Question Number 178347 by Acem last updated on 15/Oct/22
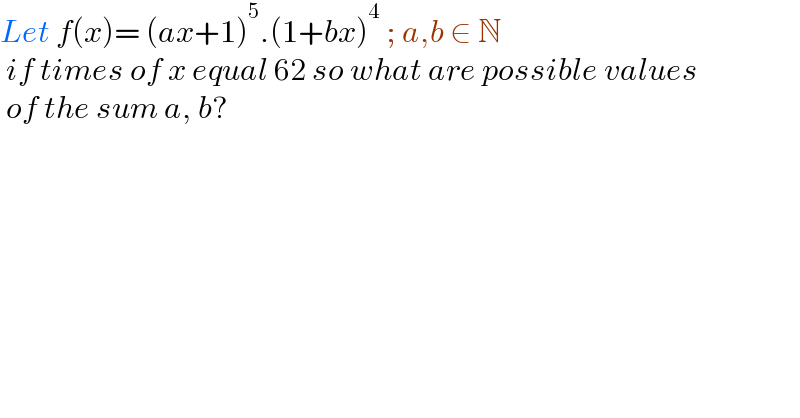
$${Let}\:{f}\left({x}\right)=\:\left({ax}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{5}} .\left(\mathrm{1}+{bx}\right)^{\mathrm{4}} \:;\:{a},{b}\:\in\:\mathbb{N} \\ $$$$\:{if}\:{times}\:{of}\:{x}\:{equal}\:\mathrm{62}\:{so}\:{what}\:{are}\:{possible}\:{values} \\ $$$$\:{of}\:{the}\:{sum}\:{a},\:{b}? \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by Acem last updated on 15/Oct/22

$$\left(\mathrm{1}+{ax}\right)^{\mathrm{5}} =\:\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{5}{ax}+\mathrm{10}{a}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}^{\mathrm{2}} +… \\ $$$$\:\left(\mathrm{1}+{bx}\right)^{\mathrm{4}} =\:\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{4}{bx}+\mathrm{6}{b}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}^{\mathrm{2}} +… \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${We}\:{take}\:{times}\:{x}\:{from}\:{multiplication} \\ $$$$\:\left(\mathrm{5}{a}+\mathrm{4}{b}\right){x}\:{i}.{e}.\:\mathrm{5}{a}+\mathrm{4}{b}=\:\mathrm{62}\:…\left(\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\:{We}\:{need}\:{to}\:\left({a}+{b}\right)\:{so}\:{and}\:{from}\:\left(\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$$\:\mathrm{4}\left({a}+{b}\right)\:=\:−{a}\:+\mathrm{62} \\ $$$$\:{Since}\:{a}\in\:\mathbb{N}\:\Rightarrow\:\mathrm{4}\left({a}+{b}\right)\:<\:\mathrm{62}\:\Leftrightarrow\:{a}+{b}<\:\mathrm{15}.\mathrm{5} \\ $$$$\:{Since}\:{a}+{b}\in\:\mathbb{N}\Rightarrow\:\boldsymbol{{a}}+\boldsymbol{{b}}\leqslant\:\mathrm{15}\:…\:\left(\mathrm{2}\right) \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\:{We}\:{repeat}\:{for}\:{b}\:{from}\:\left(\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$$\:\mathrm{5}\left({a}+{b}\right)=\:{b}+\mathrm{62}\:,\:{b}\in\:\mathbb{N}\:\Rightarrow\:\mathrm{5}\left({a}+{b}\right)>\:\mathrm{62}\Rightarrow\:{a}+{b}>\:\mathrm{12}.\mathrm{4} \\ $$$$\:{Since}\:{a}+{b}\in\:\mathbb{N}\Rightarrow\:\boldsymbol{{a}}+\boldsymbol{{b}}\geqslant\:\mathrm{13}…\left(\mathrm{3}\right) \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\:\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\:\&\:\left(\mathrm{3}\right)\: \\ $$$${We}\:{find}\:{that}\:{the}\:{possible}\:{values}\:{of}\:{a}+{b}\:{are}: \\ $$$$\:{a}+{b}=\:\mathrm{13}\:\:,\:\:{a}+{b}=\:\mathrm{14}\:\:,\:\:\:{a}+{b}=\:\mathrm{15} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by Tawa11 last updated on 15/Oct/22

$$\mathrm{Great}\:\mathrm{sir} \\ $$
Commented by Acem last updated on 15/Oct/22

$${Thanks}\:{Sir} \\ $$
Answered by mr W last updated on 16/Oct/22
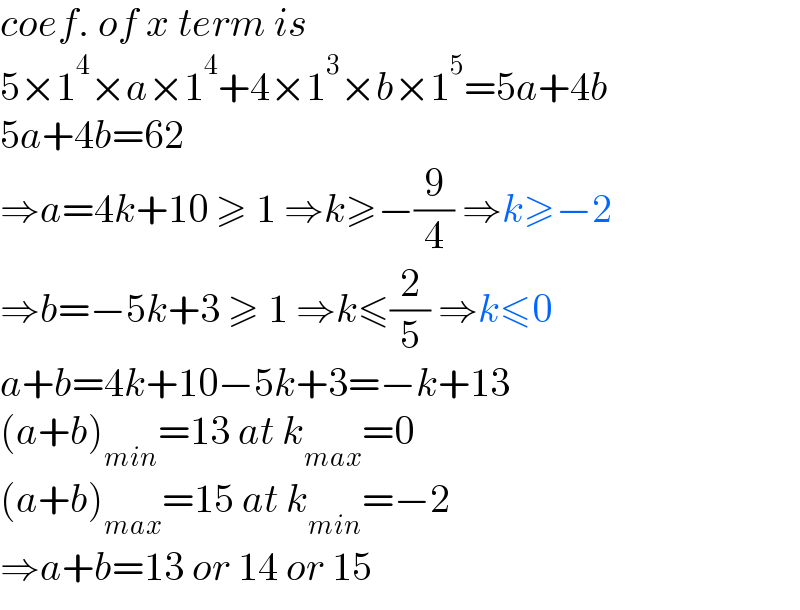
$${coef}.\:{of}\:{x}\:{term}\:{is} \\ $$$$\mathrm{5}×\mathrm{1}^{\mathrm{4}} ×{a}×\mathrm{1}^{\mathrm{4}} +\mathrm{4}×\mathrm{1}^{\mathrm{3}} ×{b}×\mathrm{1}^{\mathrm{5}} =\mathrm{5}{a}+\mathrm{4}{b} \\ $$$$\mathrm{5}{a}+\mathrm{4}{b}=\mathrm{62} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{a}=\mathrm{4}{k}+\mathrm{10}\:\geqslant\:\mathrm{1}\:\Rightarrow{k}\geqslant−\frac{\mathrm{9}}{\mathrm{4}}\:\Rightarrow{k}\geqslant−\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{b}=−\mathrm{5}{k}+\mathrm{3}\:\geqslant\:\mathrm{1}\:\Rightarrow{k}\leqslant\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{5}}\:\Rightarrow{k}\leqslant\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${a}+{b}=\mathrm{4}{k}+\mathrm{10}−\mathrm{5}{k}+\mathrm{3}=−{k}+\mathrm{13} \\ $$$$\left({a}+{b}\right)_{{min}} =\mathrm{13}\:{at}\:{k}_{{max}} =\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\left({a}+{b}\right)_{{max}} =\mathrm{15}\:{at}\:{k}_{{min}} =−\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{a}+{b}=\mathrm{13}\:{or}\:\mathrm{14}\:{or}\:\mathrm{15} \\ $$
