Question Number 108353 by bemath last updated on 16/Aug/20

$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\frac{\bigtriangleup\mathcal{B}{e}\mathcal{M}{ath}\bigtriangleup}{\ldots} \\ $$$$\:{General}\:{solution}\:{of}\: \\ $$$$\:\frac{{d}^{\mathrm{2}} {y}}{{dx}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:+\:\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}−\mathrm{2}{y}\:=\:\mathrm{sin}\:{x}\: \\ $$
Commented by bemath last updated on 16/Aug/20
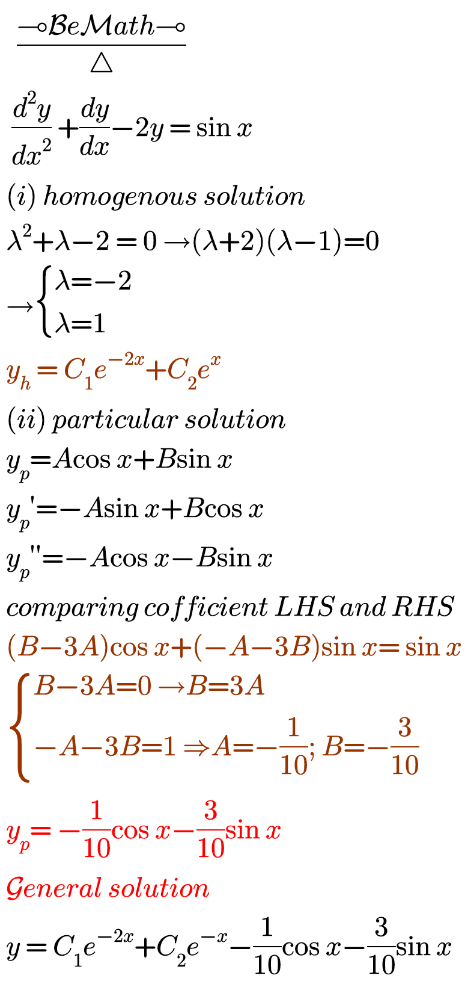
Answered by Aziztisffola last updated on 16/Aug/20

$$\mathrm{r}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{r}−\mathrm{2}=\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{r}=−\mathrm{2}\:\mathrm{or}\:\mathrm{r}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{y}_{\mathrm{h}} =\alpha\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{2x}} +\beta\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} \\ $$$$\:\mathrm{y}_{\mathrm{p}} =\mathrm{u}_{\mathrm{1}} \mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{2x}} +\mathrm{u}_{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} \\ $$$$\:\mathrm{w}\left(\mathrm{u}_{\mathrm{1}} ;\mathrm{u}_{\mathrm{2}} \right)=\begin{vmatrix}{\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{2x}} }&{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} }\\{−\mathrm{2e}^{−\mathrm{2x}} }&{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} }\end{vmatrix}=\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} +\mathrm{2e}^{−\mathrm{x}} =\mathrm{3e}^{−\mathrm{x}} \\ $$$$\:\mathrm{w}_{\mathrm{1}} =\begin{vmatrix}{\mathrm{0}}&{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} }\\{\mathrm{sin}{x}}&{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} }\end{vmatrix}=−\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} \mathrm{sin}\left(\mathrm{x}\right) \\ $$$$\:\mathrm{w}_{\mathrm{2}} =\begin{vmatrix}{\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{2x}} }&{\mathrm{0}}\\{−\mathrm{2e}^{−\mathrm{2x}} }&{\mathrm{sin}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)}\end{vmatrix}=\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{2x}} \mathrm{sin}\left(\mathrm{x}\right) \\ $$$$\:\mathrm{u}_{\mathrm{1}} =\int\frac{\mathrm{w}_{\mathrm{1}} }{\mathrm{w}}\:\mathrm{dx}=\int\frac{−\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} \mathrm{sin}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)}{\mathrm{3e}^{−\mathrm{x}} }\:\mathrm{dx}=\frac{−\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\int\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{2x}} \mathrm{sin}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{dx} \\ $$$$\:=\frac{−\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\left(−\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{2x}} \mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)+\mathrm{2}\int\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{2x}} \mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{dx}\right) \\ $$$$=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{15}}\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{2x}} \left(\mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)+\mathrm{2sin}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\right) \\ $$$$\:\mathrm{u}_{\mathrm{2}} =\int\frac{\mathrm{w}_{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{w}}\:\mathrm{dx}=\int\frac{\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{2x}} \mathrm{sin}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)}{\mathrm{3e}^{−\mathrm{x}} }\:\mathrm{dx}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\int\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} \mathrm{sin}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{dx} \\ $$$$\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\left(−\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} \mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)+\int\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} \mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\right)=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} \mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{x}\right) \\ $$$$\:\mathrm{y}=\mathrm{y}_{\mathrm{h}} +\mathrm{y}_{\mathrm{p}} \\ $$
