Question Number 120811 by fajri last updated on 03/Nov/20
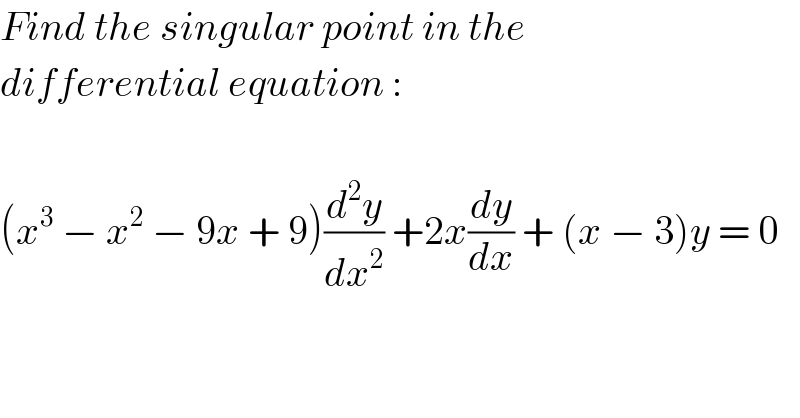
$${Find}\:{the}\:{singular}\:{point}\:{in}\:{the} \\ $$$${differential}\:{equation}\:: \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\left({x}^{\mathrm{3}} \:−\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:−\:\mathrm{9}{x}\:+\:\mathrm{9}\right)\frac{{d}^{\mathrm{2}} {y}}{{dx}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:+\mathrm{2}{x}\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}\:+\:\left({x}\:−\:\mathrm{3}\right){y}\:=\:\mathrm{0} \\ $$
Answered by 675480065 last updated on 03/Nov/20
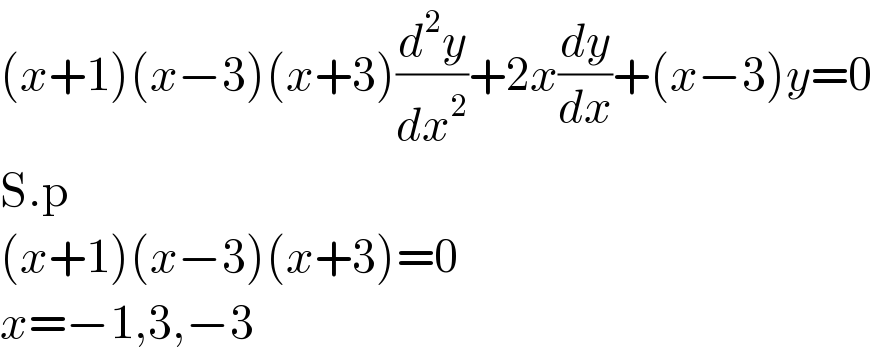
$$\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)\left({x}−\mathrm{3}\right)\left({x}+\mathrm{3}\right)\frac{{d}^{\mathrm{2}} {y}}{{dx}^{\mathrm{2}} }+\mathrm{2}{x}\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}+\left({x}−\mathrm{3}\right){y}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{S}.\mathrm{p} \\ $$$$\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)\left({x}−\mathrm{3}\right)\left({x}+\mathrm{3}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${x}=−\mathrm{1},\mathrm{3},−\mathrm{3} \\ $$
