Question Number 104265 by mohammad17 last updated on 20/Jul/20

$$\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}−{y}={sinx} \\ $$
Answered by bemath last updated on 20/Jul/20
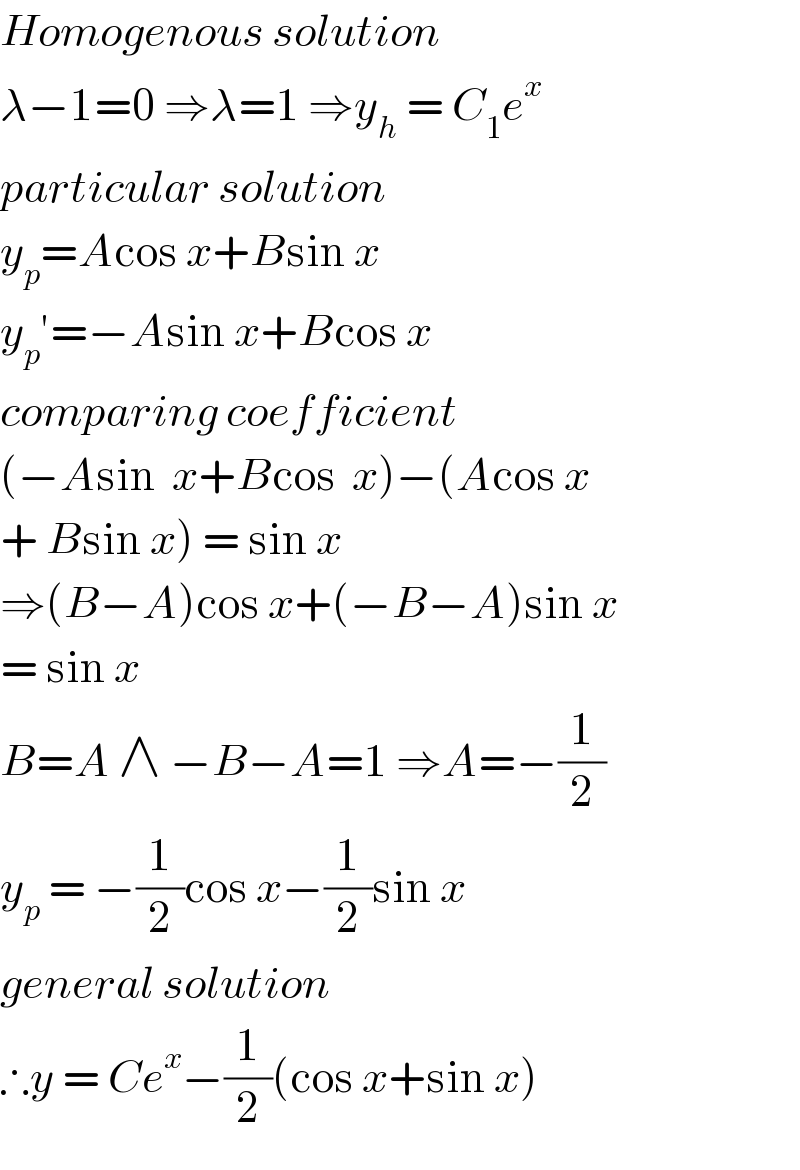
$${Homogenous}\:{solution}\: \\ $$$$\lambda−\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow\lambda=\mathrm{1}\:\Rightarrow{y}_{{h}} \:=\:{C}_{\mathrm{1}} {e}^{{x}} \\ $$$${particular}\:{solution}\: \\ $$$${y}_{{p}} ={A}\mathrm{cos}\:{x}+{B}\mathrm{sin}\:{x} \\ $$$${y}_{{p}} '=−{A}\mathrm{sin}\:{x}+{B}\mathrm{cos}\:{x} \\ $$$${comparing}\:{coefficient}\: \\ $$$$\left(−{A}\mathrm{sin}\:\:{x}+{B}\mathrm{cos}\:\:{x}\right)−\left({A}\mathrm{cos}\:{x}\right. \\ $$$$\left.+\:{B}\mathrm{sin}\:{x}\right)\:=\:\mathrm{sin}\:{x} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\left({B}−{A}\right)\mathrm{cos}\:{x}+\left(−{B}−{A}\right)\mathrm{sin}\:{x} \\ $$$$=\:\mathrm{sin}\:{x}\: \\ $$$${B}={A}\:\wedge\:−{B}−{A}=\mathrm{1}\:\Rightarrow{A}=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${y}_{{p}} \:=\:−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{cos}\:{x}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{sin}\:{x} \\ $$$${general}\:{solution}\: \\ $$$$\therefore{y}\:=\:{Ce}^{{x}} −\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left(\mathrm{cos}\:{x}+\mathrm{sin}\:{x}\right) \\ $$
Commented by mohammad17 last updated on 20/Jul/20

$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${sory}\:{sir}\:{how}\:{this}\:{i}\:{think}\:{this}\:{y}=\frac{\int{e}^{−{x}} {sinxdx}}{{e}^{−{x}} } \\ $$
Commented by mohammad17 last updated on 20/Jul/20

Commented by mohammad17 last updated on 20/Jul/20

$${is}\:{the}\:{solution}\:{its}\:{right}? \\ $$
Commented by bemath last updated on 20/Jul/20

$${yes}\:{sir} \\ $$
Commented by mohammad17 last updated on 20/Jul/20

$${thank}\:{you} \\ $$
Answered by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 20/Jul/20

$$\mathrm{IF}=\mathrm{e}^{\int−\mathrm{1dx}} =\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{y}.\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} =\int\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} \mathrm{sinxdx}=\mathrm{I} \\ $$$$\mathrm{ye}^{−\mathrm{x}} =−\mathrm{sinxe}^{−\mathrm{x}} +\int\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} \mathrm{cosxdx} \\ $$$$\mathrm{ye}^{−\mathrm{x}} =−\mathrm{sinx}\:\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} −\mathrm{cosx}\:\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} −\int\mathrm{sinx}\:\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} =\mathrm{I} \\ $$$$\mathrm{ye}^{−\mathrm{x}} =−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} \left(\mathrm{sinx}+\mathrm{cosx}\right)+\mathrm{C} \\ $$$$\mathrm{y}=\frac{−\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left(\mathrm{sinx}+\mathrm{cosx}\right)+\mathrm{Ce}^{\mathrm{x}} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by Ar Brandon last updated on 20/Jul/20

$$\left\{\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}−\mathrm{y}=\mathrm{sinx}\right\}\centerdot\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} \frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}−\mathrm{ye}^{−\mathrm{x}} =\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} \mathrm{sinx} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\frac{\mathrm{d}\left(\mathrm{ye}^{−\mathrm{x}} \right)}{\mathrm{dx}}=\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} \mathrm{sinx} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{ye}^{−\mathrm{x}} =\int\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} \mathrm{sinxdx} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=\mathrm{sinx}\int\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} \mathrm{dx}−\int\left\{\frac{\mathrm{dsinx}}{\mathrm{dx}}\int\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} \mathrm{dx}\right\}\mathrm{dx} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=−\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} \mathrm{sinx}+\int\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} \mathrm{cosxdx} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=−\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} \mathrm{sinx}+\left\{\mathrm{cosx}\int\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} \mathrm{dx}−\int\left\{\frac{\mathrm{dcosx}}{\mathrm{dx}}\int\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} \mathrm{dx}\right\}\mathrm{dx}\right\} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=−\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} \mathrm{sinx}−\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} \mathrm{cosx}−\int\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} \mathrm{sinxdx} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=\frac{−\left(\mathrm{sinx}+\mathrm{cosx}\right)\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} }{\mathrm{2}}+\mathcal{C} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{y}=−\frac{\left(\mathrm{sinx}+\mathrm{cosx}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}+\mathcal{C}\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} \\ $$
Answered by mathmax by abdo last updated on 20/Jul/20

$$\mathrm{y}^{'} −\mathrm{y}\:=\mathrm{sinx} \\ $$$$\mathrm{h}\rightarrow\mathrm{r}−\mathrm{1}\:=\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{r}\:=\mathrm{1}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{y}_{\mathrm{h}} =\mathrm{Ke}^{\mathrm{x}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{lagrange}\:\mathrm{method}\:\rightarrow\mathrm{y}^{'} \:=\mathrm{k}^{'} \:\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} \:+\mathrm{ke}^{\mathrm{x}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{e}\Rightarrow\mathrm{k}^{'} \:\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} \:+\mathrm{ke}^{\mathrm{x}} −\mathrm{ke}^{\mathrm{x}} \:=\mathrm{sinx}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{k}^{'} \:=\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} \mathrm{sinx}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{k}\:=\int\:\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} \mathrm{sinx}\:\mathrm{dx} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{Im}\left(\int\:\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{ix}} \mathrm{dx}\right)\:=\mathrm{Im}\left(\int\:\mathrm{e}^{\left(−\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{i}\right)\mathrm{x}} \mathrm{dx}\right)\:\:\mathrm{but}\: \\ $$$$\int\:\mathrm{e}^{\left(−\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{i}\right)\mathrm{x}} \mathrm{dx}\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{−\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{i}}\:\mathrm{e}^{\left(−\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{i}\right)\mathrm{x}} \:+\mathrm{c}\:=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{i}}\:\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} \left(\mathrm{cosx}\:+\mathrm{sinx}\right) \\ $$$$=−\frac{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{i}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} \left\{\mathrm{cosx}\:+\mathrm{isinx}\right\}\:=−\frac{\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} }{\mathrm{2}}\left\{\mathrm{cosx}+\mathrm{isinx}+\mathrm{icosx}−\mathrm{sinx}\right\}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\mathrm{Im}\left(\int…\right)\:=−\frac{\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} }{\mathrm{2}}\left\{\mathrm{cosx}\:+\mathrm{sinx}\right\}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{general}\:\mathrm{solution}\:\mathrm{is} \\ $$$$\left(−\frac{\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} }{\mathrm{2}}\left\{\mathrm{cosx}\:+\mathrm{sinx}\right\}\:+\mathrm{c}\right)\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} \:=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left(\mathrm{cosx}\:+\mathrm{sinx}\right)\:+\mathrm{ce}^{\mathrm{x}} \\ $$
