Question Number 38206 by prof Abdo imad last updated on 22/Jun/18

$${calculate}\:{lim}_{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} \:\frac{{x}\:{coth}\left({x}\right)−\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$
Commented by math khazana by abdo last updated on 25/Jun/18
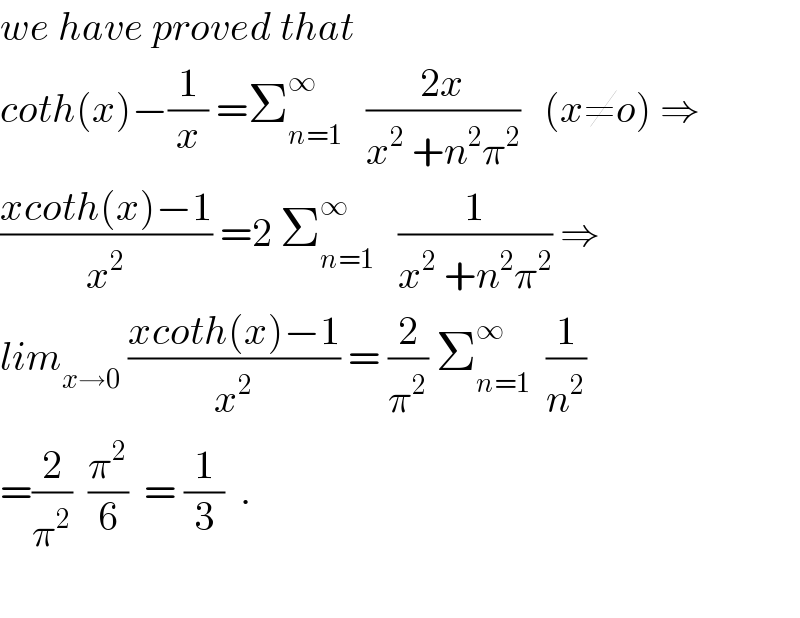
$${we}\:{have}\:{proved}\:{that}\: \\ $$$${coth}\left({x}\right)−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}\:=\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{1}} ^{\infty} \:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+{n}^{\mathrm{2}} \pi^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\:\:\left({x}\neq{o}\right)\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\frac{{xcoth}\left({x}\right)−\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:=\mathrm{2}\:\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{1}} ^{\infty} \:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+{n}^{\mathrm{2}} \pi^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${lim}_{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} \:\frac{{xcoth}\left({x}\right)−\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\pi^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{1}} ^{\infty} \:\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\pi^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\:\frac{\pi^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{6}}\:\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\:\:. \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 23/Jun/18

$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{{x}\left(\frac{{e}^{{x}} +{e}^{−{x}} }{{e}^{{x}} −{e}^{−{x}} }\right)−\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$${e}^{{x}} =\mathrm{1}+{x}+\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}!}+\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{3}!}+… \\ $$$${e}^{−{x}} =\mathrm{1}−{x}+\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}!}−\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{3}!}+… \\ $$$${x}\left(\frac{{e}^{{x}} +{e}^{−{x}} }{{e}^{{x}} −{e}^{−{x}} }\right)={x}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}+\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}!}+\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{4}} }{\mathrm{4}!}+…}{{x}+\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{3}!}+\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{5}} }{\mathrm{5}!}+…}\right)=\frac{\mathrm{1}+\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}!}+…}{\mathrm{1}+\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{3}!}+..} \\ $$$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\frac{\mathrm{1}+\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}!}+\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{4}} }{\mathrm{4}!}+..}{\mathrm{1}+\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{3}!}+\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{4}} }{\mathrm{5}!}+..}\:−\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}!}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}!}\right)+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} {f}\left({x}\right)}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$${when}\:{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}\:\:{f}\left({x}\right)\rightarrow\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{6}}=\frac{\mathrm{3}−\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{6}}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\mathcal{A}{NS} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
