Question Number 48172 by Abdo msup. last updated on 20/Nov/18
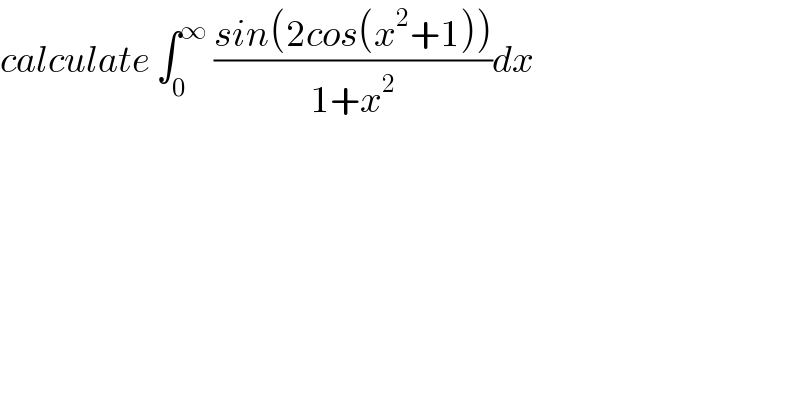
$${calculate}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\frac{{sin}\left(\mathrm{2}{cos}\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}\right)\right)}{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{dx} \\ $$
Commented by Abdo msup. last updated on 25/Nov/18
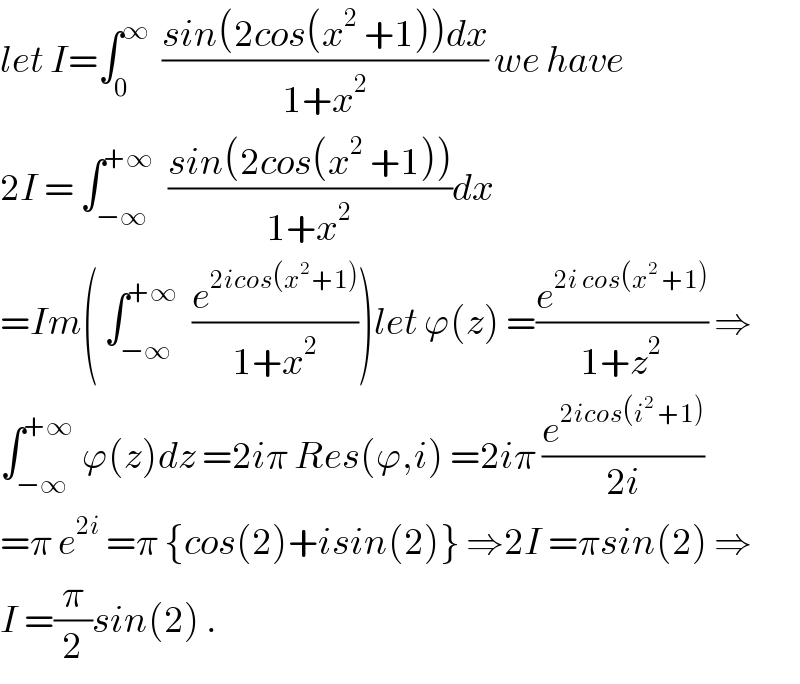
$${let}\:{I}=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\:\frac{{sin}\left(\mathrm{2}{cos}\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{1}\right)\right){dx}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:{we}\:{have} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}{I}\:=\:\int_{−\infty} ^{+\infty} \:\:\frac{{sin}\left(\mathrm{2}{cos}\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{1}\right)\right)}{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{dx} \\ $$$$={Im}\left(\:\int_{−\infty} ^{+\infty} \:\:\frac{{e}^{\mathrm{2}{icos}\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}\:} +\mathrm{1}\right)} }{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right){let}\:\varphi\left({z}\right)\:=\frac{{e}^{\mathrm{2}{i}\:{cos}\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{1}\right)} }{\mathrm{1}+{z}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\int_{−\infty} ^{+\infty} \:\varphi\left({z}\right){dz}\:=\mathrm{2}{i}\pi\:{Res}\left(\varphi,{i}\right)\:=\mathrm{2}{i}\pi\:\frac{{e}^{\mathrm{2}{icos}\left({i}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{1}\right)} }{\mathrm{2}{i}} \\ $$$$=\pi\:{e}^{\mathrm{2}{i}} \:=\pi\:\left\{{cos}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)+{isin}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\right\}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{2}{I}\:=\pi{sin}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${I}\:=\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}{sin}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\:. \\ $$
