Question Number 53778 by maxmathsup by imad last updated on 25/Jan/19
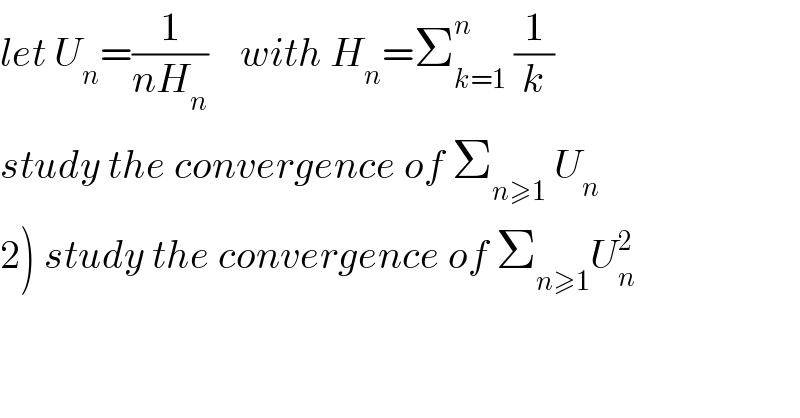
$${let}\:{U}_{{n}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{nH}_{{n}} }\:\:\:\:{with}\:{H}_{{n}} =\sum_{{k}=\mathrm{1}} ^{{n}} \:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{k}} \\ $$$${study}\:{the}\:{convergence}\:{of}\:\sum_{{n}\geqslant\mathrm{1}} \:{U}_{{n}} \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{2}\right)\:{study}\:{the}\:{convergence}\:{of}\:\sum_{{n}\geqslant\mathrm{1}} {U}_{{n}} ^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
Commented by maxmathsup by imad last updated on 18/Feb/19
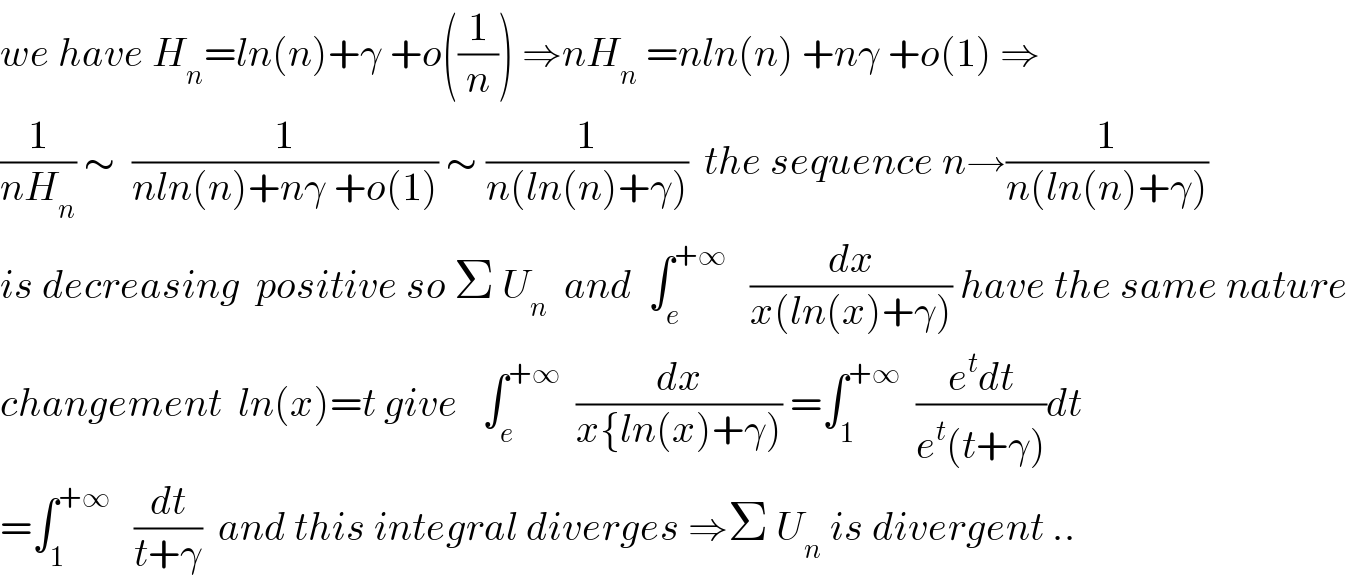
$${we}\:{have}\:{H}_{{n}} ={ln}\left({n}\right)+\gamma\:+{o}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}\right)\:\Rightarrow{nH}_{{n}} \:={nln}\left({n}\right)\:+{n}\gamma\:+{o}\left(\mathrm{1}\right)\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{nH}_{{n}} }\:\sim\:\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{nln}\left({n}\right)+{n}\gamma\:+{o}\left(\mathrm{1}\right)}\:\sim\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}\left({ln}\left({n}\right)+\gamma\right)}\:\:{the}\:{sequence}\:{n}\rightarrow\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}\left({ln}\left({n}\right)+\gamma\right)} \\ $$$${is}\:{decreasing}\:\:{positive}\:{so}\:\Sigma\:{U}_{{n}} \:\:{and}\:\:\int_{{e}} ^{+\infty} \:\:\:\frac{{dx}}{{x}\left({ln}\left({x}\right)+\gamma\right)}\:{have}\:{the}\:{same}\:{nature} \\ $$$${changement}\:\:{ln}\left({x}\right)={t}\:{give}\:\:\:\int_{{e}} ^{+\infty} \:\:\frac{{dx}}{{x}\left\{{ln}\left({x}\right)+\gamma\right)}\:=\int_{\mathrm{1}} ^{+\infty} \:\:\frac{{e}^{{t}} {dt}}{{e}^{{t}} \left({t}+\gamma\right)}{dt} \\ $$$$=\int_{\mathrm{1}} ^{+\infty} \:\:\:\frac{{dt}}{{t}+\gamma}\:\:{and}\:{this}\:{integral}\:{diverges}\:\Rightarrow\Sigma\:{U}_{{n}} \:{is}\:{divergent}\:.. \\ $$
