Question Number 189496 by Tawa11 last updated on 17/Mar/23

$$\int\:\mathrm{xe}^{\frac{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}} \:\mathrm{dx} \\ $$
Answered by BaliramKumar last updated on 18/Mar/23
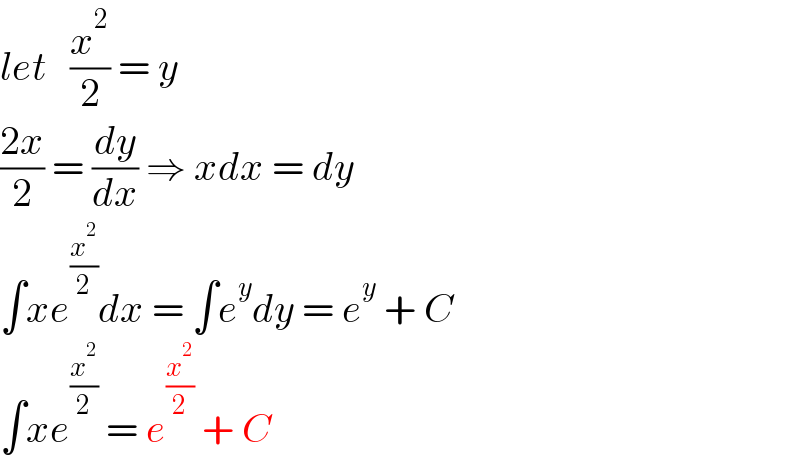
$${let}\:\:\:\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}\:=\:{y} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\:=\:\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}\:\Rightarrow\:{xdx}\:=\:{dy} \\ $$$$\int{xe}^{\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}} {dx}\:=\:\int{e}^{{y}} {dy}\:=\:{e}^{{y}} \:+\:{C} \\ $$$$\int{xe}^{\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}} \:=\:{e}^{\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}} \:+\:{C} \\ $$
Answered by Frix last updated on 17/Mar/23
![Use your eyes (and brains): ∫xe^(x^2 /2) dx=∫d[e^(x^2 /2) ] or simply use t=e^(x^2 /2) ⇒ ∫dt=t=e^(x^2 /2)](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q189499.png)
$$\mathrm{Use}\:\mathrm{your}\:\mathrm{eyes}\:\left(\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{brains}\right): \\ $$$$\int{x}\mathrm{e}^{\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}} {dx}=\int{d}\left[\mathrm{e}^{\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}} \right] \\ $$$$\mathrm{or}\:\mathrm{simply}\:\mathrm{use}\:{t}=\mathrm{e}^{\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}} \:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\int{dt}={t}=\mathrm{e}^{\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}} \\ $$
