{C}\: \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\left({aldolaimy}\right) \\ $$
Answered by alephzero last updated on 12/Apr/22
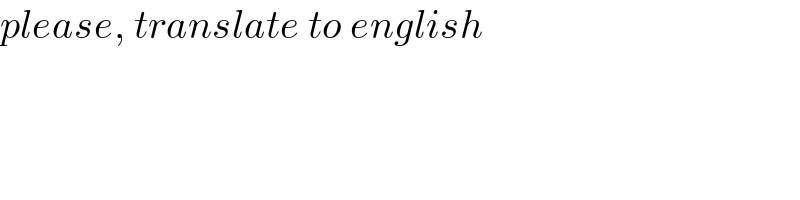
$${please},\:{translate}\:{to}\:{english} \\ $$
