Question Number 185054 by mnjuly1970 last updated on 16/Jan/23
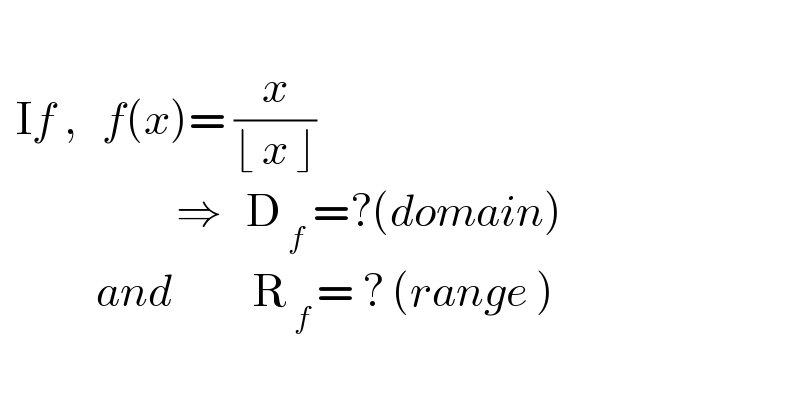
$$ \\ $$$$\:\:\mathrm{I}{f}\:,\:\:\:{f}\left({x}\right)=\:\frac{{x}}{\lfloor\:{x}\:\rfloor}\:\:\: \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\Rightarrow\:\:\:\mathrm{D}_{\:{f}} \:=?\left({domain}\right)\:\: \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:{and}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{R}_{\:{f}\:} =\:?\:\left({range}\:\right) \\ $$
Answered by mahdipoor last updated on 16/Jan/23
![D_f =R−{x∈R,[x]=0}=R−[0,1) x=n+ε⇒y=(x/([x]))=((n+ε)/n)=1+(ε/n) −1<(ε/n)<1⇒0<y<2⇒R_f =(0,2)](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q185056.png)
$${D}_{{f}} ={R}−\left\{{x}\in{R},\left[{x}\right]=\mathrm{0}\right\}={R}−\left[\mathrm{0},\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$${x}={n}+\epsilon\Rightarrow{y}=\frac{{x}}{\left[{x}\right]}=\frac{{n}+\epsilon}{{n}}=\mathrm{1}+\frac{\epsilon}{{n}} \\ $$$$−\mathrm{1}<\frac{\epsilon}{{n}}<\mathrm{1}\Rightarrow\mathrm{0}<{y}<\mathrm{2}\Rightarrow{R}_{{f}} =\left(\mathrm{0},\mathrm{2}\right) \\ $$
Commented by mnjuly1970 last updated on 16/Jan/23

$$\:\:{zendeh}\:{bsshid}\:\:{ali}\:{bood}\:… \\ $$
