Question Number 54699 by rahul 19 last updated on 09/Feb/19
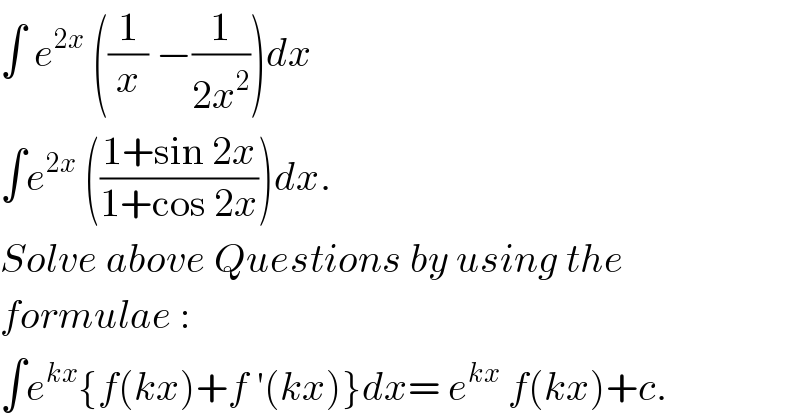
$$\int\:{e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} \:\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}\:−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right){dx} \\ $$$$\int{e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} \:\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{2}{x}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{2}{x}}\right){dx}. \\ $$$${Solve}\:{above}\:{Questions}\:{by}\:{using}\:{the} \\ $$$${formulae}\:: \\ $$$$\int{e}^{{kx}} \left\{{f}\left({kx}\right)+{f}\:'\left({kx}\right)\right\}{dx}=\:{e}^{{kx}} \:{f}\left({kx}\right)+{c}. \\ $$
Commented by maxmathsup by imad last updated on 10/Feb/19
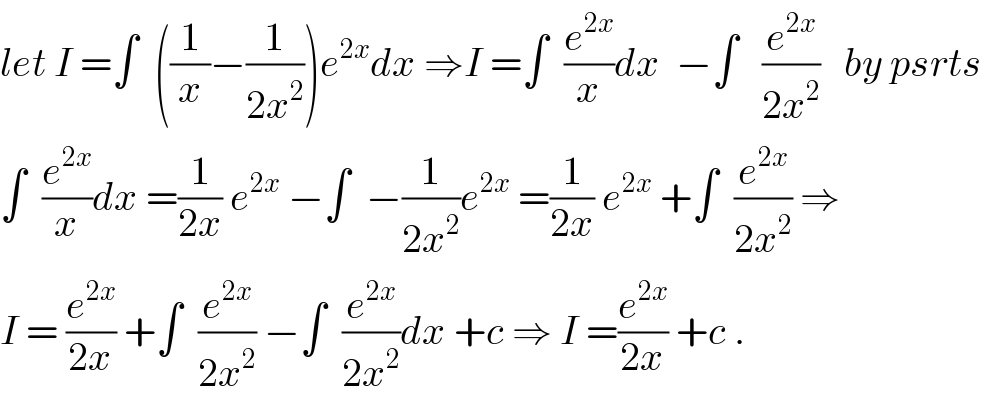
$${let}\:{I}\:=\int\:\:\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right){e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} {dx}\:\Rightarrow{I}\:=\int\:\:\frac{{e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} }{{x}}{dx}\:\:−\int\:\:\:\frac{{e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} }{\mathrm{2}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\:\:{by}\:{psrts} \\ $$$$\int\:\:\frac{{e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} }{{x}}{dx}\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{x}}\:{e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} \:−\int\:\:−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} \:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{x}}\:{e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} \:+\int\:\:\frac{{e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} }{\mathrm{2}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${I}\:=\:\frac{{e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} }{\mathrm{2}{x}}\:+\int\:\:\frac{{e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} }{\mathrm{2}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:−\int\:\:\frac{{e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} }{\mathrm{2}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{dx}\:+{c}\:\Rightarrow\:{I}\:=\frac{{e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} }{\mathrm{2}{x}}\:+{c}\:. \\ $$
Commented by rahul 19 last updated on 10/Feb/19
thank you profAbdo .
Commented by maxmathsup by imad last updated on 11/Feb/19
$${you}\:{are}\:{welcome}\:{sir}. \\ $$
Answered by kaivan.ahmadi last updated on 09/Feb/19
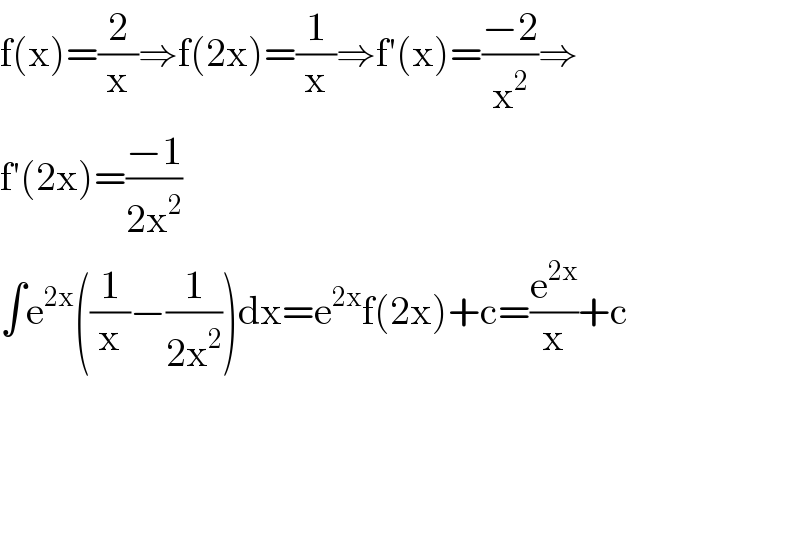
$$\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)=\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{x}}\Rightarrow\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{2x}\right)=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{x}}\Rightarrow\mathrm{f}'\left(\mathrm{x}\right)=\frac{−\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\mathrm{f}'\left(\mathrm{2x}\right)=\frac{−\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2x}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\int\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{2x}} \left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{x}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right)\mathrm{dx}=\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{2x}} \mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{2x}\right)+\mathrm{c}=\frac{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{2x}} }{\mathrm{x}}+\mathrm{c} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by rahul 19 last updated on 09/Feb/19
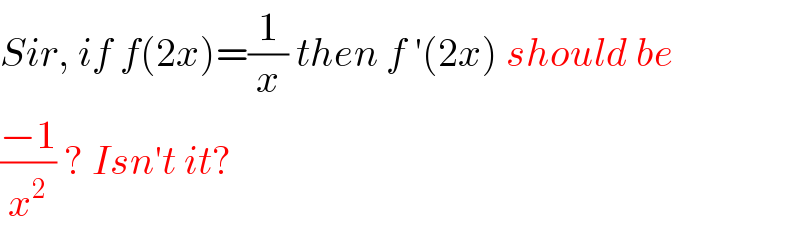
$${Sir},\:{if}\:{f}\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right)=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}\:{then}\:{f}\:'\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right)\:{should}\:{be} \\ $$$$\frac{−\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:?\:{Isn}'{t}\:{it}? \\ $$
Commented by kaivan.ahmadi last updated on 09/Feb/19

$$\mathrm{yes}\:\mathrm{it}\:\mathrm{is},\mathrm{thank}\:\mathrm{you}.\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{answer}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{your}\:\mathrm{integral}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{not}\:\mathrm{true},\mathrm{because} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{kx}} \mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{kx}\right)\right)^{'} =\mathrm{ke}^{\mathrm{2x}} \left(\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{kx}\right)+\mathrm{f}'\left(\mathrm{kx}\right)\right) \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 09/Feb/19
![1)(1/2)∫[(1/x)×(d/dx)(e^(2x) )+e^(2x) (d/dx)((1/x))]dx (1/2)∫(d/dx)((1/x)e^(2x) )dx (1/2)((e^(2x) /x))+c 2)∫e^(2x) (((1+2sinxcosx)/(2cos^2 x))) ∫e^(2x) ((1/2)sec^2 x+tanx)dx (1/2)∫[e^(2x) ×(d/dx)(tanx)+tanx×(d/dx)(e^(2x) )]dx =(1/2)∫(d/(dx ))(e^(2x) tanx)dx ((e^(2x) tanx)/2)+c](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q54706.png)
$$\left.\mathrm{1}\right)\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int\left[\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}×\frac{{d}}{{dx}}\left({e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} \right)+{e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} \frac{{d}}{{dx}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}\right)\right]{dx} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int\frac{{d}}{{dx}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}{e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} \right){dx} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left(\frac{{e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} }{{x}}\right)+{c} \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{2}\right)\int{e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} \left(\frac{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{2}{sinxcosx}}{\mathrm{2}{cos}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}}\right) \\ $$$$\int{e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} \left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{sec}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}+{tanx}\right){dx} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int\left[{e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} ×\frac{{d}}{{dx}}\left({tanx}\right)+{tanx}×\frac{{d}}{{dx}}\left({e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} \right)\right]{dx} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int\frac{{d}}{{dx}\:}\left({e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} {tanx}\right){dx} \\ $$$$\frac{{e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} {tanx}}{\mathrm{2}}+{c} \\ $$
Commented by rahul 19 last updated on 10/Feb/19
thank you sir ��
but how to do by using given formulae ?
