Question Number 104845 by john santu last updated on 24/Jul/20
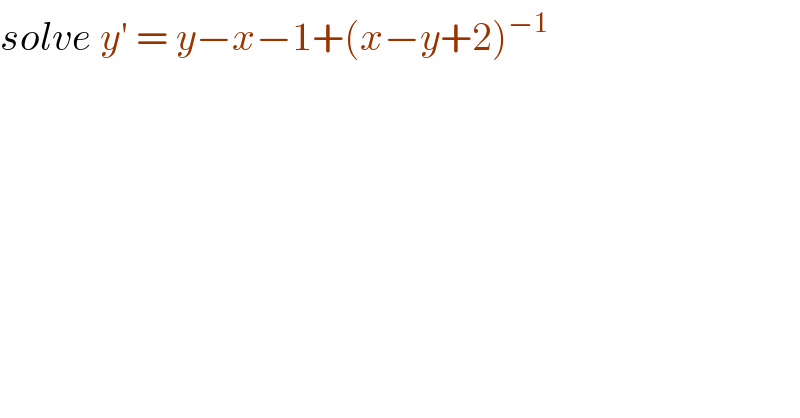
$${solve}\:{y}'\:=\:{y}−{x}−\mathrm{1}+\left({x}−{y}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{−\mathrm{1}} \\ $$
Answered by john santu last updated on 24/Jul/20

$$\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}\:=\:−\left({x}−{y}+\mathrm{2}\right)+\mathrm{1}+\left({x}−{y}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{−\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$${set}\:{x}−{y}+\mathrm{2}\:=\:{m}\: \\ $$$$\frac{{dm}}{{dx}}\:=\:\mathrm{1}−\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}\:\Rightarrow\:\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}\:=\:\mathrm{1}−\frac{{dm}}{{dx}} \\ $$$$\Leftrightarrow\:\mathrm{1}−\frac{{dm}}{{dx}}\:=\:−{m}+\mathrm{1}+{m}^{−\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\frac{{dm}}{{dx}}\:=\:\frac{{m}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}}{{m}}\:\Rightarrow\:\frac{{m}.{dm}}{{m}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}}\:=\:{dx} \\ $$$$\int\left(\:\frac{{m}}{{m}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}}\right){dm}\:=\:\int\:{dx}\: \\ $$$$\int\:\frac{{d}\left({m}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}\right)}{{m}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}}\:=\:\mathrm{2}{x}\:+\:{c} \\ $$$$\mathrm{ln}\:\left({m}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}\right)\:=\:\mathrm{2}{x}\:+\:{c} \\ $$$${m}^{\mathrm{2}} \:=\:{Ce}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} \:+\:\mathrm{1}\: \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\left({x}−{y}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \:=\:{Ce}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} \:+\:\mathrm{1}\: \\ $$
