Question Number 115464 by bemath last updated on 26/Sep/20
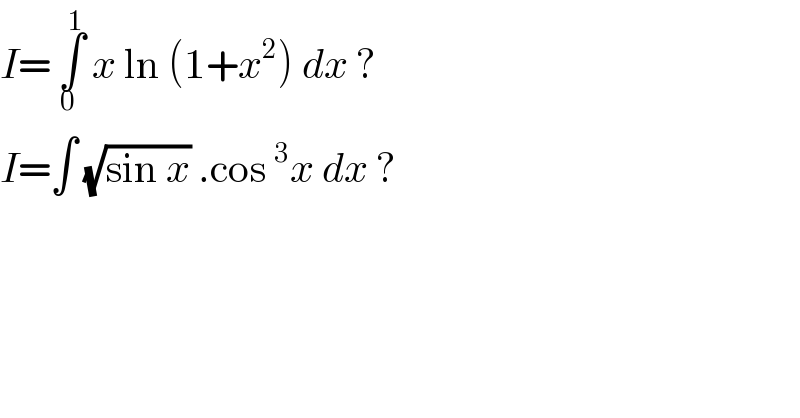
$${I}=\:\underset{\mathrm{0}\:} {\overset{\mathrm{1}} {\int}}\:{x}\:\mathrm{ln}\:\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\:{dx}\:? \\ $$$${I}=\int\:\sqrt{\mathrm{sin}\:{x}}\:.\mathrm{cos}\:^{\mathrm{3}} {x}\:{dx}\:? \\ $$
Answered by malwaan last updated on 26/Sep/20
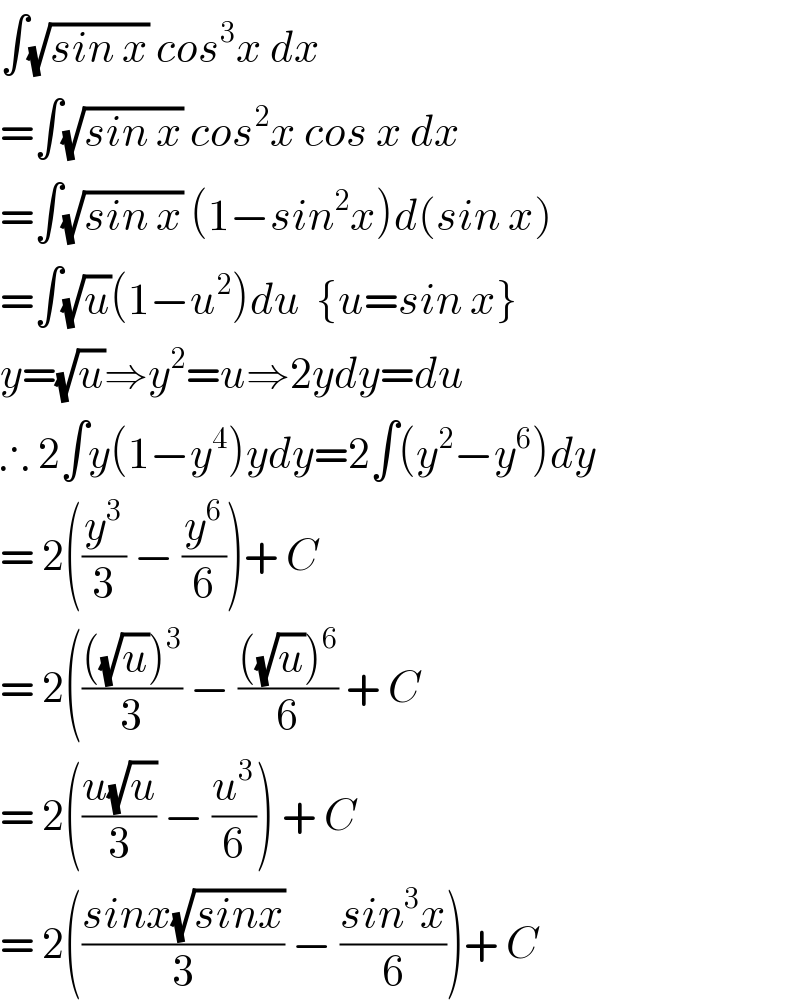
$$\int\sqrt{{sin}\:{x}}\:{cos}^{\mathrm{3}} {x}\:{dx} \\ $$$$=\int\sqrt{{sin}\:{x}}\:{cos}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}\:{cos}\:{x}\:{dx} \\ $$$$=\int\sqrt{{sin}\:{x}}\:\left(\mathrm{1}−{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}\right){d}\left({sin}\:{x}\right) \\ $$$$=\int\sqrt{{u}}\left(\mathrm{1}−{u}^{\mathrm{2}} \right){du}\:\:\left\{{u}={sin}\:{x}\right\} \\ $$$${y}=\sqrt{{u}}\Rightarrow{y}^{\mathrm{2}} ={u}\Rightarrow\mathrm{2}{ydy}={du} \\ $$$$\therefore\:\mathrm{2}\int{y}\left(\mathrm{1}−{y}^{\mathrm{4}} \right){ydy}=\mathrm{2}\int\left({y}^{\mathrm{2}} −{y}^{\mathrm{6}} \right){dy} \\ $$$$=\:\mathrm{2}\left(\frac{{y}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{3}}\:−\:\frac{{y}^{\mathrm{6}} }{\mathrm{6}}\right)+\:{C} \\ $$$$=\:\mathrm{2}\left(\frac{\left(\sqrt{{u}}\right)^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{3}}\:−\:\frac{\left(\sqrt{{u}}\right)^{\mathrm{6}} }{\mathrm{6}}\:+\:{C}\right. \\ $$$$=\:\mathrm{2}\left(\frac{{u}\sqrt{{u}}}{\mathrm{3}}\:−\:\frac{{u}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{6}}\right)\:+\:{C} \\ $$$$=\:\mathrm{2}\left(\frac{{sinx}\sqrt{{sinx}}}{\mathrm{3}}\:−\:\frac{{sin}^{\mathrm{3}} {x}}{\mathrm{6}}\right)+\:{C} \\ $$
Commented by bemath last updated on 26/Sep/20

$${gave}\:{kudos} \\ $$
Commented by malwaan last updated on 26/Sep/20
$${gave}\:{kudos} \\ $$$${What}\:{is}\:{this}\:?{please} \\ $$
Commented by bemath last updated on 26/Sep/20
$${gave}\:{kudos}\:=\:{give}\:{compliments} \\ $$
Commented by bemath last updated on 26/Sep/20
������
Answered by malwaan last updated on 26/Sep/20
![∫x ln(1+x^2 )dx u=ln(1+x^2 )⇒du=((2x)/(1+x^2 )) dx dv = xdx⇒v=(x^2 /2) ∫udv=uv−∫vdu ∴∫x ln(1+x^2 )dx= (x^2 /2)ln(1+x^2 )−∫(x^3 /(1+x^2 )) dx =(x^2 /2)ln(1+x^2 )−∫[x−(x/(1+x^2 ))]dx =(x^2 /2)ln(1+x^2 )− (x^2 /2) + (1/2)ln(1+x^2 )+C ∴ _0 ∫^1 x ln(1+x^2 )dx = [(1/2)ln(2)− (1/2) +(1/2)ln(2)]− [0] =ln(2)−(1/2)](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q115477.png)
$$\int{x}\:{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right){dx} \\ $$$${u}={ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\Rightarrow{du}=\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:{dx} \\ $$$${dv}\:=\:{xdx}\Rightarrow{v}=\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\int{udv}={uv}−\int{vdu} \\ $$$$\therefore\int{x}\:{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right){dx}= \\ $$$$\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)−\int\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:{dx} \\ $$$$=\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)−\int\left[{x}−\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right]{dx} \\ $$$$=\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)−\:\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}\:+\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)+{C} \\ $$$$\therefore\:\:_{\mathrm{0}} \int^{\mathrm{1}} {x}\:{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right){dx} \\ $$$$=\:\left[\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)−\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\right]−\:\left[\mathrm{0}\right] \\ $$$$={ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
Answered by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 26/Sep/20
![∫_0 ^1 xlog(1+x^2 )dx =[log(1+x^2 )(x^2 /2)]_0 ^1 −∫_0 ^1 (x^2 /2).((2x)/(1+x^2 )) =(1/2)log(2)−∫_0 ^1 x−(x/(1+x^2 )) =(1/2)log(2)−(1/2)+[(1/2)log(1+x^2 )]_0 ^1 =log(2)−(1/2)](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q115479.png)
$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \mathrm{xlog}\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\mathrm{dx} \\ $$$$=\left[\mathrm{log}\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\frac{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} −\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \frac{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}.\frac{\mathrm{2x}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{log}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)−\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \mathrm{x}−\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{log}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}+\left[\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{log}\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{log}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
Answered by Ar Brandon last updated on 26/Sep/20
![I=∫_0 ^1 xln(1+x^2 )dx=(1/2)∫_0 ^1 2xln(1+x^2 )dx =(1/2)∫_0 ^1 ln(1+x^2 )d(x^2 )=[(((1+x^2 )[ln(1+x^2 )−1])/2)]_0 ^1 =(ln2−1)+(1/2)=ln2−(1/2)](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q115485.png)
$$\mathcal{I}=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} {x}\mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\mathrm{d}{x}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \mathrm{2}{x}\mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\mathrm{d}{x} \\ $$$$\:\:\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\mathrm{d}\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)=\left[\frac{\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\left[\mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)−\mathrm{1}\right]}{\mathrm{2}}\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:=\left(\mathrm{ln2}−\mathrm{1}\right)+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}=\mathrm{ln2}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
Answered by mathmax by abdo last updated on 26/Sep/20
![I =∫_0 ^1 xln(1+x^2 )dx by parts we get I =[(x^2 /2)ln(1+x^2 )]_0 ^1 −∫_0 ^1 (x^2 /2).((2x)/(1+x^2 ))dx =((ln(2))/2)−∫_0 ^1 (x^3 /(x^2 +1))dx but ∫_0 ^1 (x^3 /(x^2 +1))dx =∫_0 ^1 ((x(x^2 +1)−x)/(x^2 +1))dx =∫_0 ^1 xdx−∫_0 ^1 ((xdx)/(x^2 +1)) =(1/2)−[(1/2)ln(1+x^2 )]_0 ^1 =(1/2)−(1/2)ln(2) ⇒I =((ln(2))/2)−(1/2) +((ln(2))/2) =ln(2)−(1/2)](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q115511.png)
$$\mathrm{I}\:=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\mathrm{xln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\mathrm{dx}\:\:\mathrm{by}\:\mathrm{parts}\:\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{get}\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{I}\:=\left[\frac{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} −\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \frac{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}.\frac{\mathrm{2x}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\mathrm{dx}\:=\frac{\mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}−\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \frac{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}\mathrm{dx}\:\mathrm{but} \\ $$$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\frac{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{1}}\mathrm{dx}\:=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \frac{\mathrm{x}\left(\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}\right)−\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{1}}\mathrm{dx}\:=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \mathrm{xdx}−\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\frac{\mathrm{xdx}}{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}−\left[\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{I}\:=\frac{\mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:+\frac{\mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
