Question Number 174199 by Shrinava last updated on 26/Jul/22
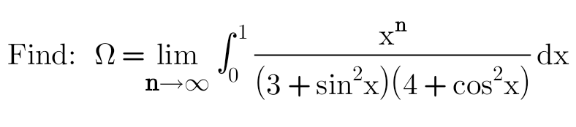
Answered by Mathspace last updated on 27/Jul/22
![℧=∫_R (x^n /((3+sin^2 x)(4+cos^2 x)))χ_([0,1]) (x)dx =∫_R f_n (x)dx we have f_n →0 (cs) and ∣f_n ∣≤(1/(12)) so by theorem of cv dominee lim ∫_R f_n dx =∫_R lim f_n dx=0](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q174204.png)
$$\mho=\int_{{R}} \frac{{x}^{{n}} }{\left(\mathrm{3}+{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}\right)\left(\mathrm{4}+{cos}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}\right)}\chi_{\left[\mathrm{0},\mathrm{1}\right]} \left({x}\right){dx} \\ $$$$=\int_{{R}} {f}_{{n}} \left({x}\right){dx}\:{we}\:{have}\:{f}_{{n}} \rightarrow\mathrm{0}\:\left({cs}\right) \\ $$$${and}\:\mid{f}_{{n}} \mid\leqslant\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{12}}\:\:{so}\:{by}\:{theorem}\:{of} \\ $$$${cv}\:{dominee}\:{lim}\:\int_{{R}} {f}_{{n}} {dx} \\ $$$$=\int_{{R}} {lim}\:{f}_{{n}} {dx}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$
Commented by Shrinava last updated on 11/Aug/22
$$\mathrm{Cool}\:\mathrm{der}\:\mathrm{sir}\:\mathrm{thank}\:\mathrm{you} \\ $$
