Question Number 54897 by gunawan last updated on 14/Feb/19
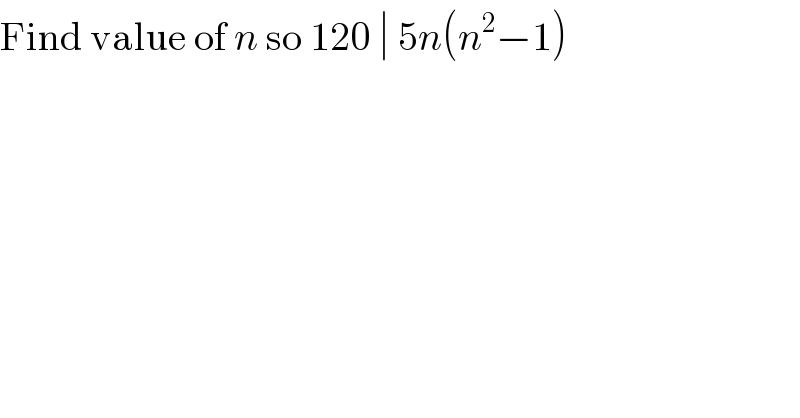
$$\mathrm{Find}\:\mathrm{value}\:\mathrm{of}\:{n}\:\mathrm{so}\:\mathrm{120}\:\mid\:\mathrm{5}{n}\left({n}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$
Commented by jahanara@gmail.com last updated on 02/May/19

$${so}\:{easy} \\ $$
Answered by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 14/Feb/19
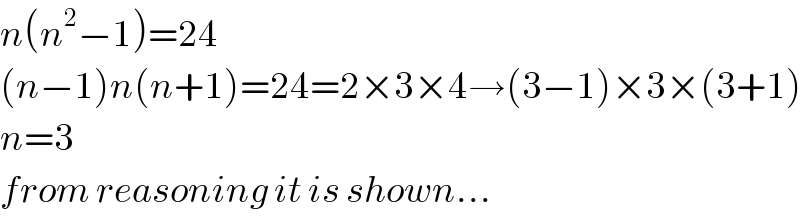
$${n}\left({n}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{24} \\ $$$$\left({n}−\mathrm{1}\right){n}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{24}=\mathrm{2}×\mathrm{3}×\mathrm{4}\rightarrow\left(\mathrm{3}−\mathrm{1}\right)×\mathrm{3}×\left(\mathrm{3}+\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$${n}=\mathrm{3} \\ $$$${from}\:{reasoning}\:{it}\:{is}\:{shown}… \\ $$
Answered by kaivan.ahmadi last updated on 14/Feb/19

$$\mathrm{24}\mid\mathrm{n}\left(\mathrm{n}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{n}−\mathrm{1}\right)\mathrm{n}\left(\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{24k}=\mathrm{2}×\mathrm{3}×\mathrm{4}×\mathrm{k} \\ $$$$\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{multiple}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{three}\:\mathrm{sequential}\:\mathrm{nuber}\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{must}\:\mathrm{divide}\:\mathrm{24} \\ $$$$\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{3} \\ $$$$\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{7} \\ $$$$\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{8} \\ $$$$\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{9} \\ $$$$\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{12} \\ $$$$\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{13} \\ $$$$\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{15} \\ $$$$\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{16} \\ $$$$\vdots \\ $$$$\mathrm{excusme},\overset{} {\:}\mathrm{i}\:\mathrm{cant}\:\mathrm{find}\:\mathrm{general}\:\mathrm{result} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by MJS last updated on 15/Feb/19

$$\mathrm{case}\:\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}\mid\left({n}−\mathrm{1}\right)\:\wedge\:\mathrm{4}\mid\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{1}.\mathrm{1}\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{3}\mid\left({n}−\mathrm{1}\right)\:\Rightarrow\:{n}=\mathrm{12}{k}+\mathrm{7} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{1}.\mathrm{2}\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{3}\mid{n}\:\Rightarrow\:{n}=\mathrm{12}{k}+\mathrm{3} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{1}.\mathrm{3}\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{3}\mid\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)\:\Rightarrow\:{n}=\mathrm{12}{k}+\mathrm{11} \\ $$$$\mathrm{case}\:\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\mathrm{4}\mid\left({n}−\mathrm{1}\right)\:\wedge\:\mathrm{2}\mid\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{2}.\mathrm{1}\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{3}\mid\left({n}−\mathrm{1}\right)\:\Rightarrow\:{n}=\mathrm{12}{k}+\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{2}.\mathrm{2}\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{3}\mid{n}\:\Rightarrow\:{n}=\mathrm{12}{k}+\mathrm{9} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{2}.\mathrm{3}\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{3}\mid\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)\:\Rightarrow\:{n}=\mathrm{12}{k}+\mathrm{5} \\ $$$$\mathrm{case}\:\mathrm{3} \\ $$$$\mathrm{8}\mid{n} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{3}.\mathrm{1}\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{3}\mid\left({n}−\mathrm{1}\right)\:\Rightarrow\:{n}=\mathrm{24}{k}+\mathrm{16} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{3}.\mathrm{2}\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{3}\mid{n}\:\Rightarrow\:{n}=\mathrm{24}{k} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{3}.\mathrm{3}\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{3}\mid\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)\:\Rightarrow\:{n}=\mathrm{24}{k}+\mathrm{8} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:{n}=\mathrm{2}{k}+\mathrm{1}\:\vee\:{n}=\mathrm{8}{k} \\ $$
