Question Number 55229 by maxmathsup by imad last updated on 19/Feb/19
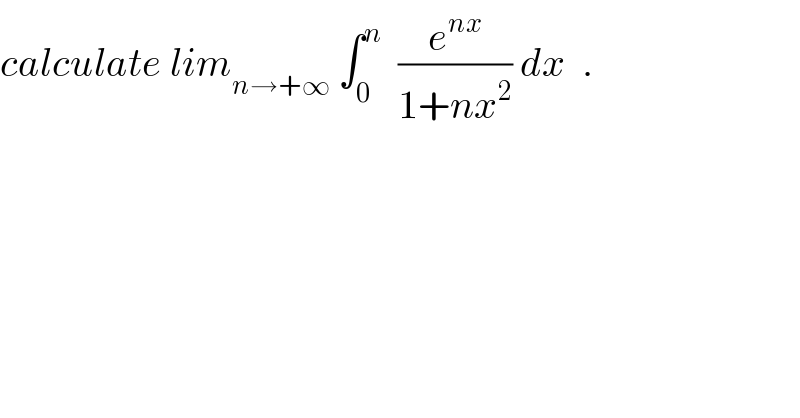
$${calculate}\:{lim}_{{n}\rightarrow+\infty} \:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{{n}} \:\:\frac{{e}^{{nx}} }{\mathrm{1}+{nx}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:{dx}\:\:. \\ $$
Commented by maxmathsup by imad last updated on 25/Feb/19
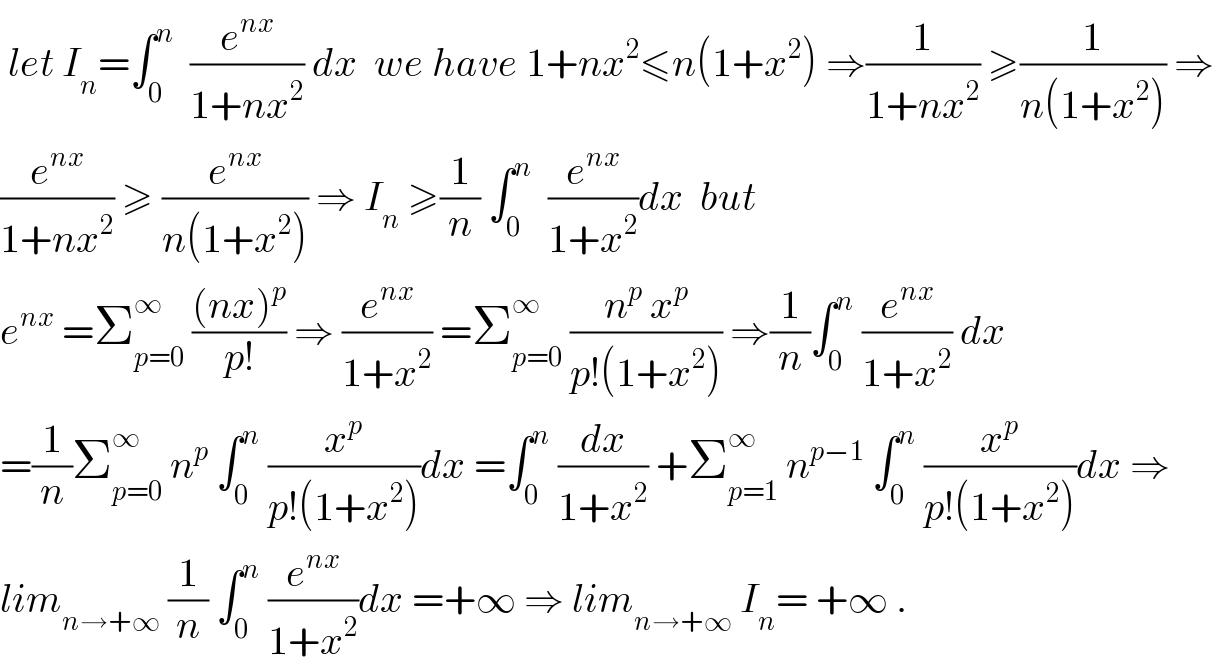
$$\:{let}\:{I}_{{n}} =\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{{n}} \:\:\frac{{e}^{{nx}} }{\mathrm{1}+{nx}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:{dx}\:\:{we}\:{have}\:\mathrm{1}+{nx}^{\mathrm{2}} \leqslant{n}\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\:\Rightarrow\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+{nx}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\geqslant\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\frac{{e}^{{nx}} }{\mathrm{1}+{nx}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\geqslant\:\frac{{e}^{{nx}} }{{n}\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)}\:\Rightarrow\:{I}_{{n}} \:\geqslant\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{{n}} \:\:\frac{{e}^{{nx}} }{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{dx}\:\:{but} \\ $$$${e}^{{nx}} \:=\sum_{{p}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\frac{\left({nx}\right)^{{p}} }{{p}!}\:\Rightarrow\:\frac{{e}^{{nx}} }{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:=\sum_{{p}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\frac{{n}^{{p}} \:{x}^{{p}} }{{p}!\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)}\:\Rightarrow\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{{n}} \:\frac{{e}^{{nx}} }{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:{dx} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}\sum_{{p}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:{n}^{{p}} \:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{{n}} \:\frac{{x}^{{p}} }{{p}!\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)}{dx}\:=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{{n}} \:\frac{{dx}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:+\sum_{{p}=\mathrm{1}} ^{\infty} \:{n}^{{p}−\mathrm{1}} \:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{{n}} \:\frac{{x}^{{p}} }{{p}!\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)}{dx}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${lim}_{{n}\rightarrow+\infty} \:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{{n}} \:\frac{{e}^{{nx}} }{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{dx}\:=+\infty\:\Rightarrow\:{lim}_{{n}\rightarrow+\infty} \:{I}_{{n}} =\:+\infty\:. \\ $$
