Question Number 106314 by Study last updated on 04/Aug/20

Answered by bemath last updated on 04/Aug/20

$$\mathrm{GP}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{S}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}−\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{1}.\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)+\mathrm{1}\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{3}} +… \\ $$
Commented by Study last updated on 04/Aug/20
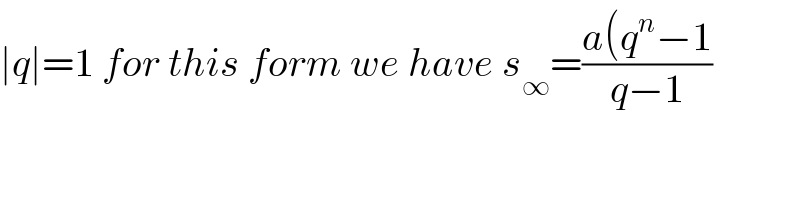
$$\mid{q}\mid=\mathrm{1}\:{for}\:{this}\:{form}\:{we}\:{have}\:{s}_{\infty} =\frac{{a}\left({q}^{{n}} −\mathrm{1}\right.}{{q}−\mathrm{1}} \\ $$
Answered by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 04/Aug/20

$${S}=\mathrm{1}+{x}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{x}^{\mathrm{3}} +{x}^{\mathrm{4}} +{x}^{\mathrm{5}} +{x}^{\mathrm{6}} +{x}^{\mathrm{7}} +… \\ $$$${S}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}−{x}} \\ $$$${S}=\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{1}+… \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{1}}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${It}\:{is}\:\:{a}\:{Mean}\:{of}\:{the}\:{probable}\:{value} \\ $$
Answered by Her_Majesty last updated on 04/Aug/20

$${sum}\:{doesn}'{t}\:{exist} \\ $$
