Question Number 55214 by maxmathsup by imad last updated on 19/Feb/19
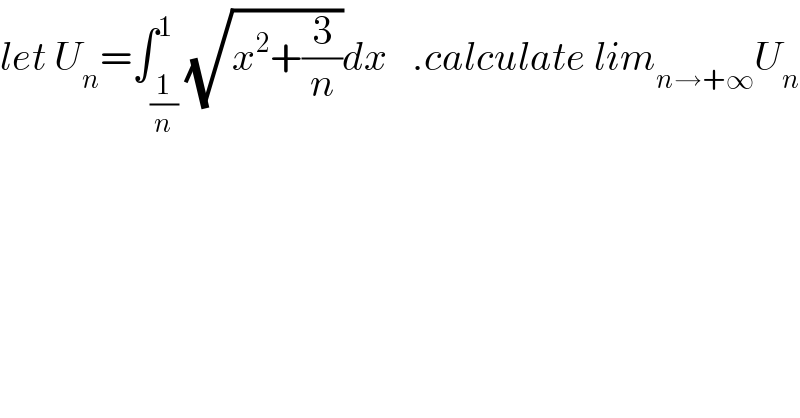
$${let}\:{U}_{{n}} =\int_{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \sqrt{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\frac{\mathrm{3}}{{n}}}{dx}\:\:\:.{calculate}\:{lim}_{{n}\rightarrow+\infty} {U}_{{n}} \\ $$
Commented by maxmathsup by imad last updated on 19/Feb/19
,1]) (x)dx =∫_R f(n)dx with f_n (x) =(√(x^2 +(3/n)))χ_(](1/n),1]) (x)dx the sequence of functions f_n (x) verify f_n (x)→^(cs) x on ]0,1] and ∣f_n (x)∣=f_n (x) ≤(√(x^2 +1)) ∀x∈]0,1] theorem of convergence dominee give lim_(n→+∞) ∫_R f_n (x)dx =∫_R lim_(n→+∞) f_n (x)dx =∫_0 ^1 x dx =[(x^2 /2)]_0 ^1 =(1/2) ⇒lim_(n→+∞) U_n =(1/2) .](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q55225.png)
$${we}\:{have}\:{U}_{{n}} =\int_{{R}} \:\sqrt{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\frac{\mathrm{3}}{{n}}}\:\chi_{\left.\right]\left.\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}},\mathrm{1}\right]} \left({x}\right){dx}\:=\int_{{R}} {f}\left({n}\right){dx}\:{with} \\ $$$${f}_{{n}} \left({x}\right)\:=\sqrt{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\frac{\mathrm{3}}{{n}}}\chi_{\left.\right]\left.\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}},\mathrm{1}\right]} \left({x}\right){dx}\:\:\:\:{the}\:{sequence}\:{of}\:{functions}\:{f}_{{n}} \left({x}\right)\:{verify} \\ $$$$\left.{f}_{{n}} \left.\left(\left.{x}\left.\right)\rightarrow^{{cs}} \:{x}\:\:\:\:{on}\:\right]\mathrm{0},\mathrm{1}\right]\:\:{and}\:\:\mid{f}_{{n}} \left({x}\right)\mid={f}_{{n}} \left({x}\right)\:\leqslant\sqrt{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{1}}\:\:\:\forall{x}\in\right]\mathrm{0},\mathrm{1}\right]\:\:{theorem}\:{of} \\ $$$${convergence}\:{dominee}\:{give}\:\:{lim}_{{n}\rightarrow+\infty} \:\int_{{R}} {f}_{{n}} \left({x}\right){dx} \\ $$$$=\int_{{R}} \:{lim}_{{n}\rightarrow+\infty} {f}_{{n}} \left({x}\right){dx}\:=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} {x}\:{dx}\:=\left[\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\:\Rightarrow{lim}_{{n}\rightarrow+\infty} {U}_{{n}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:. \\ $$
Answered by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 19/Feb/19
![∫_(1/n) ^1 (√(x^2 +((√(3/n)) )^2 )) dx formula ∫(√(x^2 +a^2 )) dx=(x/2)(√(x^2 +a^2 )) +(a^2 /2)ln(x+(√(x^2 +a^2 )) ) =∣(x/2)(√(x^2 +(3/n))) +(3/(n×2))ln(x+(√(x^2 +(3/n))) )∣_(1/n) ^1 =[{(1/2)(√(1+(3/n))) +(3/(2n))ln(1+(√(1+(3/n))) }−{(1/(2n))(√((1/n^2 )+(3/n))) +(3/(2n))ln((1/n)+(√((1/n^2 )+(3/n))) )] when n→∞ (1/2)×1=(1/2)](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q55216.png)
$$\int_{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \sqrt{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\left(\sqrt{\frac{\mathrm{3}}{{n}}}\:\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\:{dx} \\ $$$${formula} \\ $$$$\int\sqrt{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{a}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:{dx}=\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\sqrt{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{a}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:+\frac{{a}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}{ln}\left({x}+\sqrt{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{a}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\right) \\ $$$$=\mid\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\sqrt{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\frac{\mathrm{3}}{{n}}}\:+\frac{\mathrm{3}}{{n}×\mathrm{2}}{ln}\left({x}+\sqrt{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\frac{\mathrm{3}}{{n}}}\:\right)\mid_{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$=\left[\left\{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{3}}{{n}}}\:+\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}{n}}{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{3}}{{n}}}\:\right\}−\left\{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{n}}\sqrt{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }+\frac{\mathrm{3}}{{n}}}\:+\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}{n}}{ln}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}+\sqrt{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }+\frac{\mathrm{3}}{{n}}}\:\right)\right]\right.\right. \\ $$$${when}\:{n}\rightarrow\infty \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}×\mathrm{1}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
