Question Number 105404 by bemath last updated on 28/Jul/20

$${Cube}\:{ABCD}.{EFGH}\:{with} \\ $$$${length}\:{side}\:\mathrm{2}\:{cm}.\:{Point}\:{P}\:{is}\:{the} \\ $$$${center}\:{of}\:{ABFE}\:{plane}.\:{The} \\ $$$${distance}\:{of}\:{HP}\:{line}\:{and}\:{the}\:{BG} \\ $$$${line}\:{is}\:\_\_\: \\ $$
Answered by john santu last updated on 28/Jul/20
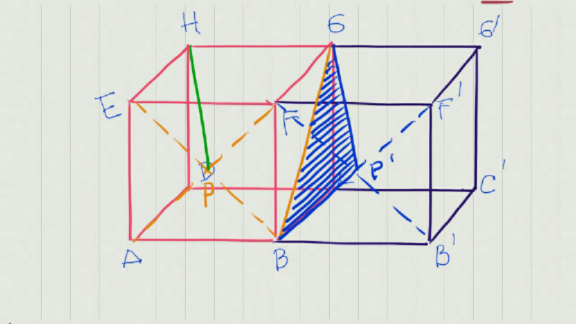
Commented by john santu last updated on 28/Jul/20
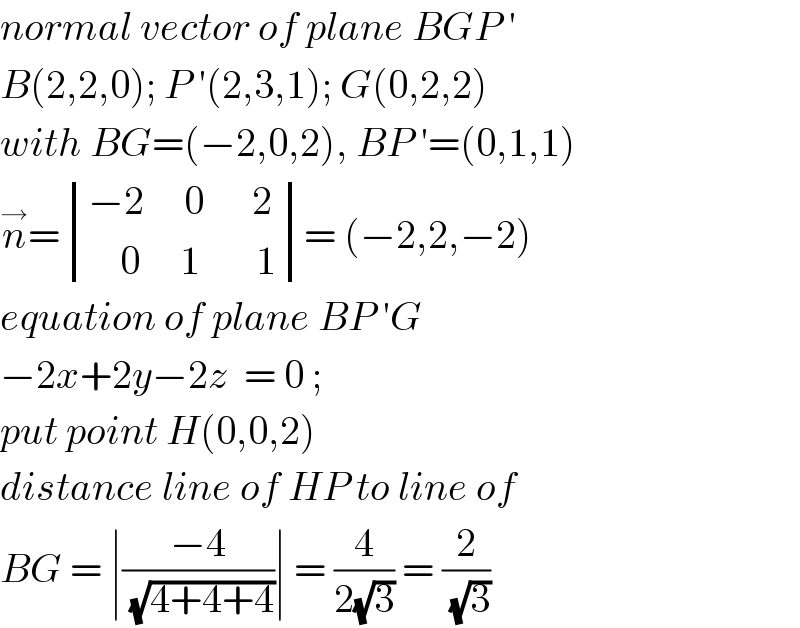
$${normal}\:{vector}\:{of}\:{plane}\:{BGP}\:' \\ $$$${B}\left(\mathrm{2},\mathrm{2},\mathrm{0}\right);\:{P}\:'\left(\mathrm{2},\mathrm{3},\mathrm{1}\right);\:{G}\left(\mathrm{0},\mathrm{2},\mathrm{2}\right) \\ $$$${with}\:{BG}=\left(−\mathrm{2},\mathrm{0},\mathrm{2}\right),\:{BP}\:'=\left(\mathrm{0},\mathrm{1},\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$$\overset{\rightarrow} {{n}}=\begin{vmatrix}{−\mathrm{2}\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{0}\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{2}}\\{\:\:\:\:\mathrm{0}\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{1}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{1}}\end{vmatrix}=\:\left(−\mathrm{2},\mathrm{2},−\mathrm{2}\right) \\ $$$${equation}\:{of}\:{plane}\:{BP}\:'{G}\: \\ $$$$−\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{2}{y}−\mathrm{2}{z}\:\:=\:\mathrm{0}\:; \\ $$$${put}\:{point}\:{H}\left(\mathrm{0},\mathrm{0},\mathrm{2}\right)\: \\ $$$${distance}\:{line}\:{of}\:{HP}\:{to}\:{line}\:{of} \\ $$$${BG}\:=\:\mid\frac{−\mathrm{4}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{4}+\mathrm{4}+\mathrm{4}}}\mid\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}} \\ $$
Commented by john santu last updated on 28/Jul/20
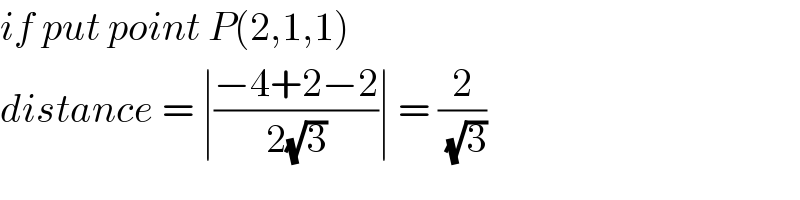
$${if}\:{put}\:{point}\:{P}\left(\mathrm{2},\mathrm{1},\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$${distance}\:=\:\mid\frac{−\mathrm{4}+\mathrm{2}−\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}\mid\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}} \\ $$
