Question Number 176292 by mokys last updated on 15/Sep/22

Answered by floor(10²Eta[1]) last updated on 16/Sep/22
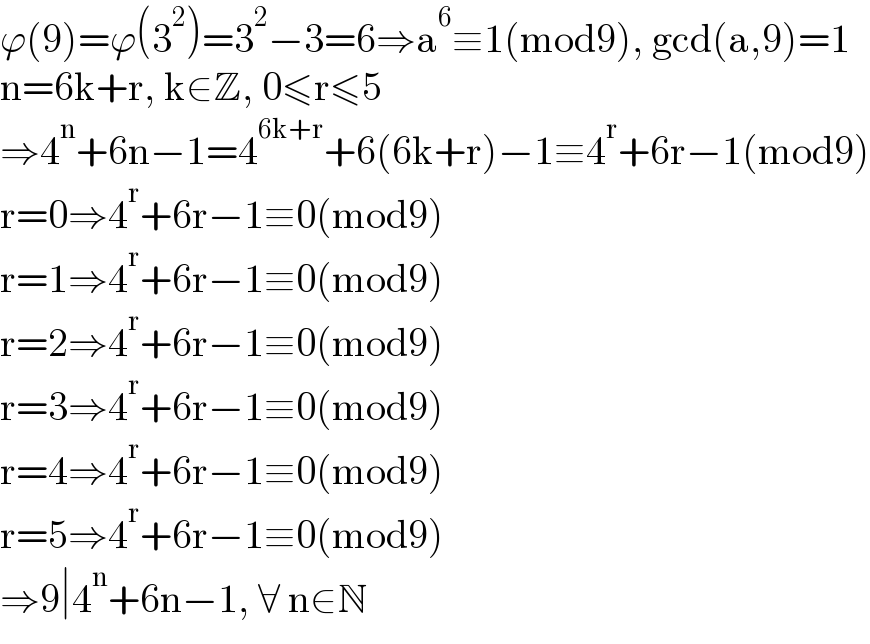
$$\varphi\left(\mathrm{9}\right)=\varphi\left(\mathrm{3}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)=\mathrm{3}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{3}=\mathrm{6}\Rightarrow\mathrm{a}^{\mathrm{6}} \equiv\mathrm{1}\left(\mathrm{mod9}\right),\:\mathrm{gcd}\left(\mathrm{a},\mathrm{9}\right)=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{6k}+\mathrm{r},\:\mathrm{k}\in\mathbb{Z},\:\mathrm{0}\leqslant\mathrm{r}\leqslant\mathrm{5} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{4}^{\mathrm{n}} +\mathrm{6n}−\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{4}^{\mathrm{6k}+\mathrm{r}} +\mathrm{6}\left(\mathrm{6k}+\mathrm{r}\right)−\mathrm{1}\equiv\mathrm{4}^{\mathrm{r}} +\mathrm{6r}−\mathrm{1}\left(\mathrm{mod9}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{r}=\mathrm{0}\Rightarrow\mathrm{4}^{\mathrm{r}} +\mathrm{6r}−\mathrm{1}\equiv\mathrm{0}\left(\mathrm{mod9}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{r}=\mathrm{1}\Rightarrow\mathrm{4}^{\mathrm{r}} +\mathrm{6r}−\mathrm{1}\equiv\mathrm{0}\left(\mathrm{mod9}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{r}=\mathrm{2}\Rightarrow\mathrm{4}^{\mathrm{r}} +\mathrm{6r}−\mathrm{1}\equiv\mathrm{0}\left(\mathrm{mod9}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{r}=\mathrm{3}\Rightarrow\mathrm{4}^{\mathrm{r}} +\mathrm{6r}−\mathrm{1}\equiv\mathrm{0}\left(\mathrm{mod9}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{r}=\mathrm{4}\Rightarrow\mathrm{4}^{\mathrm{r}} +\mathrm{6r}−\mathrm{1}\equiv\mathrm{0}\left(\mathrm{mod9}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{r}=\mathrm{5}\Rightarrow\mathrm{4}^{\mathrm{r}} +\mathrm{6r}−\mathrm{1}\equiv\mathrm{0}\left(\mathrm{mod9}\right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{9}\mid\mathrm{4}^{\mathrm{n}} +\mathrm{6n}−\mathrm{1},\:\forall\:\mathrm{n}\in\mathbb{N} \\ $$
Answered by a.lgnaoui last updated on 16/Sep/22
![n=1 4^1 +6−1=9 n=2 4^2 +12−1=27=3×9 n=3 4^3 +18−1=81=9^2 n=4 4^4 +24−1=279=31×9 ....................................... n+1 4^(n+1) +6(n+1)−1=4^(n+1) +6n+5 4[4^n +6n−1]+(9−18n) =4(4^n +6n−1)+9(1−2n) n∈N^∗ Somme de 2 nombres divisibles par 9 donc divisible ar 9](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q176299.png)
$${n}=\mathrm{1}\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{4}^{\mathrm{1}} +\mathrm{6}−\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{9} \\ $$$${n}=\mathrm{2}\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{4}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{12}−\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{27}=\mathrm{3}×\mathrm{9} \\ $$$${n}=\mathrm{3}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{4}^{\mathrm{3}} +\mathrm{18}−\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{81}=\mathrm{9}^{\mathrm{2}} \: \\ $$$${n}=\mathrm{4}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{4}^{\mathrm{4}} +\mathrm{24}−\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{279}=\mathrm{31}×\mathrm{9} \\ $$$$………………………………… \\ $$$${n}+\mathrm{1}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{4}^{{n}+\mathrm{1}} +\mathrm{6}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)−\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{4}^{{n}+\mathrm{1}} +\mathrm{6}{n}+\mathrm{5} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{4}\left[\mathrm{4}^{{n}} +\mathrm{6}{n}−\mathrm{1}\right]+\left(\mathrm{9}−\mathrm{18}{n}\right) \\ $$$$\:=\mathrm{4}\left(\mathrm{4}^{{n}} \:+\mathrm{6}{n}−\mathrm{1}\right)+\mathrm{9}\left(\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{2}{n}\right)\:\:\:\:{n}\in\mathbb{N}^{\ast} \:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\: \\ $$$${Somme}\:{de}\:\mathrm{2}\:{nombres}\:{divisibles}\:{par}\:\mathrm{9}\:\:\: \\ $$$${donc}\:\:\:\:{divisible}\:{ar}\:\mathrm{9} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
