Question Number 37938 by Fawomath last updated on 19/Jun/18

Commented by abdo.msup.com last updated on 19/Jun/18
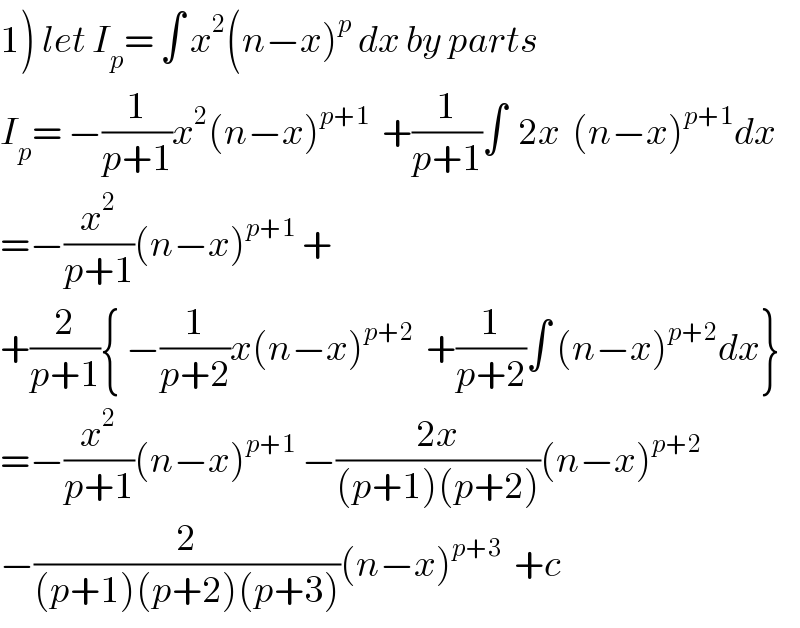
$$\left.\mathrm{1}\right)\:{let}\:{I}_{{p}} =\:\int\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \left({n}−{x}\right)^{{p}} \:{dx}\:{by}\:{parts} \\ $$$${I}_{{p}} =\:−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{p}+\mathrm{1}}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \left({n}−{x}\right)^{{p}+\mathrm{1}} \:\:+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{p}+\mathrm{1}}\int\:\:\mathrm{2}{x}\:\:\left({n}−{x}\right)^{{p}+\mathrm{1}} {dx} \\ $$$$=−\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{p}+\mathrm{1}}\left({n}−{x}\right)^{{p}+\mathrm{1}} \:+ \\ $$$$+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{{p}+\mathrm{1}}\left\{\:−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{p}+\mathrm{2}}{x}\left({n}−{x}\right)^{{p}+\mathrm{2}} \:\:+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{p}+\mathrm{2}}\int\:\left({n}−{x}\right)^{{p}+\mathrm{2}} {dx}\right\} \\ $$$$=−\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{p}+\mathrm{1}}\left({n}−{x}\right)^{{p}+\mathrm{1}} \:−\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}}{\left({p}+\mathrm{1}\right)\left({p}+\mathrm{2}\right)}\left({n}−{x}\right)^{{p}+\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\left({p}+\mathrm{1}\right)\left({p}+\mathrm{2}\right)\left({p}+\mathrm{3}\right)}\left({n}−{x}\right)^{{p}+\mathrm{3}} \:\:+{c} \\ $$
Commented by abdo.msup.com last updated on 19/Jun/18
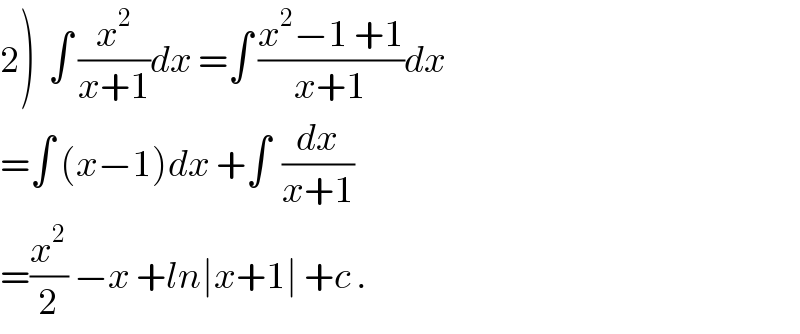
$$\left.\mathrm{2}\right)\:\:\int\:\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{x}+\mathrm{1}}{dx}\:=\int\:\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}\:+\mathrm{1}}{{x}+\mathrm{1}}{dx} \\ $$$$=\int\:\left({x}−\mathrm{1}\right){dx}\:+\int\:\:\frac{{dx}}{{x}+\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$=\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}\:−{x}\:+{ln}\mid{x}+\mathrm{1}\mid\:+{c}\:. \\ $$
Commented by abdo.msup.com last updated on 19/Jun/18
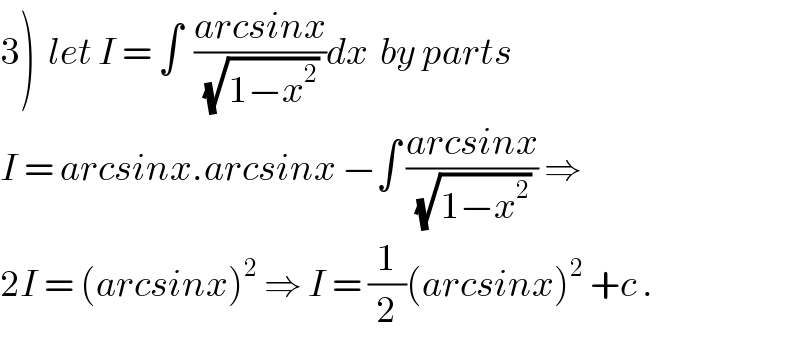
$$\left.\mathrm{3}\right)\:\:{let}\:{I}\:=\:\int\:\:\frac{{arcsinx}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }}{dx}\:\:{by}\:{parts} \\ $$$${I}\:=\:{arcsinx}.{arcsinx}\:−\int\:\frac{{arcsinx}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}{I}\:=\:\left({arcsinx}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \:\Rightarrow\:{I}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left({arcsinx}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \:+{c}\:. \\ $$
Commented by abdo.msup.com last updated on 19/Jun/18
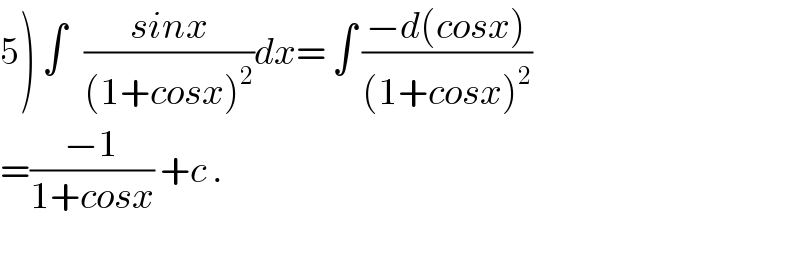
$$\left.\mathrm{5}\right)\:\int\:\:\:\frac{{sinx}}{\left(\mathrm{1}+{cosx}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{dx}=\:\int\:\frac{−{d}\left({cosx}\right)}{\left(\mathrm{1}+{cosx}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$=\frac{−\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+{cosx}}\:+{c}\:. \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by abdo.msup.com last updated on 19/Jun/18
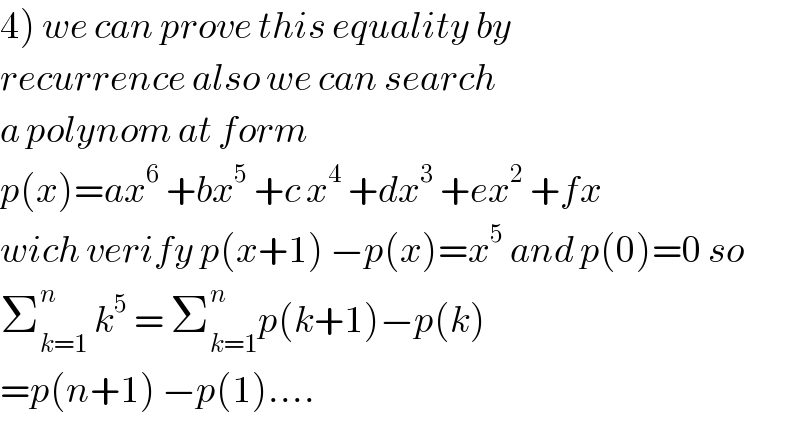
$$\left.\mathrm{4}\right)\:{we}\:{can}\:{prove}\:{this}\:{equality}\:{by}\: \\ $$$${recurrence}\:{also}\:{we}\:{can}\:{search}\: \\ $$$${a}\:{polynom}\:{at}\:{form}\: \\ $$$${p}\left({x}\right)={ax}^{\mathrm{6}} \:+{bx}^{\mathrm{5}} \:+{c}\:{x}^{\mathrm{4}} \:+{dx}^{\mathrm{3}} \:+{ex}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+{fx}\: \\ $$$${wich}\:{verify}\:{p}\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)\:−{p}\left({x}\right)={x}^{\mathrm{5}} \:{and}\:{p}\left(\mathrm{0}\right)=\mathrm{0}\:{so} \\ $$$$\sum_{{k}=\mathrm{1}} ^{{n}} \:{k}^{\mathrm{5}} \:=\:\sum_{{k}=\mathrm{1}} ^{{n}} {p}\left({k}+\mathrm{1}\right)−{p}\left({k}\right) \\ $$$$={p}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)\:−{p}\left(\mathrm{1}\right)…. \\ $$
Answered by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 19/Jun/18
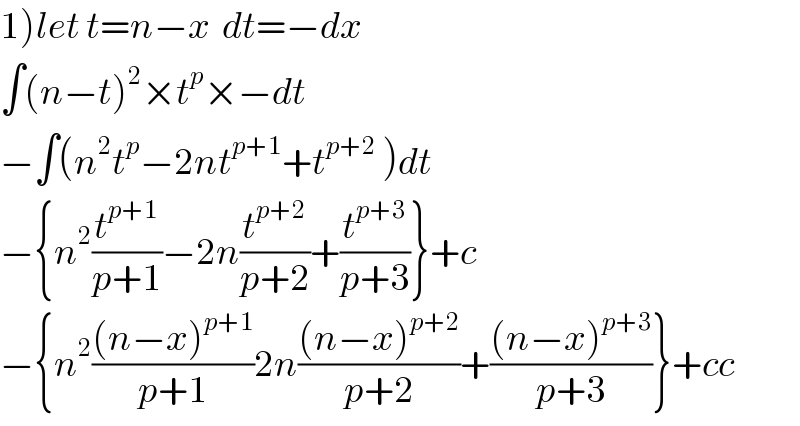
$$\left.\mathrm{1}\right){let}\:{t}={n}−{x}\:\:{dt}=−{dx} \\ $$$$\int\left({n}−{t}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} ×{t}^{{p}} ×−{dt} \\ $$$$−\int\left({n}^{\mathrm{2}} {t}^{{p}} −\mathrm{2}{nt}^{{p}+\mathrm{1}} +{t}^{{p}+\mathrm{2}} \:\right){dt} \\ $$$$−\left\{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} \frac{{t}^{{p}+\mathrm{1}} }{{p}+\mathrm{1}}−\mathrm{2}{n}\frac{{t}^{{p}+\mathrm{2}} }{{p}+\mathrm{2}}+\frac{{t}^{{p}+\mathrm{3}} }{{p}+\mathrm{3}}\right\}+{c} \\ $$$$−\left\{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} \frac{\left({n}−{x}\right)^{{p}+\mathrm{1}} }{{p}+\mathrm{1}}\mathrm{2}{n}\frac{\left({n}−{x}\right)^{{p}+\mathrm{2}} }{{p}+\mathrm{2}}+\frac{\left({n}−{x}\right)^{{p}+\mathrm{3}} }{{p}+\mathrm{3}}\right\}+{cc} \\ $$
Answered by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 19/Jun/18
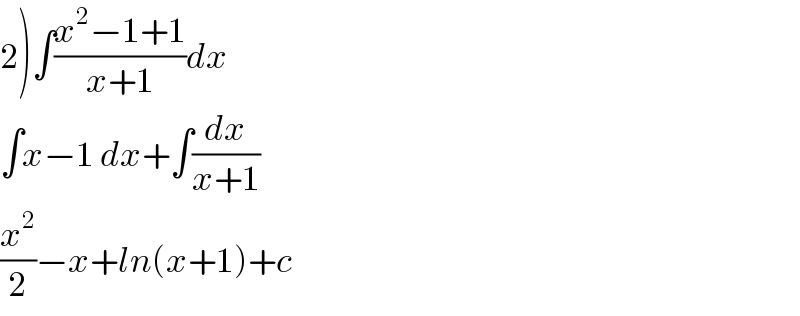
$$\left.\mathrm{2}\right)\int\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{1}}{{x}+\mathrm{1}}{dx} \\ $$$$\int{x}−\mathrm{1}\:{dx}+\int\frac{{dx}}{{x}+\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}−{x}+{ln}\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)+{c} \\ $$
Answered by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 19/Jun/18
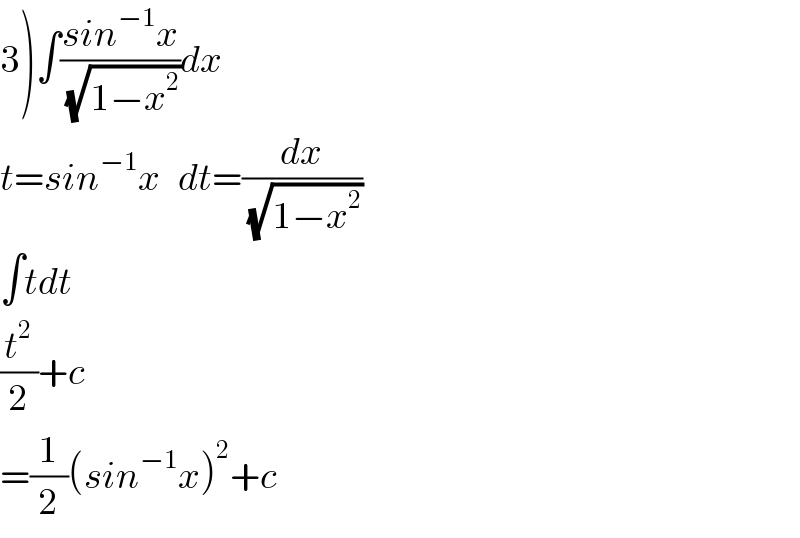
$$\left.\mathrm{3}\right)\int\frac{{sin}^{−\mathrm{1}} {x}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }}{dx}\:\: \\ $$$${t}={sin}^{−\mathrm{1}} {x}\:\:\:{dt}=\frac{{dx}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }} \\ $$$$\int{tdt} \\ $$$$\frac{{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}+{c} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left({sin}^{−\mathrm{1}} {x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +{c} \\ $$
Answered by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 19/Jun/18
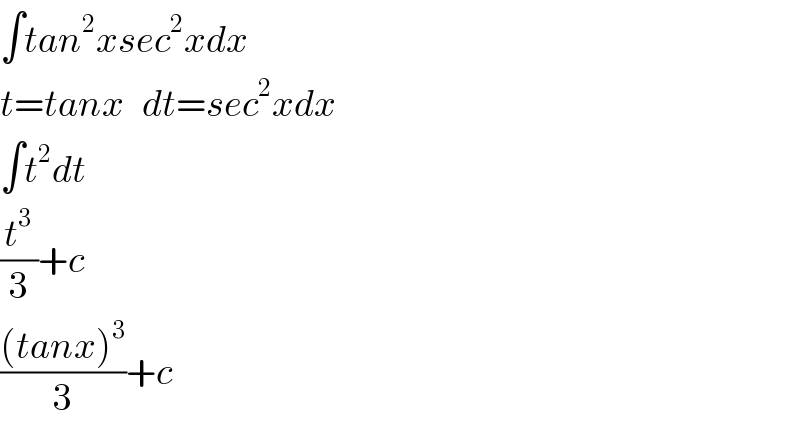
$$\int{tan}^{\mathrm{2}} {xsec}^{\mathrm{2}} {xdx} \\ $$$${t}={tanx}\:\:\:{dt}={sec}^{\mathrm{2}} {xdx} \\ $$$$\int{t}^{\mathrm{2}} {dt} \\ $$$$\frac{{t}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{3}}+{c} \\ $$$$\frac{\left({tanx}\right)^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{3}}+{c} \\ $$
Answered by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 19/Jun/18
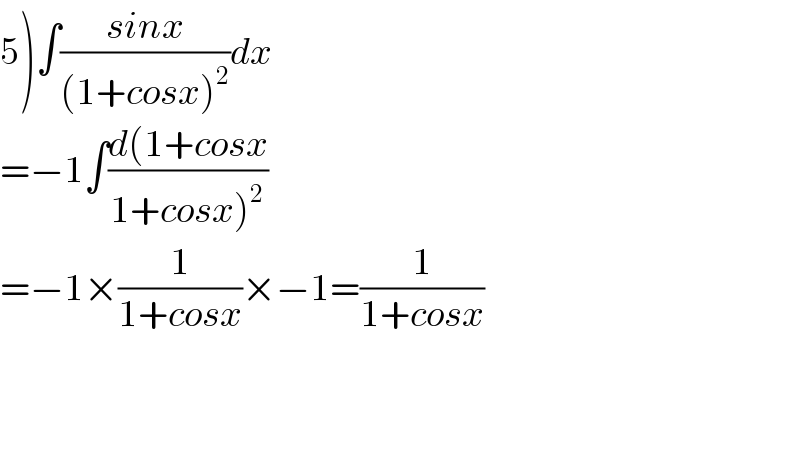
$$\left.\mathrm{5}\right)\int\frac{{sinx}}{\left(\mathrm{1}+{cosx}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{dx} \\ $$$$=−\mathrm{1}\int\frac{{d}\left(\mathrm{1}+{cosx}\right.}{\left.\mathrm{1}+{cosx}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\overset{} {\:} \\ $$$$=−\mathrm{1}×\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+{cosx}}×−\mathrm{1}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+{cosx}} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$
